- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 17th Edition.
About
Aphasia is a condition where the patient has a language problem. He cannot understand, express words or sentences, repeat, read or write. The person’s intelligence is usually not affected.
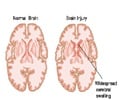
Aphasia occurs when a part of the brain is damaged, for example, in cases of
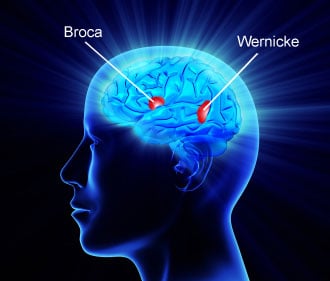
Aphasia is diagnosed through clinical examination aided with diagnostic studies such as CT scan, MRI, PET scan or using SPECT imaging. Some patients recover completely when the underlying cause is treated whereas some may worsen progressively. A number of patients benefit with