- Nerve Disease and Bladder Control - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/urologic-disease/nerve-disease-and-bladder-control/pages/facts.aspx)
- Overactive bladder - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/overactive-bladder/basics/causes/con-20027632)
What are Bladder Spasms?
Bladder spasms occur when the bladder muscle undergoes a sudden involuntary squeezing movement or a spasm. The bladder spasm, otherwise known as detrusor contraction causes a sudden, strong sensation to urinate, most often resulting in leakage of urine. This condition is called urge continence or overactive bladder.
The urinary bladder works in coordination with the neuromuscular system to retain and release urine. Any condition that affects the coordination of this system can result in derangement of the function of the urinary bladder.
Local conditions at the urinary bladder level or the flow of urine can also result in irritation and spasm.

What Causes Bladder Spasms?
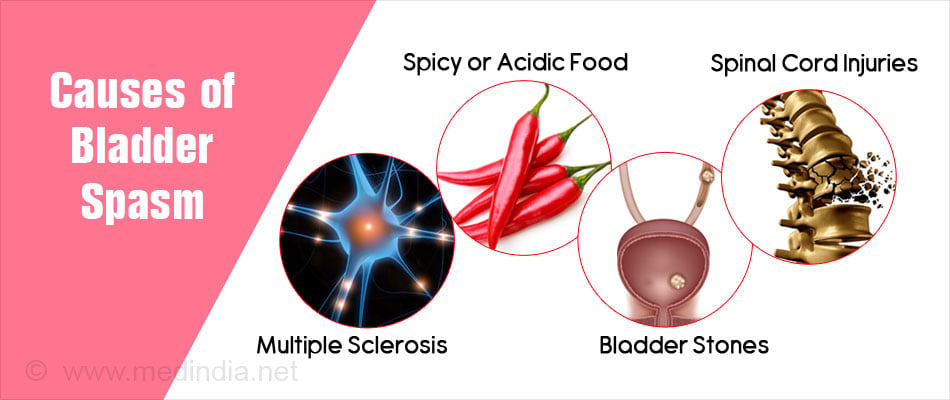
Bladder spasms can be caused by many conditions including:
- Neurological conditions like stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease.
- Overproduction or high production of urine due to any condition affecting the kidney or endocrine system e.g. diabetes.
- Spicy or acidic food intake.
- High fluid intake or intake of alcohol or caffeine containing beverages by the person.
- Intake of medicines like furosemide that increases the production of urine.
- Infections affecting the urinary bladder like a urinary tract infection.
- Abnormalities in the bladder like stones or a tumor in the bladder.
- Conditions which obstruct the flow of the urine; for example an enlarged prostate due to hypertrophy or tumor.
- Previous surgeries done for incontinence that obstruct the urine flow.
- Accidents that affect the spinal cord and neuromuscular coordination with the bladder.
- Infections in the brain or the spinal cord can also affect the neuromuscular coordination resulting in spasms.
- If the bladder is not completely emptied or in conditions of constipation.
What are the Symptoms of Bladder Spasms?
Mostly commonly the following symptoms are seen in connection with an overactive bladder:
- Sudden urge to pass urine
- Frequent urination
- Waking up in the night to urinate (nocturia)
- Urinary incontinence
- Abdominal Pain
What are the Complications of Bladder Spasms?
Urinary incontinence, increased frequency of urination and nocturia (excessive urination during the night) can result, thus affecting the quality of life of the patient. It can result in
- Emotional disturbances
- Sleeplessness
- Decreased confidence
- Depression
How do you Diagnose Urinary Spasms?
Identifying the underlying condition requires a proper history taking and clinical examination. The investigations require to check any abnormalities that might exist in the central nervous system (brain, spinal cord), or any abnormalities in the kidney or local abnormalities near the urinary bladder. The investigations done include -
1. Urodynamics
These are tests done to check whether the bladder is functioning well. Inefficient emptying of the bladder may result in spasm of the bladder.
- Measuring the flow of the urine using an uroflowmeter, to identify the volume of urine and the speed of the urine voided.
- Bladder pressures are measured using cystometry. Here the pressure within the bladder and the pressure in the surrounding region are measured during filling of bladder.
2. Imaging Investigation
- An x-ray investigation, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography images are imaging techniques that are used to visualize the central nervous system and the urinary tract to identify any abnormal conditions.
3. Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- An electroencephalogram or an electromyogram may be used to identify the electric function in the central nervous system and the muscular system respectively to identify abnormalities.
What are the Treatment Modalities for Bladder Spasms?
The options for treatment include medical, surgical treatment and lifestyle changes for coping with the condition.
1. Medical treatment includes drugs that help in reducing the symptoms of bladder spasms and reduce urinary incontinence. These drugs come under the class of antispasmodics.
Examples are tolterodine, oxybutynin chloride, and trospium chloride.
Drugs indicated for depression (antidepressants) also help in bladder relaxation and reduce spasm. Examples are amitriptyline and nortriptyline.

Onabotulinumtoxin A injections (Botox) for the bladder help in reducing the urinary incontinence by paralysis of the muscle in the bladder. This is given in small doses and has temporary results.
2. Surgical treatment is employed in patients who are suffering from severe symptoms when all other treatment modalities have failed. It aims at increasing the capacity of the bladder or bringing down the pressure of the bladder.
Surgical modalities include:
- Surgery to increase bladder capacity
- Bladder removal
- Urinary diversion
- Artificial sphincter
3. Lifestyle changes are also required to enable the patient to cope with his/her conditions. These include:
- Exercises for the pelvic floor muscles called Kegel exercises. Strengthening the muscles help in reducing the contractions of the muscles.
- Training of the bladder and also setting a time for voiding urine. Practice should also include complete voiding of urine so as to reduce the urge of incontinence.
- Catheterization may be required in case of incomplete voiding of urine.
What are the Measures to Reduce or Prevent the Symptoms of Bladder Spasms?
- Control weight to appropriate levels
- Reduce intake of drinks containing alcohol and caffeine
- Reduce fluid intake following consultation of physician