What is Diabetes?
- Chronic health condition
- Insufficient insulin produced /used
- Affects sugar breakdown
Introduction
- Food eaten converted to glucose
- Glucose produces energy
- Insulin breaks down glucose
- Diabetics do not sufficiently produce or use insulin
- Causes blood sugar build-up in blood
Types
Type I diabetes
- Mostly occurs in children/young adult
- Insulin production affected
Type II diabetes
- Mostly occur in adults
- Body is partially/ fully insulin resistant
- Blood sugar level increases
Gestational diabetes
- Occurs in pregnant women

- Causes problems in mother and baby
Symptoms
- Increased thirst
- Excessive urination
- Weight loss

- Weakness
- Vision changes
- Dry skin / dehydration
- Numbness in hands/ feet
Diagnosis
- Fasting blood glucose level> 126 mg/dL
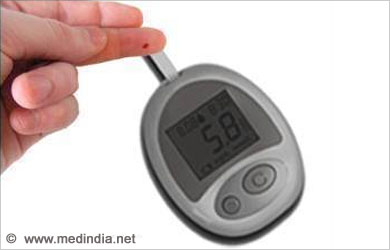
- Random Blood Glucose> 200 mg/dL
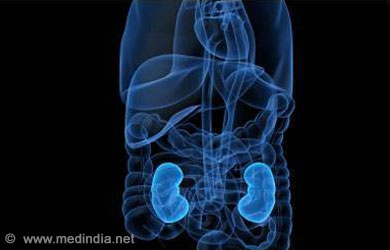
Complications of diabetes
- Diabetic Retinopathy (eye)
- Kidney Disease
- Heart Disease and Stroke
- Nerve Disease
- Impotence (sexual disorder)
Treatment
Type I diabetes
- Daily Insulin injections
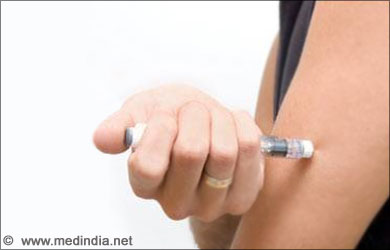
- Insulin cannot be taken as a pill
Type II diabetes
- Healthy diet and exercise brings down glucose level.
- Some people need diabetic medicine or insulin
Medications to lower blood glucose level
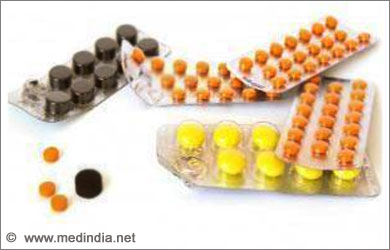
- Sulfonylurea drugs & Meglitinedes: Produces insulin in the pancreas
- Biguanides: decreases glucose in liver
- µ- glucosidase inhibitors: Slows the absorption of starch
- Consult a diabetologist or general physician




