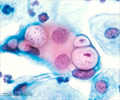
Chlamydia infection causes inflammation of mucous membranes, which is hardly noticeable, yet can progress to a stage where antibiotics are ineffective.

Stary said, "In every second person, the disease produces no symptoms. If it is discovered at an early stage, it is, in principle, easily treated with antibiotics."
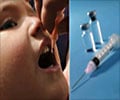
The team has successfully managed to mimic a Chlamydia infection in a mouse model using nanotechnology to develop a protective vaccine, which activates two waves of immune cells and which is administered directly to the mucosa.
Inactive Chlamydiae was bound to immune stimulants by means of special nanoparticles and is administered through a mucosal surface. It serves to inform memory cells in lymph nodes about the nature and location of the supposed infection.
“The antigen must carry this adjuvant, which acts like a turbocharger for the human immune response. Both the antigen and the adjuvant are completely useless on their own," said Stary.
This finding could also lead to the successful development of an effective strategy for vaccinating against other types of mucosal infection.
Advertisement