- Eosinophilic Esophagitis - Medline Plus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, USA - (https://medlineplus.gov/eosinophilicesophagitis.html)
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis - American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology - (https://www.aaaai.org/conditions-and-treatments/related-conditions/eosinophilic-esophagitis)
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis - Mayo Clinic - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/eosinophilic-esophagitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20372197)
- Ahmed M. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: an update. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016 May 6; 7(2): 207-13. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27158535)
What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune condition where the esophagus (food pipe) becomes inflamed due to accumulation of large numbers of a type of white blood cells (WBC) called eosinophils that accumulate in the tissues lining the wall of the esophagus. These eosinophils release chemicals that cause an allergic reaction and inflammation. Normally, there are no eosinophils in the esophagus, but their numbers increase rapidly (eosinophilia) during an allergic reaction, which can damage the esophagus.
Epidemiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis is increasingly being reported over the past few decades, largely due to better diagnostic methods as well as increased awareness amongst doctors. The current prevalence of EoE is estimated to be 50-100 per 100,000 population. Eosinophilic esophagitis is more prevalent in Caucasians and in males, with a male to female ratio of 3:1. However, it has also been reported in American African, Asian, and Hispanic populations.
What are the Causes of Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Some of the major causes of EoE are briefly highlighted below:
- Environmental Allergens: These include pollen, dust mites, animal dander, and molds.
- Food Allergens: Certain types of food can cause allergy, which include milk and other dairy products, eggs, soy, gluten-containing cereals, legumes, tree nuts, peanuts, fish and shellfish.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): In this disease, the stomach contents flow backwards (refluxes) into the esophagus, which becomes damaged due to acidic stomach juices, often leading to EoE.

What are the Symptoms & Signs of Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Some of the major symptoms and signs in children and adults are highlighted below:
Symptoms in Children
- Difficulty feeding (infants)
- Difficulty eating (children)
- Failure to thrive (infants)
- Decreased appetite
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Abdominal pain
- Regurgitation or vomiting
- Blockage of esophagus by food (impaction)
Symptoms in Adults
- Dysphagia
- Impaction
- Heartburn
- Chest pain
- Abdominal pain
- Regurgitation

How do you Diagnose Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
There are several tests that are used to diagnose EoE, which are briefly described below:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are used to detect an antibody termed immunoglobulin E (IgE), which is generated against a particular antigen (an allergen in this case) present either in food or environmental sources. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is used to detect the antibodies.
- Skin Prick Test: This test uses small needles coated with a variety of allergens used for pricking the skin. The prick introduces the allergens into the skin. If a skin reaction occurs for a particular allergen or several allergens, this indicates a positive test.
- Patch Test: This type of test uses a sticky patch on which minute drops of the various allergens are coated in a checkerboard pattern. The patch is usually stuck on the patient’s back. The appearance of an allergic reaction(s) indicates a positive test.
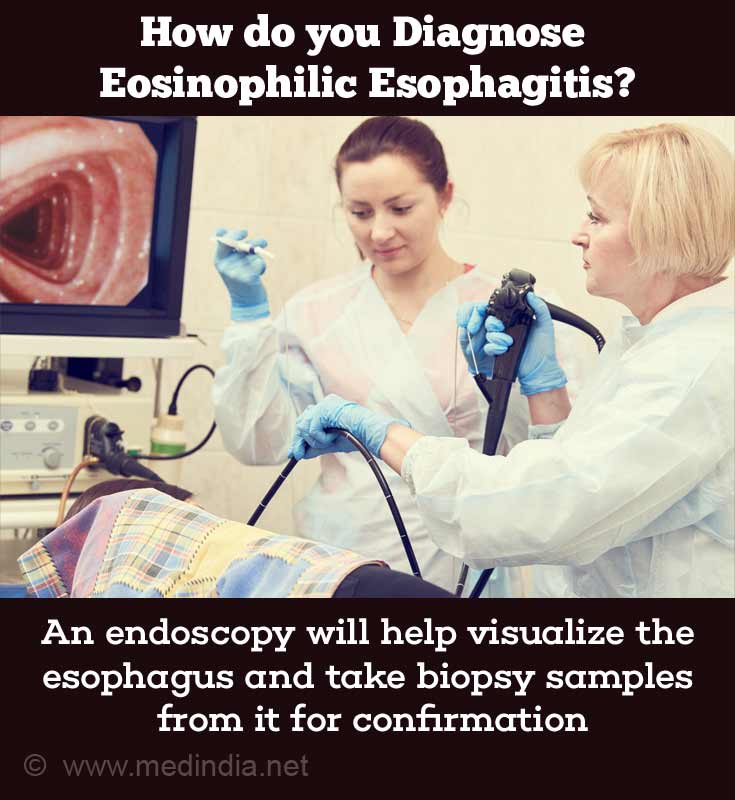
- Endoscopy: This procedure uses an endoscope to visualize and take biopsy samples from within the esophagus. An endoscope is a narrow tube that is fitted with a camera at its tip along with miniature cutting instruments to obtain tissue samples. These tissue samples are observed under the microscope to detect the presence of any eosinophils. Some of the characteristic pathological features that can be seen with an endoscope include inflammation and swelling, narrowing of the lumen (stricture), vertical furrows, horizontal rings, and white spots.
How do you Treat Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Treatment can involve several approaches such as:
- Avoiding Allergens: If any of the tests discussed above are positive for a particular allergen, then that allergen must be avoided. If the allergen is in food, then that particular food must not be consumed. If the allergen is from an environmental source such as pollens, then exposure to pollens must be prevented.
- Specialized Diet: In case of children and adults, all food that causes allergy must be eliminated from the diet, which is termed as an elimination diet. In case of babies and infants having severe food allergy to multiple allergens, an elemental diet is recommended, where a formulation consisting of amino acids, sugars, fats, vitamins and minerals are administered through a feeding tube.
- Medications: For treating inflammation,
topical corticosteroids at low doses are generally recommended. Two such steroids are fluticasone or budesonide, which are in liquid form and can be swallowed and since these are not absorbed into the bloodstream, there are no side-effects. If acid reflux is the cause of EoE, drugs belonging to the category ofproton-pump inhibitors (PPI) , such as omeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole are used for preventing acid production in the stomach. - Dilation:If the lumen of the esophagus becomes very narrow, or there is total blockage due to extensive inflammation, an endoscope-guided dilation procedure is carried out to open up the esophagus, so that food can pass easily.

What are the Risk Factors for Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
The major risk factors for EoE include the following:
- Predisposition to Allergies: If a person is allergic to food or environmental allergens, or suffers from atopic dermatitis, celiac disease, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, or allergic conjunctivitis, he/she may exhibit EoE.
- Climate: People living in cold and dry climates are more susceptible to developing EoE.
- Season: People are more prone to developing EoE during spring or autumn, since pollens and other environmental allergens are higher during these seasons.
- Heredity:It has been suggested that EoE may have a genetic component as it has been observed to run in families. A person having a family member who suffers from EoE is more susceptible to developing the disease.
- Age:The disease occurs irrespective of age, in both children as well as adults, although it was earlier thought to be a childhood disease.
- Sex:Eosinophilic esophagitis is more prevalent in males than in females.
- Race: Caucasians are more at risk of developing EoE.






