Normal Vaginal Bleeding
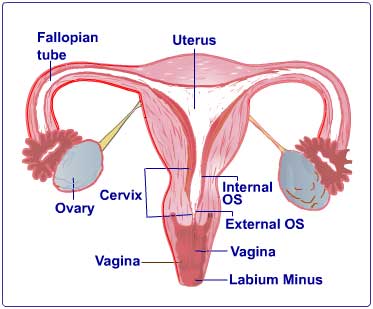
Normal vaginal bleeding is the periodic, bloody discharge from a woman’s uterus during menstruation. It is also known as menorrhea and is characterized by cyclic hormonal changes.
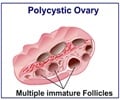
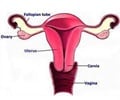
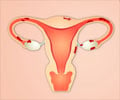
The ovaries in every woman produces an egg, each month, which travels through the fallopian tube and reaches the uterus. If the egg meets a sperm fertilization occurs and an embryo is formed. Otherwise the egg, along with the inner lining of the uterus, breaks down and bleeding occurs through the vagina.
The ovaries also produces hormones which controls the development of female body characteristics and regulate the menstrual cycle.
Menarche is when menstruation first begins in a girl and menopause is when menstruation stops in middle age.
Normally menstrual bleeding lasts for 3 to 5 days and during this phase a woman loses about 40 ml of blood and 35 ml of serous fluid. Initially the discharge is bloody but after a couple of days it is more watery or lightly blood stained. The normal range of blood loss varies between 2 to 16 tea-spoonfuls or from 10 to 80 mls. It is due to this monthly blood loss that women are more susceptible to iron deficiency anemia with low hemoglobin. This is more common among vegetarians