Women who do not attend cervical screening appointments will often provide a sample if they are sent a self-sampling kit.
‘Testing for high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) infection is replacing cytology as the screening test for cervical cancer.’





The first review included 56 studies which assessed the accuracy of HPV testing on samples taken by the woman herself versus those collected by a clinician. It found that HPV tests based on a technology called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) were just as good at detecting cervical pre-cancer (CIN2+ or CIN3+) in samples taken by the woman herself as they were in samples taken by a clinician.
However, HPV tests based on a process called signal amplification were not quite as good on self-samples. Both types of HPV tests returned a slightly greater number of false positives when used on self-samples rather than samples taken by a clinician, meaning that a few more women who took their own samples would be told they have a positive screening test without presence of cervical precancer.
The second analysis included 25 trials comparing the impact of offering self-sampling kits instead of screening appointments to under screened women, including those who had not been attending previous screening appointments.
Women sent self-sampling kits were found to be more than twice as likely to respond by providing a sample for testing than they were to respond to an invitation or reminder letter asking them to attend an appointment with a clinician to have a sample taken for testing.
Advertisement
The authors point out that there was a lack of detailed data on potentially influential factors in the studies and that this might be overcome by pooling individual patient data from the best individual trials.
Advertisement
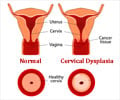
Cervical cancer rates have come down in countries in Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand in response to the introduction of widespread screening programmes.
However, incidence has not dropped to the same extent in areas such as Eastern Europe, where coverage is low or the quality of screening is not as good, and 85% of cervical cancer cases occur in less developed countries where there is often no screening at all.
It should be noted that, in recent years incidence has stopped decreasing, and has even started rising in countries with good cytology screening programmes. These observations support introduction of more effective prevention strategies such as HPV vaccination and HPV screening, including self-sampling.
Use of self-sampling for HPV testing may increase coverage substantially, the authors say. "The highest participation rates in our systematic review were observed in studies that included door-to-door invitation scenarios conducted in Latin America or Africa. However, the direct offer of a self sampling kit by a health professional might also be an effective strategy to reach non-responders in countries with established screening programmes."
They recommend that a PCR-based HPV test should be used where resources allow, but where they do not the less expensive signal-based HPV test may still provide benefits.
Source-Eurekalert