An antiseptic drug can prevent recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) and antibiotic resistance. Over 50% of women suffer from UTI in their lifetimes.

‘An antiseptic drug can prevent recurrent urinary tract infections as well as antibiotic resistance.’





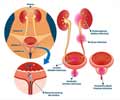
“Over 50 percent of women will suffer from a urinary tract infection in their lifetimes,” says Chris Harding at The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.UK guidelines recommend a daily low-dose antibiotic as a preventative therapy for recurrent UTIs. However, long-term use of these drugs raises the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Unlike antibiotics that kill bacteria, methenamine Hippurate is an antiseptic drug that sterilizes urine, inhibiting the growth of certain bacteria. The antiseptic has shown promise for UTI prevention, but the evidence is inconclusive.
To learn more, researchers studied 205 women who had on average six UTIs a year. Every day for 12 months, 102 of the participants took an antibiotic, while the remaining 103 were given a methenamine hippurate pill.
Over the year, those in the antibiotic group had on average 0.89 UTI episodes, compared with 1.38 episodes among those taking methenamine hippurate.
Advertisement
Four of the participants who took it daily were admitted to the hospital as a result of a UTI, and six of the same group reported fever during an infection. Overall, 34 people in the antibiotic group and 35 in the antiseptic group had side effects, most of which were mild.
Nevertheless, growing concerns around antibiotic resistance could make methenamine hippurate a viable preventative option if future research supports its use.
Source-Medindia