- Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE) - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/gap/cgi-bin/GetPdf.cgi?id=phd001525.1)
- Mini Mental State Examination - (https://patient.info/doctor/mini-mental-state-examination-mmse)
- The Mental Status Examination - (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2016/1015/p635.html)
- Pros and Cons of Various Screening Tools for Dementia - (https://leader.pubs.asha.org/do/10.1044/pros-and-cons-of-screening-tools-for-assessing-dementia/full/#:~:text=Advantages%20of%20the%20MMSE%20include,and%20cultural%20background%20affect%20scores.)
- The Mini-Mental State Examination: Strengths and weaknesses of a clinical instrument - (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285738407_The_Mini-Mental_State_Examination_Strengths_and_weaknesses_of_a_clinical_instrument)
- [The minimental state examination--an up-to-date review] - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17078433/#:~:text=Disadvantages%20of%20the%20MMSE%20include,bias%20in%20the%20MMSE's%20scores.)
- Limitations of the Mini-Mental State Examination - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2743549/)
- MIRECC Mini-Mental State Examination - (https://web.stanford.edu/~ashford/MIRECC_MMSE.html)
What is Mini-Mental Score?
Cognition forms the base of one’s life. However, the decline in cognition due to various risk factors may adversely affect the qualitative functioning of life, especially in older adults.
There are three standardized screening tests to assess the cognitive status of the person: Mini-Mental Status Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), and Saint Louis University Mental Status (SLUMS) exam.
Among them, one of the extensively used standardized tests is Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE). The test comprises of assessing various aspects of cognition like orientation, memory (immediate and delayed), attention, and language.
Procedure and Interpretation of MMSE Scores
The Mini-Mental State Examination is also perhaps the most often used cognitive screening measure at the bedside. It involves asking a set of 30 questions to establish the cognitive status of the person. The test generally takes about 10 minutes.
Various aspects included in the MMSE are:
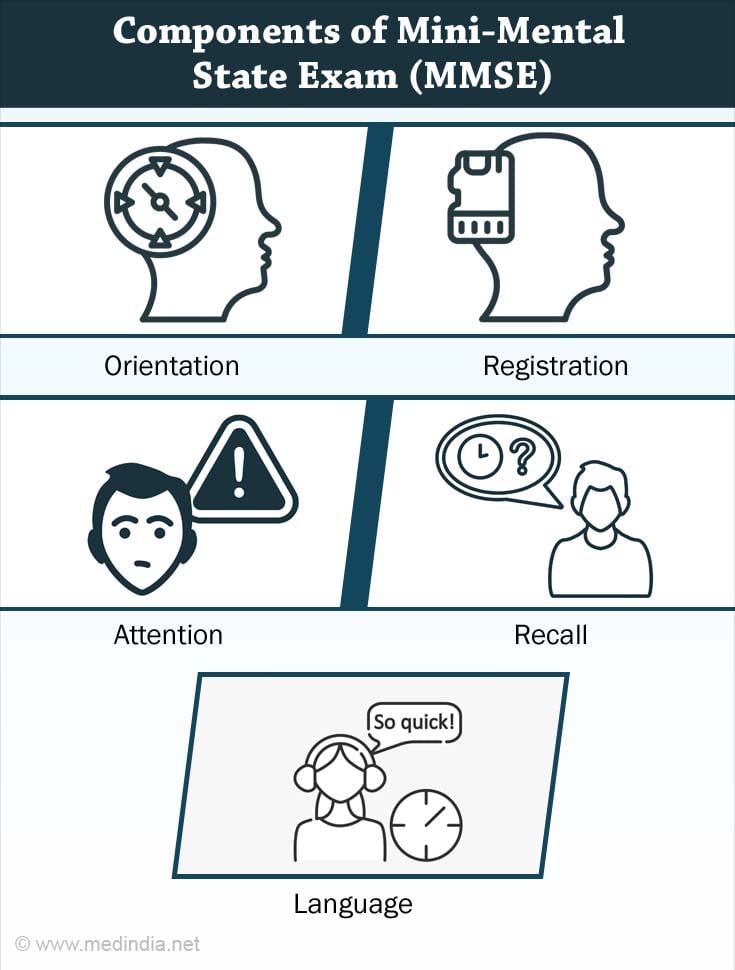
Orientation:
- What is the year?
- What season of the year is it?
- What is the month?
- What is the date or day of the month?
- What is the day of the week?
- What state are we in?
- What county are we in?
- What city/town are we in?
- What floor of this building are we on?
- What is the name or address of this place?
Registration:
The patient is given a chance to repeat three named objects by the examiner. For example, the examiner provides the name of three objects:
- Apple
- Watch
- Pen
and asks them to repeat it (with an immediate recall of each object scoring one point). Note that the examiner has to give three trials initially.
Attention:
The examiner gives the word and asks the patient to spell it forward and backward. For example, a word like “WORLD” is asked to spell out loud forwards (WORLD) and backward (“DLROW”) (with each letter holding one point — total score of 5 points for a correct sequence).
- D
- L
- R
- O
- W
Recall:
The examiner asks the patient to recall the three objects to test delayed verbal recall (each object scoring one point).
- Apple
- Watch
- Pen
Language:
- Examiner holds up an object (wristwatch or pencil) and asks the patient to name it to test the language.
- Watch
- Pencil
- The patient is also tested further for language by asking them to repeat a phrase. E.g.,
- “No ifs, ands, or buts”
- The examiner instructs the patients to take the blank sheet of paper in the right hand (from the examiner) and then fold the paper in half and put it down on their lap (each step scoring one point).
- Took paper in the right hand
- Folded paper in half
- Put the paper down
- Now, the examiner shows the written instruction on a page (e.g., “Close Your Eyes”) and asks the patient to do so (the patient has to reach the instruction and close their eyes in this case)
- Closes eyes
- The patient is then allowed to write any complete sentence on a piece of paper and say the sentence out loud.
- Sentence
- The patient is provided with a design on paper (horizontal overlapping pentagons) and asked to re-draw the same.
- Correct figure of pentagon/ horizontal overlapping
For the above questions:
- 0 denotes an incorrect answer
- 1 denotes a correct answer
Scoring of MMSE
Scoring below the level of education-adjusted cut-off on the MMSE may indicate cognitive impairment. Generally, a score of 24to30 is normal depending on age, and education among total MMSE score = 30.
- Education levels of 7th grade or lower: MMSE score of 22 or below
- Education level till only high school: MMSE score of 24 or below
- Education level of high school graduate: MMSE score of 25 or below
- Education level of college or higher: MMSE score of 26 or below
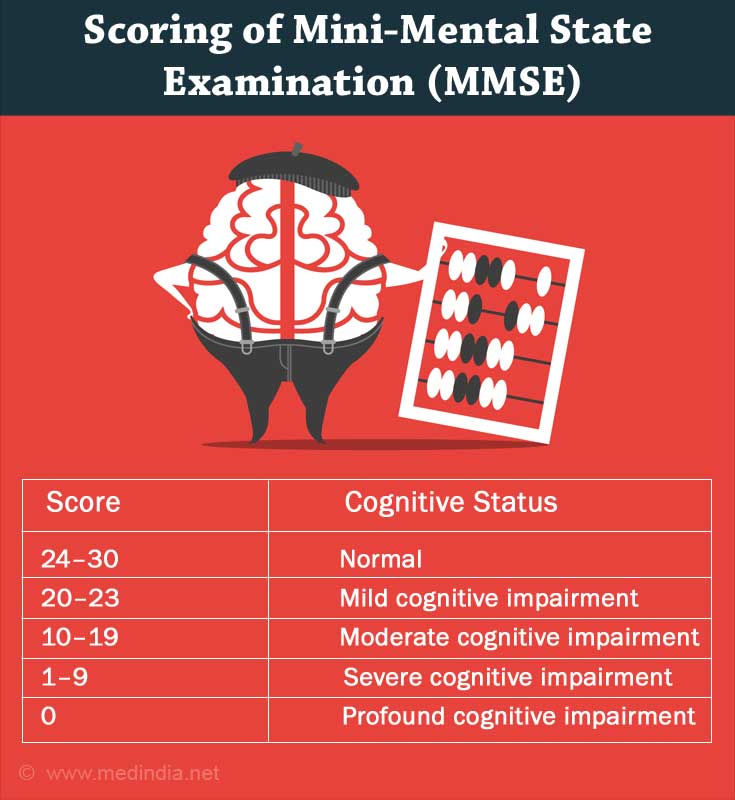
In general,
A score of
- 20–23 — Mild cognitive impairment
- 10–19 — Moderate cognitive impairment
- 1–9 — Severe cognitive impairment
- 0 — Profound cognitive impairment
In case of any functional disability, illiterate, or unable to deliver a response to a question, the examiner is supposed to specify the problem involved. The examiner then records the total MMSE score on the MMSE test form. If there is an oddity or lower MMSE score, the patient is referred for further neurology workup.
Advantages of Mini-Mental Score

- Various translated versions available in multiple languages
- The test provides conciseness and ease of administration
- Helps in the quick assessment of orientation, language functioning, and memory
- High levels of acceptance
Disadvantages of Mini-Mental Score
Although the test has its benefits, there are certain disadvantages like:
- Narrowed scope
- Mild cognitive impairment/ subtle memory losses cannot be detected efficiently
- The complexity of interpretation/inaccuracy according to different socio-economic contexts (education, age, and cultural background)
- Challenges in recording severe dementia cases and their changes
- Misleading data may be evident in the case of untrained professionals