- Acute bronchitis - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2278319/pdf/0540238.pdf)
- Albert RH. Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Bronchitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010 Dec 1;82(11):1345-1350.
- Bronchitis Symptom - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/basics/symptoms/con-20014956)
What is Acute Bronchitis?
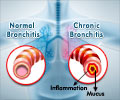
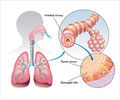
Acute bronchitis, commonly known as a chest cold, is a short-term inflammation of lower respiratory tract affecting the air tubes (bronchi) of the lungs.
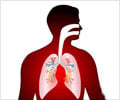
The upper airways consisting of the nose and throat lead to the trachea or windpipe. The windpipe bifurcates at its lower end to form the left and right bronchi. These further branch out to carry inhaled air into the lungs and provide a path for the exhaled air to move out.
Acute bronchitis occurs suddenly and usually lasts for 3-10 days. About 5% of adults have been reported to seek medical advice for bronchitis annually.
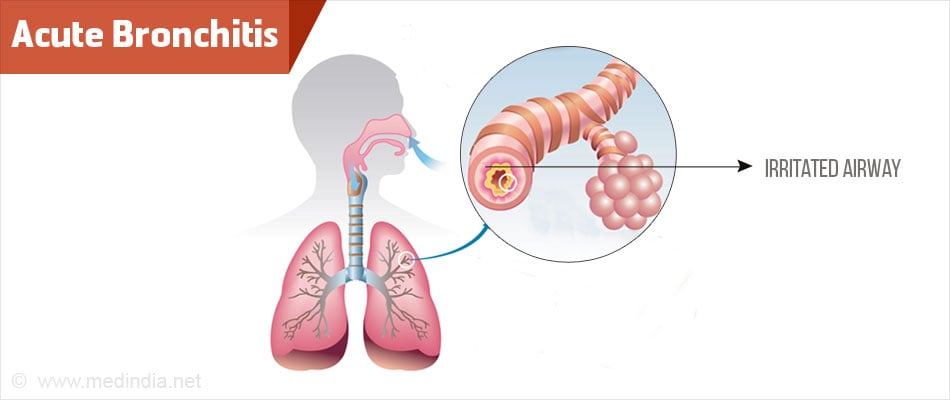
What are the Causes of Acute Bronchitis?
Viruses are considered to be the main causative organisms of acute bronchitis, being responsible for up to 95% of cases in healthy adults. The most common viruses that may cause acute bronchitis are rhinovirus, adenovirus, influenza A and B, and parainfluenza virus. Bacteria like Bordetella pertussis and Mycoplasma pneumoniae and can also cause bronchitis especially in people with underlying health problems.. Individuals who are exposed to tobacco smoke, air pollution, dust, vapors, and fumes can also develop acute bronchitis.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Acute Bronchitis?
The symptoms of acute bronchitis typically persist for approximately three weeks.
- Cough with or without sputum production, which is the primary symptom
- Wheezing
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Fever if present may be due to pneumonia or influenza
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Sore throat from persistent coughing

- Fatigue
How do you Diagnose Acute Bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is often diagnosed based on the symptoms and examination of the patient. In some cases, like when there is a probability of secondary infection, the physician may suggest additional testing. Rapid diagnostic tests that exist to detect the presence of organisms linked to acute bronchitis may also be needed.
Tests to diagnose acute bronchitis may include:
- Sputum Tests: Inflammation of the airways may cause them secrete thick mucus called sputum. The sputum is cultured to check for the presence of bacteria that may need treatment with antibiotics.
- Pulmonary Function Test: During a pulmonary function test, a device called a spirometer is used to test lung function. It measures how much air the lungs can hold and how quickly air gets out of lungs.
- Chest X-ray or CT scan: A chest X-ray or computerized tomography (CT) scan is used for patients whose physical examination suggests pneumonia or heart failure.
How do you Treat Acute Bronchitis?
A patient with acute bronchitis should receive adequate rest and symptomatic treatment.
Antibiotics and Antiviral drugs- Antibiotics for acute bronchitis should be avoided as far as possible. Antibiotics like cefaclor, Amoxicillin, doxycycline and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole may be used if the patient at a risk of suffering from complications like pneumonia, or for serious causes of acute bronchitis like whooping cough. For infection with influenza A virus, antiviral drugs like oseltamivir or zanamivir can be used.
Anti-tussive Therapy- Patients with bronchitis may find relief with cough suppressants or expectorants like hydrocodone, guaifenesin, dextromethorphan, carbetapentane or benzonatate, which may be used for a temporary basis.
Bronchodilators- Short-acting bronchodilators like albuterol relax the bronchi and may be useful in patients with wheezing.
Alternative Therapy- Studies have revealed the benefits of echinacea, pelargonium, and honey in acute bronchitis. The trials of echinacea in patients with bronchitis and the common cold have showed positive results.
How do you Prevent Acute Bronchitis?
Avoiding lung irritants is very important for preventing acute bronchitis as well as treating it.
- Avoid cigarette smoke. The most important step is to quit smoking. Cigarette smoke increases your risk of acute or chronic bronchitis.

- Get vaccinated. Many cases of acute bronchitis result from influenza A virus. Getting a yearly flu shot can help protect you from getting the flu.
- Wash your hands. To reduce your risk of catching a viral infection, wash your hands frequently and make using hand sanitizers a habit.
- Wear a surgical mask. When you are around people suffering from acute bronchitis, avoid touching your mouth, nose, or eyes. These body parts are very susceptible to infection so the use of masks in public may prevent acute bronchitis.
- Stay away from strong fumes. Cover your nose when you use paint, paint remover, varnish, or other substances with strong fumes. This will help protect your lungs and prevent acute bronchitis.
Health Tips
- You should learn to practice good hygiene. Washing your hands regularly and well, particularly during cold season, helps to limit your exposure to germs and bacteria and can help you to avoid viral infections.
- Get vaccinated with the flu vaccine yearly.