- What Causes Amnesia? - (https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/psychpedia/amnesia)
- United states of amnesia: rescuing memory loss from diverse conditions - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc5992608/)
- Amnesia - An Overview - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/amnesia#types)
- Amnesia / Memory Loss - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/amnesia)
- Amnesia - Health Library - (https://www.winchesterhospital.org/health-library/article?id=917219)
Overview
Amnesia, is a neurodegenerative disease and its common symptom is memory loss. Diagnosis of amnesia may involve a range of blood tests and scans but its treatment does not require hospitalization. Prognosis of amnesia depends on the underlying cause.
Amnesia, in ordinary terms, means profound memory loss.
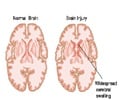
It can be caused by a physical injury inflicted on the brain, by brain damage caused by a traumatic or an emotional experience or by an infection.
In many cases, amnesia is associated with neurodegenerative diseases in which the primary symptom is memory loss. In most cases the amnesiacs are quite aware of their memory loss problem.
There are several types of amnesia, the main symptoms include an inability to recall old memories or an inability to remember new ones.
Diagnosis ranges from physical examination and blood tests to MRI brain scans. The treatment for amnesia depends on the cause but in the vast majority of cases hospitalization is generally not required.
The prognosis of this condition varies with the underlying cause, for instance, curbing alcohol intake in a person can revive his memory in a very short period, if that is the original cause of his memory loss.
However, in case of severe brain injury, without permanent damage, it may take up to months or even years, before the person recovers. In some unfortunate cases amnesia is life long as it never goes away.
Brain researchers have always sought the help of amnesiacs to determine the memory-processing function of the brain. Contrary to what was believed earlier that memory is a single entity, recent research reveals that the brain has multiple systems for storing, processing and drawing on one’s memory.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
United states of amnesia: rescuing memory loss from diverse conditions
Go to source)