About
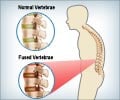
Ankylosing spondylitis is a condition that affects the lower back. The term ankylosing spondylitis describes the nature of the disease- ‘ankylosing’ which refers to ‘fusing together’ and ‘spondylitis’ which refers to ‘inflammation of vertebral bone’.
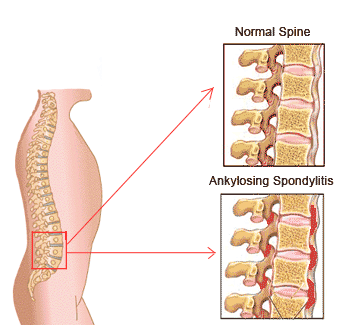
Ankylosing spondylitis can result in intermittent episodes of back pain that occur throughout life, or can occur in the form of severe chronic disease that attacks the spine, peripheral joints and other body organs resulting in severe joint and back stiffness, loss of motion and deformity as life progresses. It is a progressive disease; the pelvic region is affected first followed by lower back, chest wall, neck, shoulder, hips, knees, jaw, eyes, lungs, heart and bowel.
The cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown and unclear. However, it may have a genetic association.
Ankylosing spondylitis cannot be cured. The treatment is aimed to relieve pain, preserve joint mobility and prevent deformity of the spine.
The doctor may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce the swelling and pain. Corticosteroids, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors or disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs can be used to calm the swelling and immune system. Surgery is recommended if pain or joint damage is severe. Exercises and physiotherapy can help improve posture and breathing.
Although ankylosing spondylitis is an irreversible long-term condition, patients who get the right treatment can live relatively normal and independent lives.