What are Phytonutrients?
The familiar advice of eating more fruits, vegetables and whole grains stands on firmer scientific ground today than ever. The colors and flavors of fruits and vegetables result from the bounty of phytochemicals found in plant-based foods. Adding color to your palate is a sure-shot way to promote a healthy lifestyle.
Phytochemicals are gaining increasing popularity for their disease combating qualities.
Phytonutrients are non-nutrient compounds present in plants which function as anti-oxidants, enhance immune system, mimic hormones, detoxify carcinogens and suppress development of diseases, thus rendering a host of health benefits. People consuming generous servings of fruits and vegetables and eating whole grains on a regular basis are less likely to develop cardiovascular diseases, cancer, type 2 diabetes or premature ageing.
A variety of over-the-counter phytonutrient supplements are available in tablet, capsule, powder or liquid forms. They aim at providing phytonutrients without modifying a person’s eating pattern. However, supplements are not as effective as phytonutrients derived by eating natural foods.
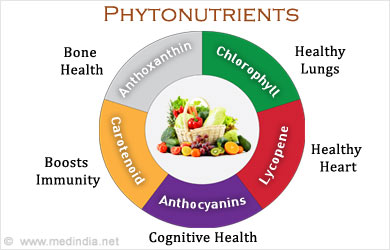
The different Types of Phytonutrients
The various kinds of phytonutrients are Carotenoids, Flavonoids, Lignans, Saponins, Phytic acid, Sulfides and Thiols, Terpenes.
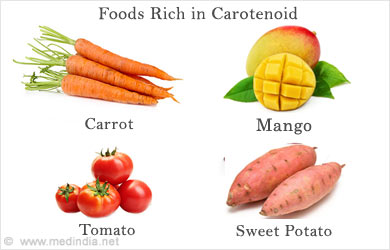
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are present in yellow, orange and red colored fruits and vegetables such as pumpkin, carrot, mango, tomato and sweet potato. These phytonutrients boost immunity and promote a healthy heart. Carotenoids, include lycopene, beta-carotene, lutein and zeaxanthin, which promote eye health and reduce the risk of cancer since they possess anti-oxidant properties. Beta-Carotene is a pre-cursor to vitamin A, which maintains a strong immune system, strong hair and smooth skin. Lutein and zeaxanthin reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration of the eyes, which may cause loss of vision. Egg yolk is an excellent source of lutein and zeaxanthin.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids possess anti-oxidant properties, free-radical scavenging capacity, heart disease prevention and anti-cancer compounds. Flavonoids are present in berries, dark chocolate, citrus fruits, green tea and onions, scavenge carcinogens by inhibiting conversion of nitrates into carcinogenic nitrosamines. Gingerol found in ginger and rutin present in tomato, parsley and apricots are different types of flavonoids found in foods.
Saponins
Saponins are phytonutrients found in beans and legumes which lower cholesterol levels by blocking absorption of cholesterol. They bind with bile acids and cholesterol which reduces cholesterol absorption. They also possess anti-cancer compounds and anti-diabetic properties as well as have a protective effect on liver.

Phytic acid
Phytic acid is considered an anti-nutrient since it reduces absorption of minerals like iron, zinc and manganese yet it lowers the risk of health problems. It inhibits hardening of the arteries and platelet formation. Foods higher in phytic acid such as legumes, cereals, nuts and oilseeds inhibit tumor growth, and reduce the risk of breast and prostate cancer.
Lignans
Lignans found in sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds, flaxseeds and soya bean regulate hormones, promote hair regeneration, reduce hair fall, lower the risk of heart diseases and maintain stable sugar levels. These phytonutrients mimic the role of estrogen and are thus called phytoestrogens. They lower the risk of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women.

Health Benefits of Phytonutrients
Phytonutrients function as anti-oxidants which protect against cellular damage caused by free radicals. Other benefits of phytonutrients include:
Heart Health
Carotenoids and flavonoids lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases by inhibiting oxidation of cholesterol in arteries which may result in hypertension, atherosclerosis and heart attack. Allylic sulphide found in garlic, leeks and onions lower hypertension.
Eating foods rich in lignans lowers the three risk factors of heart diseases - hypertension, cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
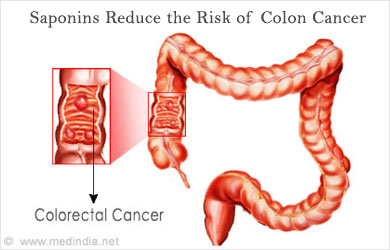
Lower Cancer Risk
According to research conducted at Linus Pauling Institute, secondary bile acids promote colon cancer. By binding to bile acids, saponins reduce the amount of secondary bile acids produced, thereby reducing the risk of colon cancer. Cruciferous vegetables contain phytochemicals- indoles and sulforaphane which ward off cancer by stimulating production of anti-cancer enzymes. Lignans reduce the risk of breast, ovarian and uterine cancer.
Good for Urinary Tract
Cranberries contain Proanthocyanidins, Phenolic Acids and Anthocyanins which function as a barrier to bacteria which may otherwise latch on the urinary tract lining resulting in Urinary Tract infections (UTI). Phytic acid promotes kidney health by lowering the chances of kidney stones.
Maintain Stable Sugar Levels
Phytic acid plays a role in pancreatic function and insulin secretion which reduces glycemic response of meals, benefiting diabetics by maintaining stable sugar levels.







