- Evaluating drugs used to treat enlarged prostate - (https://www.consumerreports.org/cro/2012/05/enlarged-prostate-drugs/index.htm)
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370093)
- Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men - (https://www.andrologyaustralia.org/your-health/lower-urinary-tract-symptoms-luts-in-men/)
- Androgens and Estrogens in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Past, Present and Future. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21620560)
- How is an enlarged prostate treated? - (https://prostatecanceruk.org/prostate-information/further-help/enlarged-prostate/enlarged-prostate-treatment)
- Enlarged Prostate - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000381.htm)
- Benign Prostate Enlargement - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostate-enlargement/treatment/)
- Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems/prostate-enlargement-benign-prostatic-hyperplasia)
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
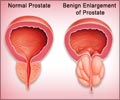
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, also called BPH, is a condition where a man’s prostate enlarges. It is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction. It is not cancer neither does it increase the risk of cancer. This condition happens with age, primarily in men above 50 years of age.
Prostate is a small gland in the pelvis region, found only in males. It is located under the bladder and is about the size of a walnut. It makes prostate fluid which is part of the semen and is essential for a man’s fertility.
As the prostate enlarges, it squeezes the urethra. As the urethra becomes narrow, it has to work hard to empty out. This causes the bladder walls to become thick, which causes the bladder to contract even when it contains a small amount of urine leading to loss of bladder control. The hormone related to testosterone, known as dihydroxy testosterone or DHT, plays an important role in causing BPH.
BPH is not a serious or life-threatening disease. However, if left untreated, it can lead to complications like:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Blood in the urine
- Bladder damage
- Bladder stones and
- Kidney damage
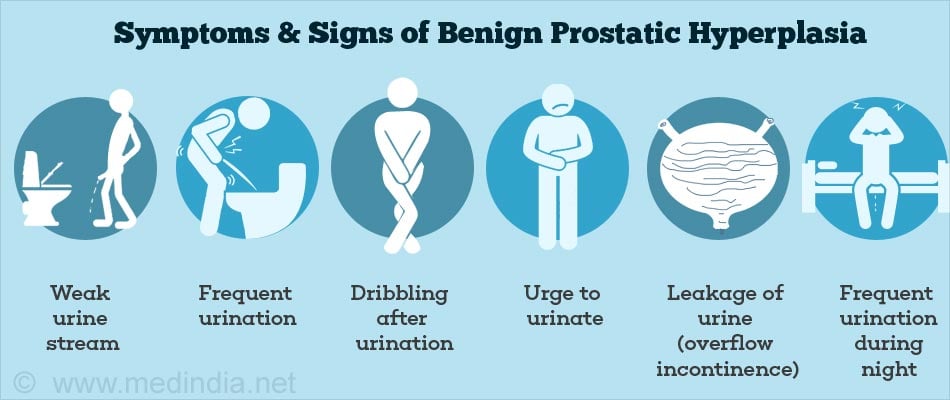
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
The symptoms of BPH can be similar to symptoms of prostate cancer.
Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) are the most common symptoms associated with BPH.
These include:
- weak direction of urine
- dribbling after urination
- strain or discomfort while passing urine
- need to pass urine multiple times during the night
- an urgent feeling to urinate
- urinary incontinence
- urine which has unusual smell or color
Urinary retention caused due to blocked urethra can also be caused because of taking cold and allergy medications which contain decongestants such as pseudoephedrine. These medications prevent the bladder neck from relaxing and thus hinder in releasing urine.
If one observes severe symptoms like pain in back, side or abdomen, pain or discomfort when passing urine or cloudy or bloody urine, the physician must be contacted as these may require immediate attention.
What are the Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
The treatment options for BPH would depend on the severity of the symptoms.
The options include:
Lifestyle changes:
As soon as one starts getting urinary problems, one must first try to make lifestyle changes to get relief from the symptoms. These include:
- reducing or eliminating the intake of alcohol, caffeine, antihistamines (e.g. diphenhydramine), artificial sweeteners and decongestants (e.g. pseudoephedrine)
- going to the bathroom immediately with the first urge
- reducing fluid intake before going to sleep
- control blood sugar, as it helps reduce frequent urination
Medications:
If the symptoms persist or worsen, one must consider treatment with drugs, after consulting a health provider.
Catheters:
These are recommended when there is chronic urine retention.
Surgery:
Generally, surgery is not required for men suffering from BPH. If none of the treatment options work, then surgery may be performed, to remove part or the full prostate gland.
What are Drugs Approved to Treat Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
There are four broad classes of drugs used to treat enlarged prostate:
Alpha-blockers (also called as alpha-1-receptor blockers):
These are generally the first line of treatment as they act immediately, providing relief from urinary problems in days or a few weeks time. They relax the muscles around the bottom of the bladder making it easy for passage of urine.
Some of the approved drugs include:
- Alfuzosin
- Doxazosin
- Tamsulosin
- Terazosin
- Silodosin
Tamsulosin is the most commonly used drug for BPH.
Alpha blockers reach their maximum effect within a month’s time.

5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (5ARIs): These are also known as androgen reducing compounds or enzyme inhibitors.
These drugs block the production of hormone dihydrotestosterone that causes the prostate to enlarge. They help in slowing the growth of prostate or shrink the prostate. When the prostate becomes smaller again, it no longer pushes against the bladder and urethra as much.
These can take several months to provide relief with the maximum effect usually reached after about six months.
The two main drugs under this category include:
- Finasteride – the most commonly used drug
- Dutasteride – this is also prescribed in combination with Tamsulosin
Anti-cholinergics:
These medications help relax the muscles in the bladder and urinary tract. These are less commonly used for treating BPH and are less effective too. At times, these are used to treat overactive bladder syndrome or incontinence. Hence, they might be more suitable for men who have any of these conditions along with an enlarged prostate.
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors:
Tadalafil is the most commonly prescribed drug under this category. It is approved for erectile dysfunction. The US FDA has now included BPH in the approved indications of Tadalafil. It relaxes the muscles in prostate and around the opening of bladder, making it easy to urinate.
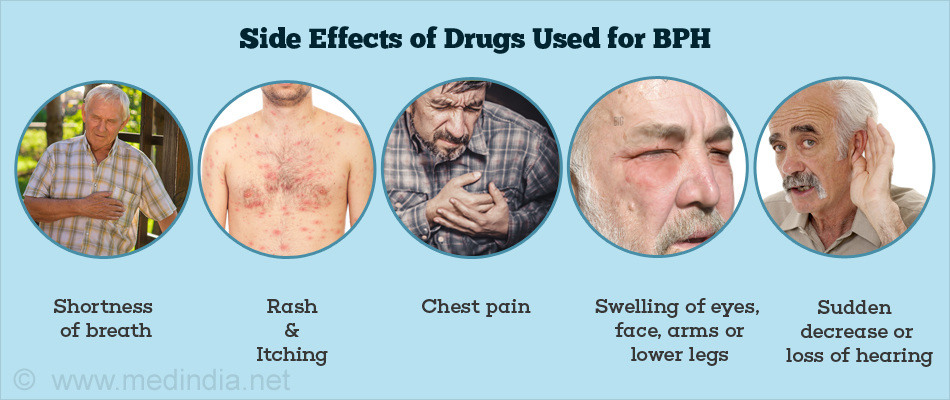
What are the Side Effects of Drugs Used for BPH?
Some medications used to treat BPH may have side effects which could be serious. Hence, one must contact the healthcare provider immediately on observing any of the following symptoms.
- Shortness of breath
- Rash
- Itching
- Chest pain
- Swelling of eyes, face, arms or lower legs
- Sudden decrease or loss of hearing
The common side effects of different categories of drugs are:
Alpha-blockers:
The most common side effects of alpha-blockers are reduced semen during ejaculation (dry orgasm), erectile dysfunction, upset stomach, headache, stuffy or runny nose and low blood pressure.
Alpha-blockers are also given to reduce high blood pressure. Hence caution must be used when given along with other hypertension medications or impotence drugs, as both these medications have blood pressure lowering effect. Also, blood pressure should also be monitored in patients who are on alpha blockers but who do not have hypertension.
Tamsulosin and Terazosin may cause dizziness or fainting due to low blood pressure.
These drugs can also affect the pupils; hence, the eye surgeon must be informed before cataract surgery.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors:
These drugs may increase the risk of high-grade prostate cancer. The most common side effect of ARIs are decreased sex drive, ejaculation problems, decreased ability to get an erection and enlarged mammary glands.
These medications also reduce the level of “prostate-specific antigen” (PSA) in blood. Hence, patients who take these inhibitors for BPH, must inform their health care providers, before doing any PSA test.
Anti-cholinergics:
Side effects of these drugs include blurred vision, constipation, dry eyes, indigestion and urinary tract infections. If men suffering from weak urine flow take these drugs, the problems can worsen.
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor:
Side effects of Tadalafil include headaches, indigestion, back pain and itching or swelling in nose (rhinitis).
What Precautions Must be Taken by Males Suffering from BPH?
The men suffering from BPH must follow these recommendations to manage BPH.
- Reduce alcohol intake
- Decrease the salt intake and avoid using table salt
- Do not allow the bladder to get full, one must urinate as soon as the urge is felt
- Perform Kegel exercises
- Men who are suffering from BPH, must avoid the use of androgens. Some studies indicate testosterone, a sex steroid, makes the prostate grow and thus increases the symptoms of BPH