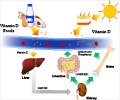
Vitamin D deficiency is linked to the risk of contracting coronavirus infection, says a new study.

‘Vitamin D is vital to the function of the immune system and vitamin D supplements have been shown to lower the risk of viral respiratory tract infections.’
Read More..




"Our statistical analysis suggests this may be true for the COVID-19 infection."Read More..
The research team studied 489 UChicago Medicine patients whose vitamin D level was measured within a year before being tested for COVID-19. Patients who had vitamin D deficiency (< 20ng/ml) that was not treated were almost twice as likely to test positive for the COVID-19 coronavirus compared to patients who had sufficient levels of the vitamin.
The study, Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, was published in JAMA Network Open. Findings were previously reported on medRxiv, a preprint server for the health sciences.
"Understanding whether treating Vitamin D deficiency changes COVID-19 risk could be of great importance locally, nationally and globally," Meltzer said. "Vitamin D is inexpensive, generally very safe to take, and can be widely scaled."
Researchers stress the importance of experimental studies to assess if vitamin D supplementation can reduce the risk, and potentially severity, of COVID-19.
Advertisement
Advertisement