- Biomechanics of the Ankle - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc4994968/)
- Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) - (https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/ankle-fractures-broken-ankle/)
- Stability in Ankle Fractures - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5994620/)
- Pott's Fracture - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc5531910/)
- Ankle Fracture Medication - (https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/824224-medication)
- Fractures of the Ankle Joint - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4075279/)
- Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle): Anatomy, Symptoms, Treatment - (https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_ankle-fractures.asp)
- Bimalleolar and Trimalleolar Fractures - (https://ace-pt.org/ace-physical-therapy-and-sports-medicine-institute-bimalleolar-trimalleolar-fractures)
- X-Ray Exam: Lower Leg (Tibia and Fibula) - (https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/xray-lower-leg.html)
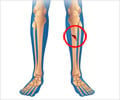
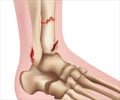
What is a Bimalleolar Fracture / Broken Ankle?
Bimalleolar fractures occur when there is a break at the lower ends of the fibula and tibia at the ankle.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle)
Go to source)
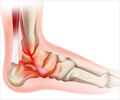
When the lower projections or malleoli of the fibula and the tibia are displaced from their known positions due to a fracture, it results in a displaced bimalleolar fracture or a bimalleolar fracture dislocation. The use of “bi” indicates a fracture in 2 bones. The fracture can be determined with an X-ray.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Stability in Ankle Fractures
Go to source) However, the damage to the cartilage that lines the bones cannot be determined with an X-ray image. Individuals who experience such fractures are prone to arthritis at the ankle. Bimalleolar ankle fractures are also known as Potts fractures (a misnomer) after Sir Percival Pott, who first described the mechanics behind ankle fractures.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pott's Fracture
Go to source)
Ankle fractures occur at a rate of 174 cases out of 100,000 persons in the world. They commonly occur due to falls, road accidents, and sporting events. Based on the kind of injury and the number of bones that are broken, ankle fractures are divided into 3 main categories as unimalleolar, bimalleolar, and trimalleolar fractures. Many kinds of classifications on fractures exist. Among these, the Danis-Weber classification is the widely used in the classification of lateral malleolar fractures.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Fractures of the Ankle Joint
Go to source)
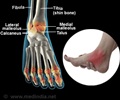
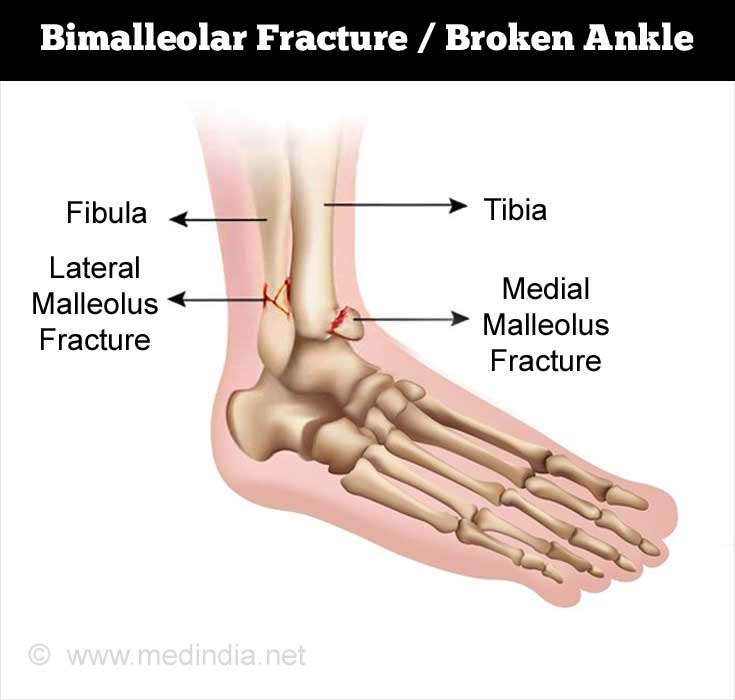
Structure of the Ankle
The ankle consists of the lower ends of the tibia and fibula, the bones of the leg, and the talus, a bone of the foot. The lower ends of the tibia and the fibula are connected with ligaments and form a syndesmosis joint. The lower end of the tibia projects on the inner side of the ankle to form a prominence called the medial malleolus, while the lower end of the fibula projects outwards at the ankle to form the lateral malleolus.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Biomechanics of the Ankle
Go to source)
According to the Weber classification, fracture of the lateral malleolus at the syndesmosis joint constitutes a Type B Weber fracture. A fracture of the lateral malleolus above the syndesmosis joint constitutes a Type C Weber fracture, while below the syndesmosis joint it constitutes a Type A Weber fracture.
Bimalleolar Fracture Classification
Based on the Weber classification, bimalleolar fractures that occur at the level of the syndesmosis are classified as Type B fractures. These fractures are often unstable and require surgical intervention unless there are other health complications in the individual that make surgery inadvisable.
Bimalleolar Fractures that occur in the lateral and medial malleoli and are called true bimalleolar fractures. The lateral malleolus indicates the lower end of the fibula. The medial malleolus indicates the lower end of the tibia.
Bimalleolar equivalent fractures include the lateral malleoli as well as injury to the deltoid ligament on the inner side of the ankle. These fractures are very unstable and require surgery as treatment.
Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis of Bimalleolar Fractures
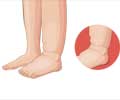
Bimalleolar fractures are caused by road accidents, falls, among others and can be diagnosed with a physical examination and a radiological evaluation. Swelling, inability to bear weight, and dislocated bones are some of the symptoms.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle): Anatomy, Symptoms, Treatment
Go to source)
Causes of Bimalleolar Fracture
Bimalleolar fractures occur due to the following causes:
- Road accidents
- Falls
- Falling on a gradient
- Twisting the ankle

Signs and Symptoms of a Bimalleolar Fracture
Some of the common symptoms of a broken ankle resemble those of a sprain. Unless examined by a physician, the correct diagnosis cannot be made. Following are some of the symptoms observed in an ankle fracture:
- Tenderness in the region of the fracture, when pressure is applied
- Swelling of the fractured region
- Bruising or hematoma formation in the fractured region
- Displacement of the bones
- Inability to bear weight on the foot
- Severe pain
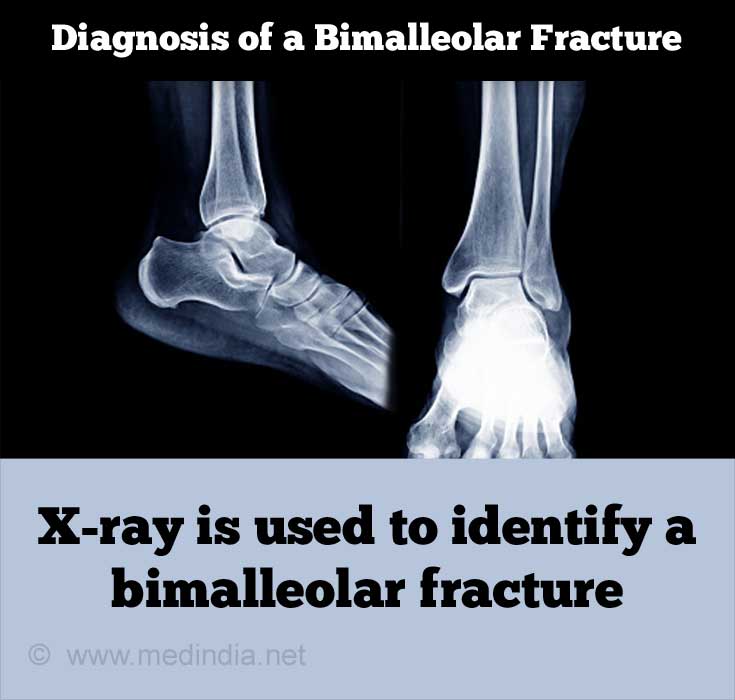
Diagnosis of a Bimalleolar Fracture
The diagnosis of a bimalleolar fracture can be confirmed by a physical examination that is combined with a radiological evaluation. Sometimes, the symptoms between an
A radiological evaluation follows an established set of procedures or an algorithm in studying the x-ray images. The physician evaluates the condition of the fibula, tibia, and the talus. The distances between the respective bones and the joints are also examined before arriving at the conclusion of a fracture.(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
X-Ray Exam: Lower Leg (Tibia and Fibula)
Go to source)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is utilized in extreme cases to identify cartilage or ligament damage.
Treatment for Bimalleolar Fractures
The displaced bones of the ankle are subjected to reduction before performing surgery. Home exercises and physiotherapy aid in the rehabilitation of individuals with ankle fractures. It takes 12 to 16 weeks for the complete recovery.
Immediate Treatment
Individuals with bimalleolar fractures need to be assessed for bone and tissue damage, in addition to the condition of their health. The treatment is decided based on the combination of the above factors.
Individuals with a suspected ankle fracture are examined immediately for nerve injuries and the condition of the soft tissue surrounding the bones. In the event of a dislocation, the bones need to be realigned to its proper position (reduction) in the presence of an anesthetic.
Surgery
The purpose of surgery in ankle fractures is to reconstruct the normal shape of the bones of the ankle, minimize ligament damage, and accelerate the recovery of the ankle. The initial reduction performed on the bones during displacement is observed in an X-ray. If the bones have set in the correct position, surgery is deferred. However, if the bones are not set properly, surgery is required in such cases. Surgery can only be performed if there is no swelling in the soft tissue surrounding the injury. During surgery, swelling creates pressure while closing the wound. This, in turn, results in infections arising in the wound.

Patients with osteoporosis, peripheral artery occlusive disease and diabetes, have to be carefully assessed for the extent of soft tissue damage and the level of damage to the bones due to a possibility of delayed healing. Patients are invariably provided a cast or a walker to minimize postoperative complications.
Conservative Treatment
A walker or a vacuum shoe is used for treating bimalleolar fractures. This is to avoid the individual from putting maximum weight on the ankle while walking. During the night, an orthosis is kept on the ankle to prevent the ankle from bearing any weight. X-rays should be taken periodically at 4, 7, 11, and 30 days following the fracture to monitor any fragment displacement or widening of the fork in the ankle bones. If the individual is old or has other health risks, surgery is not performed. Conservative treatment is advised in these cases and individuals accept that their bones will heal in an imperfect manner.
Bimalleolar Fracture Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of individuals with bimalleolar fractures includes home exercises and physiotherapy. It is necessary for individuals to perform these exercises regularly as full functionality of the ankle returns only after several months. If strengthening exercises are performed regularly, the individual will be able to walk without a limp.
Based on the type of fracture, physicians will decide the time required to put weight on the ankle. Individuals should follow the recommendations of the physician before putting weight on the ankle. If weight is put prematurely on the ankle, there will be a shift in the bones and the surgical procedure will be affected. In fractures that are treated with conservative treatment, individuals have their ankle supported in a leg orthosis. This minimizes the pain and the ankle adapts to bear weight. Initially, the ankle may be placed in a splint.
In individuals, who are treated with surgery, antithrombotic drugs are administered to reduce the pain involved until the ankle is capable of bearing the full weight and is mobile.(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Bimalleolar and Trimalleolar Fractures
Go to source)
Bimalleolar Fracture Recovery and Healing Time
The ankle fracture recovery and healing time vary between 12 to 16 weeks to achieve the full weight-bearing capacity.
Physiotherapy for Bimalleolar Fracture
Early postoperative physiotherapy treatment is recommended to improve the healing of the ankle joints, improve flexibility, and reduce the swelling in the soft tissues. Patients with ligament damage require physiotherapy to avoid ankle instability. During the recovery of the patient in the hospital, when the ankle appears to be able to bear some weight, the individual is made to lift partial weights of 10 to 20 kg. Following 6 weeks of partial weight-bearing, x-rays of the ankle are taken to observe the healing rate. The positioning screws are removed accordingly and the individual is made to lift more weights incrementally at 10 kg per week. In 12 to 16 weeks, the ankle of the individual is capable of bearing a complete weight load.
Drugs to Treat Bimalleolar Fracture
Parenteral narcotics and acetaminophen are administered to patients with a fracture. Patients are also injected with tetanus shots to prevent infection. During the surgery, short-term sedatives are administered. Antithrombotic drugs are administered following surgery until the mobility and the weight bearing capacity is restored in the ankle.(9Ankle Fracture Medication
Go to source)