- What is Abortion? - (https://www.bpas.org/abortion-care/considering-abortion/what-is-abortion/)
- Abortion - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518961/)
- Induced Abortion: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5402385/)
- Abortion in India - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/abortion_in_india)
- Abortion (Termination of Pregnancy) - (https://www.health.harvard.edu/medical-tests-and-procedures/abortion-termination-of-pregnancy-a-to-z)
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment Bill, 2021): Is it Enough for Indian Women Regarding Comprehensive Abortion Care? - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8575235/)
- A framework for analyzing sex-selective abortion: the example of changing sex ratios in Southern Caucasus - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4208631/)
- Mifepristone - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557612/)
- What Happens in Abortion - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/abortion/what-happens/)
- Induced Abortion - (https://www.acog.org/~/media/for%20patients/faq043.pdf?dmc=1&ts=20121007t1323563261)
- Misoprostol - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539873/)
- Medical abortion with methotrexate 75 mg intramuscularly and vaginal misoprostol. Contraception - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9494770/)
- Manual vacuum aspirator: a safe and effective tool for decentralization of post miscarriage care - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25404439/)
- Second-trimester abortion by dilatation and evacuation: an analysis of 11,747 cases - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6866362/)
- Genetic factors as a cause of miscarriage - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20712563/)
- Clinical care for women undergoing abortion - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK138188/)
- The political economy of abortion in India: cost and expenditure patterns - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15938166/)
- Abortion Complications - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430793/)
- About Abortion Complications - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28613544/)
About
Abortion is one of the most controversial topics in medicine. Legalization of abortion in several countries was necessary to prevent complications and deaths of women due to illegal abortions.
Abortion is the termination of pregnancy before the fetus is viable; the period of viability is often referred to between 23 and 24 weeks of gestation. In some pregnancies, the fetus is spontaneously aborted by the body. In other cases, unwanted pregnancies are medically or surgically terminated(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Abortion
Go to source).
Induced abortions are not only ethically unacceptable by some communities, but illegal abortions also put the woman at a risk of sepsis and death. This has necessitated the legalization of abortions under certain circumstances(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Induced Abortion: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Go to source). Unfortunately, even legal abortions are not always done under ideally sterile conditions and by well-qualified staff, which still puts the woman at a risk for complications.
Though contraceptive methods are widely and easily available, abortions are very commonly carried out. Statistics indicate that the number of abortions has decreased in the developed countries and is increasing in the developing countries.
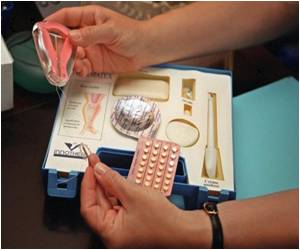
Abortion is carried out with medications or surgically depending on the duration of gestation. Medical abortion is usually done with a combination of two drugs - RU-486 or mifepristone that initiates the abortion, and a prostaglandin, which causes the uterus to contract and thereby expel the abortus. Methotrexate is used instead of mifepristone in places where mifepristone is not available. In some cases, a prostaglandin is used alone. Surgical abortion includes procedures like vacuum aspiration and dilatation and curettage.
An early abortion reduces the chances of complications in the mother as compared to an abortion in the later stages of pregnancy. Most abortions are carried out during the first trimester of pregnancy. In a majority of these cases, the pregnancy is unplanned. Later abortions are usually due to conditions like fetal abnormalities and serious illnesses in the mother, which could result in death of the woman during later pregnancy or delivery.
Abortion in India
In India, abortions are done according to the
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment Bill, 2021): Is it Enough for Indian Women Regarding Comprehensive Abortion Care?
Go to source).
The rules regarding abortion vary among different countries. Abortions in India are done in accordance with the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act of 1971, which was amended in 1975. Under this act, only qualified registered medical practitioners or
- Where the mother is suffering from a serious illness, wherein the pregnancy could endanger her life
- If the fetus is at a risk of suffering from a severe physical or mental abnormality
- If the fetus has chromosomal, genetic or structural abnormality
- Pregnancy as a consequence of rape
- Pregnancy as a consequence of contraceptive failure
- Where the socioeconomic condition of the mother does not permit a
healthy pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child
Unfortunately, in India, sex-selective abortions are a common reason for abortions. Preference for a boy child leads to abortions in case of a
A framework for analyzing sex-selective abortion: the example of changing sex ratios in Southern Caucasus
Go to source).
Laws of abortion in India
Thee Supreme Court of India declared abortion as a fundamental right and that all women have the right to safe and legal abortion under the 'Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act'.
Among other rights of women, it is believed that every mother has the right to abortion and it is a universal right. "The rights of reproductive autonomy, dignity and privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution gives an unmarried woman the right of choice as to whether or not to bear a child on a similar footing as that of a married woman,"
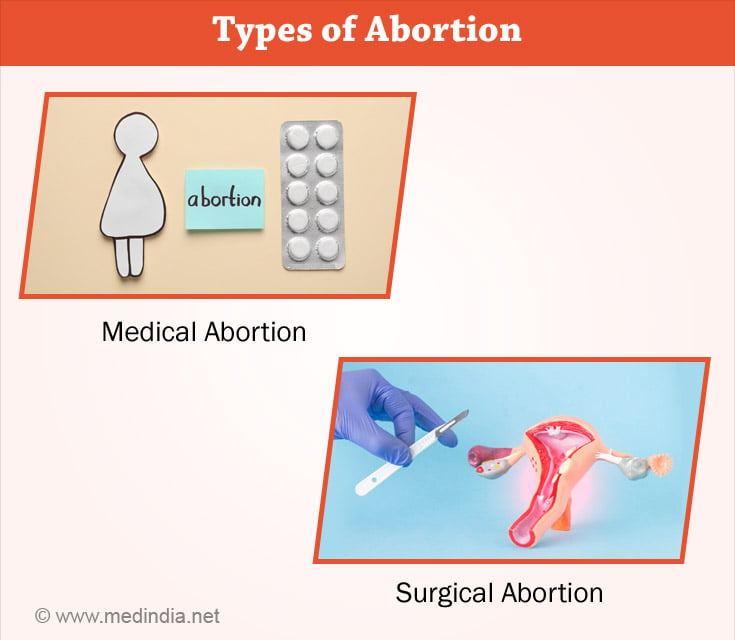
What are the Types of Abortion?
An abortion may be done either with the use of medications or performed surgically.
Induced abortions are of two types -
Medical Abortion
Medical abortion is done using certain medications that bring about termination of pregnancy. It is usually performed till 9 weeks from the last
- Mifepristone and misoprostol: mifepristone is a drug that acts as anti-progesterone;
progesterone is a hormone that helps to maintain pregnancy. It is administered as an oral tablet of 600mg and brings about abortion in 65 to 80% cases. In order to improve the results, it is followed by 400 µg ofmisoprostol 48 hours later(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Mifepristone
Go to source).Misoprostol is a prostaglandin, which brings about contraction of the uterus and dilates thecervix , which thus helps to evacuate the uterus. Misoprostol may also be administered vaginally as a single or two doses, or by sublingual (kept under the tongue) or buccal (absorbed through the mucus membranes of the mouth) routes. Gemeprost may be used as a vaginal pessary instead of misoprostol. It may also be used without mifepristone in some cases(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Misoprostol
Go to source). Medical abortion with mifepristone and misoprostol is often used for termination of twin gestations as a twin gestation is not considered a contraindication. - Methotrexate and misoprostol: Methotrexate followed by misoprostol is administered in countries where mifepristone is not available, but this combination is comparatively less effective(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Medical abortion with methotrexate 75 mg intramuscularly and vaginal misoprostol. Contraception
Go to source).
Surgical Abortion:
Surgical abortions were performed even before medical methods were available. These include:
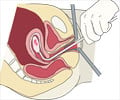
- Vacuum aspiration: Vacuum aspiration is a common surgical procedure where a vacuum is applied in the uterus to bring about abortion. It is usually performed under
local anesthesia before 12 weeks of gestation. Treatment to soften and dilate the cervix may be administered before the procedure. Very early abortions may be done manually with a syringe. These are referred to as manual aspirations or menstrual aspirations(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Manual vacuum aspirator: a safe and effective tool for decentralization of post miscarriage care
Go to source).
Chances of serious complications are low and include perforation of the uterus and incomplete abortion.
- Dilatation and evacuation: Dilatation and evacuation is the surgical procedure usually adopted for abortion during second trimester. The cervix is initially softened and dilated. This is followed by surgical evacuation of the uterus with suction curettage and manual extraction(9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Second-trimester abortion by dilatation and evacuation: an analysis of 11,747 cases
Go to source).
Up to 9 weeks of gestation, the patient may be offered either medical or surgical abortion. Studies indicate that surgical abortions are more acceptable to women. This may be due to more pain, prolonged bleeding and slightly higher failure rate with medications as compared to surgical evacuation.
Abortions after
Causes of Abortion
First trimester:
The causes of abortion in the first trimester (0-12 weeks) may be due to chromosomal abnormalities and placental problems(10✔ ✔Trusted Source
Genetic factors as a cause of miscarriage
Go to source).
Second trimester:
The causes of abortion in the second trimester (13-26 weeks) are because of infections, food poisoning, medications, weakened cervix, PCOD and long term health conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, lupus, kidney disease, and thyroid disease.
Pre-abortion Assessment and Post-abortion Treatment
Before the Abortion, the period of gestation should be confirmed.
When a woman comes to the clinic for an abortion, she should be offered counseling. Once she has decided to go ahead with the abortion, she will undergo an examination and some laboratory tests like urine and
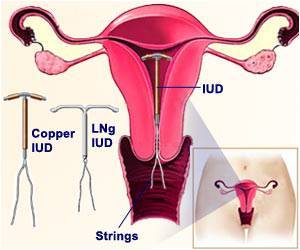
Post procedure, a contraceptive in the form of
The patient is instructed to avoid strenuous activity or the use of
Clinical care for women undergoing abortion
Go to source).
Cost of Abortion:
Abortions cost a substantial amount-first trimester abortion averages Rs. 500-1000 and second trimester abortion Rs.2000-3000. The cost of a surgical procedure of medical termination of pregnancy in India comes around 30000 INR. Abortion pill in India costs around 500 to 700 Indian Rupees in the Pharmacy(12✔ ✔Trusted Source
The political economy of abortion in India: cost and expenditure patterns
Go to source).
Home remedies after abortion
Home remedies like physical care and emotional care can be followed after abortion.
Physical care:
To reduce the chances of an infection, for 2 weeks, they should avoid:
- using tampons
- having penetrative sex
- putting anything in the vagina
- using swimming pools
It is also important to take care of oneself after having an abortion. Although the procedure itself is relatively short, it can take several days or weeks to recover physically. A person can try:
- massaging the stomach and lower back
- using a heat pack
- taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- attending follow-up appointments
Emotional care
People should take adequate time off work, speak with family members and friends, and contact a doctor if they experience mental health difficulties.
What are the Complications of Abortion?
Complications of abortion include bleeding, infection, trauma to organs, and incomplete evacuation.
Complications of medical abortion include(13✔ ✔Trusted Source
Abortion Complications
Go to source):
Nausea, vomiting ,loss of appetite , and diarrheaFever and chills- Heavy bleeding
Abdominal pain - Incomplete abortion, which may require surgical evacuation
- Rarely, infection
Complications of surgical abortion include:
- Bleeding: Though some bleeding is normal after an abortion, in cases of trauma to the uterus or incomplete abortion, bleeding may be excessive.
- Infection: Infection can result if adequate sterile precautions are not followed during the procedure. The patient may complain of a foul-smelling discharge and fever. Severe infection or sepsis could also occur.
- Abdominal cramps: The patient may complain of abdominal or
backpain and cramps during and after the procedure. - Incomplete abortion: Incomplete abortion may result in excessive bleeding and infection following the procedure.
- Trauma: The surgical instruments used during the procedure may damage the uterus or sometimes neighboring organs like bowel and
bladder (14✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Abortion Complications
Go to source).