- About Cold intolerance - (http://healthtools.aarp.org/health/cold-intolerance)
- King ICC, Belcher HJCR. Cold intolerance following collagenase Clostridium histolyticum treatment for Dupuytren contracture. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39:808-809.
- Novak CB, McCabe SJ. Prevalence of cold sensitivity in patients with hand pathology. Hand (New York, NY). 2015;10(2):173-176. doi:10.1007/s11552-014-9694-y.
- Smits, ES. Cold intolerance: From thermoregulation to nerve innervation. Rotterdam: Erasmus University. 1985.
- Zhao G, Mi J, Rui Y, Pan X, Yao Q, Qiu Y. Correlation of volumetric flow rate and skin blood flow with cold intolerance in digital replantation. Tarantino. G, ed. Medicine. 2017;96(51):e9477. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000009477
- Xiong D, He H, James J, et al. Cardiac-specific VLCAD deficiency induces dilated cardiomyopathy and cold intolerance. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2014;306(3):H326-H338. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00931.2012.
- Graham B, Schofield M. Self-Reported Symptoms of Cold Intolerance in Workers with Injuries of the Hand. Hand (New York, NY). 2008;3(3):203-209. doi:10.1007/s11552-008-9116-0.
- Descoeur J, Pereira V, Pizzoccaro A, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced cold hypersensitivity is due to remodelling of ion channel expression in nociceptors. EMBO Molecular Medicine. 2011;3(5):266-278. doi:10.1002/emmm.201100134.
- Jane. Chilled out: Cold sensitivity and MS. (Accessed Apr 5, 2018. Cited Apr. 5, 2018.)
- Cooper C, Miller J. Integrative Therapies for Fibromyalgia, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, and Myofascial Pain: The Mind-Body Connection. Inner Traditions/Bear; Simon and Schuster. 2010.
- Zhang W et al. A pilot study exploring the effects of reflexology on cold intolerance. J Acup Merid Stud. 2010;Vol.3(1):43-48.Eduardo RP et al. Effects of Daoyin Qigong in postpolio syndrome patients with cold intolerance. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. [Internet]. 2012 Sep [cited 2018 Apr 05] ; 70(9): 680- 685.
- Raynaud's. Uploaded September 8, 2017. Accessed April 5, 2018.
What is Cold Intolerance?
Cold intolerance as the word indicates, is a condition where people are unusually sensitive to cold temperatures or to a cold climate. This intolerance tends to develop in people who are thin and do not have sufficient body mass to keep them warm or in those who experience trauma to their upper limbs. People with certain health problems are intensely sensitive to cold compared to the usual feeling that a person experiences on a chilly or a rainy day.
Cold intolerance results in numbness, changes in color of the skin, weakness, and tingling sensation. Between 38% and 83% of patients who undergo trauma in their hands experience cold intolerance. Severe cold intolerance is experienced during amputations or complex trauma. Bone, nerve, and tendon injuries may also result in symptoms of cold sensitivity.
Cold intolerance develops after an injury or a disease condition and persists for a considerable time following the trauma or injury or as long as the disease condition remains untreated.
What are the Causes of Cold Intolerance?
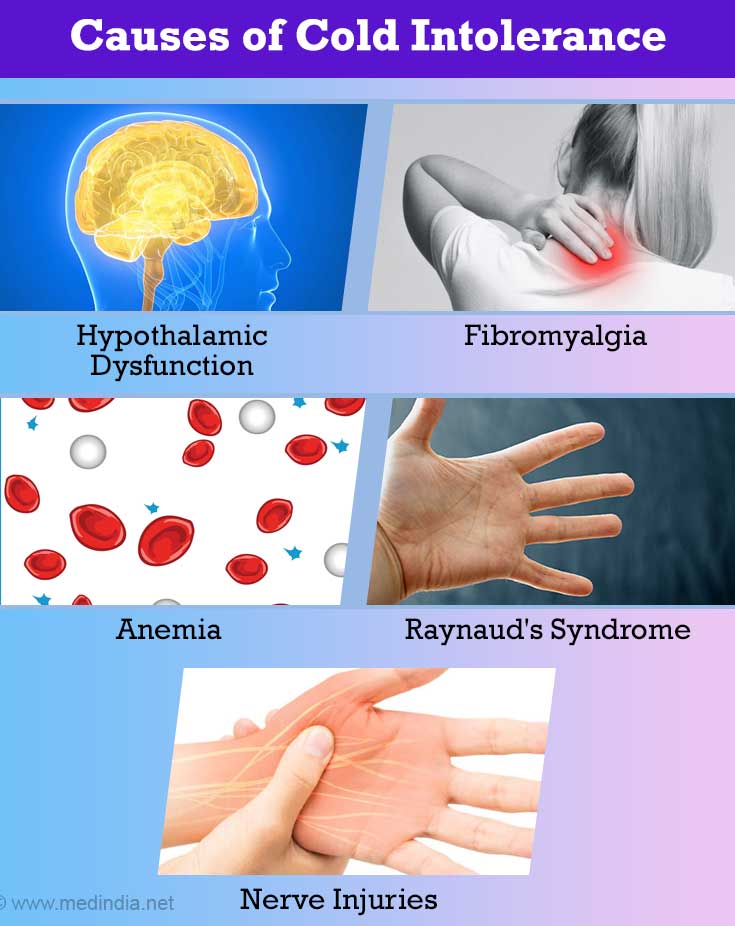
Cold intolerance is a symptom of any of the underlying medical conditions mentioned below:
- Improper functioning of the hypothalamus – this part of the brain regulates body temperature
- Trauma, injury or surgery to the upper limbs (e.g. amputation, digital replantation, injury to the tendon)
- Body pain and discomfort (fibromyalgia)
- Anemia
- Blood flow complications (e.g. Raynaud's syndrome)
- Anorexia nervosa - an eating disorder
- Hypothyroidism (deficiency in thyroid hormones)
- Chemotherapy drug-induced nerve injuries (e.g. oxaliplatin, bortezomib, thalidomide)
- Nerve injuries (e.g. multiple sclerosis)
- Enzyme treatment
- Defects in functioning of body proteins
- Altered blood supply
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Cold Intolerance?
As one can guess, the principal symptom of cold intolerance is the inability to handle cold. Some of the other symptoms are:
- A tingling sensation
- Numbness
- Stiffness or weakness in the fingers and hand when exposed to cold
- Change in skin color
- Swelling
- Normal function of injured or reconstructed limb is affected
The symptoms of cold intolerance are not related to the severity of the associated injury and tend to persist anywhere between 2 and 10 years.

How do you Diagnose Cold Intolerance?
Your physician will need to know your medical history to understand what may be causing this intolerance to cold.
The Cold Intolerance Symptom Severity (CISS) questionnaire is used as a standard to assess the symptoms of cold intolerance and its effect on your work and daily life. However, CISS can only give information for the symptoms you are experiencing due to cold intolerance. It does not give an idea of what may have caused the cold intolerance to develop.
Your physician will ask you questions to understand how you developed the symptoms of cold intolerance. Some examples are provided below:
- Describe your general health.
- Describe the symptoms you are experiencing.
- When did you begin experiencing these symptoms?
- What is your weight and height?
- Describe your diet.
- Did you ever have problems with cold earlier?
- Do you feel cold when others do not?
- Do you find your symptoms are becoming worse?
Your doctor may also recommend thyroid hormone tests and blood count to be done.
How do you Treat Cold Intolerance?
There is no effective treatment for cold intolerance since it is not clear how the symptom arises. Is it related to nerve injuries or to defects in the blood circulation? The symptom of cold intolerance may arise due to an underlying condition or injury or treatment. Hence, therapies, such as the following are recommended:
- Hand therapy
- Behavior therapy -
- Make sure you sit in warm surroundings. Hence, a warm office or house is a good way to avoid feeling cold.
- Move around to increase blood circulation and reduce any stiffness in muscles due to the cold.
- Wear warm clothing (e.g. sweaters, thermal gloves, thermal socks) if you are working in cold places (e.g. in butcher shops).
- Try and get the warmth of the sun by sitting outside.

In severe cases of cold intolerance, vasodilator-type drugs are prescribed as treatment.