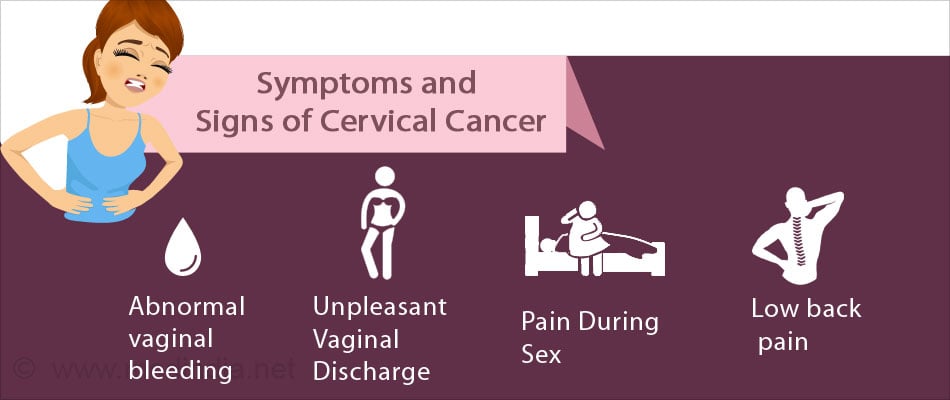
What are the Symptoms & Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer?
Pre-cancerous stages though asymptomatic, may be detected through routine screening, while the advanced stages of the disease generates a volley of signs and symptoms
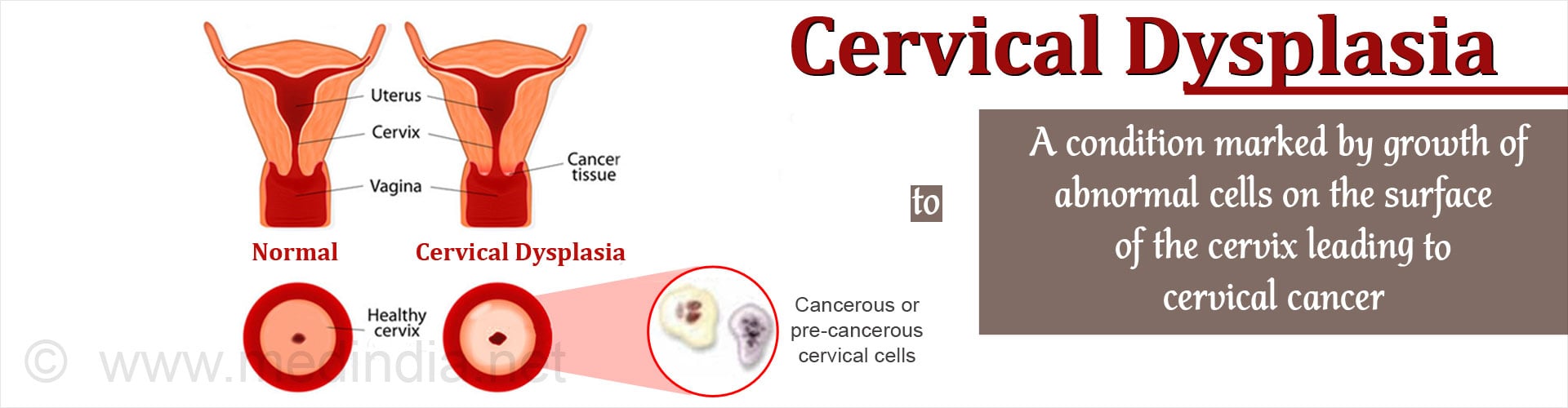
The early stages of cervical cancer are asymptomatic. A routine Pap-smear helps to detect pre-cancerous or cancerous changes in the lining cells of the uterus. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding-it can be during or after sexual intercourse, or between periods
- Foul-smelling, yellow vaginal discharge
- Low back pain
- Pain during urination (dysuria)
- Pain during sex (dyspareunia)
- Bleeding after douching
The symptoms of spread of the cancer or metastasis include:
- Constipation
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Abnormal opening in the cervix
- Ureteral obstruction
What is Cervical Cancer Screening?
Screening for cervical cancer helps in prevention and early detection of the disease when it can be treated easily.
An HPV test is a laboratory test that is used to check DNA or RNA for certain types of HPV infection. Cells are collected from the cervix and DNA or RNA from the cells is checked to find out if there is an infection caused by a type of human papillomavirus that is linked to cervical cancer.
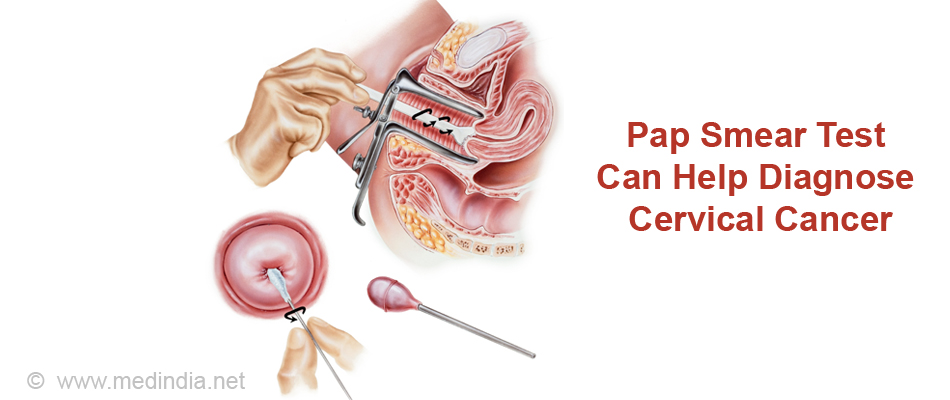
A Pap test is a procedure to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and vagina. A piece of cotton, a brush, or a small wooden stick is used to gently scrape cells from the cervix and vagina. The cells are viewed under a microscope to find out if they are abnormal. This procedure is also called a Pap smear.
What are the Diagnostic Tests for Cervical Cancer?
These tests are performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of spread of disease, when a Pap smear is positive for cancer. According to the stage of the disease, the treatment will be planned.
Cone biopsy
In this procedure, also known as conization, the doctor removes a cone-shaped piece of tissue from the cervix. A cone biopsy is not only used to diagnose pre-cancers and cancers but it can also be used as a treatment modality since it can sometimes completely remove pre-cancers and some very early cancers.
Computed tomography (CT): CT scans are usually done if the tumor is larger or if there is concern about cancer spread
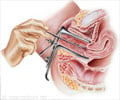
Colposcopy: A colposcopy is an examination of the vagina and cervix using a lighted magnifying instrument called a colposcope. A sample of the cervical tissue can be curetted for histological examination referred to as endocervical curettage.
Positive emission tomography (PET) scan – a specialised scan, where a mildly radioactive substance is injected into your veins so the cancerous tissue shows up more clearly;
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan – this type of scan uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed pictures of the inside of your body; it can also be used to check whether cancer has spread
X-ray - An x-ray is a way to create a picture of the structures inside of the body using a small amount of radiation. An intravenous urography is a type of x-ray that is used to view the kidneys and bladder.




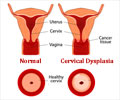






What is the symtoms of having cervical cancer?
can penis penetrate into the cervix kind regards
What is the incidence of ca cx in India in 2010? kindly support with references.
Cervirax is considered to be effective before any contact with semen, but if somebody is using coitus interruptus method of contraception is it of any use or not????
The vaccines Gardasil and Cervarix won't reduce cancer incidence or deaths. They will divert hundreds of billions of health care dollars to the coffers of pharmaceutical companies.
HPV infections, advertised to be the cause of cervical cancer, are slow and handled by our immune systems in over 90% according to the CDC/FDA/American Cancer Society
Women who don't clear HPV infection have immune problems caused by nutritional deficiencies, toxic exposure, toxin ingestion or genetics.
If an immune system can't clear an HPV infection no vaccine can help. Vaccines are passive targets and can't fix an immune system unable to identify or destroy HPV
HPV is controlled by intracellular immune response. Vaccine stimulate the humoral, antibody, response. Antibodies fight bloodborne infections and will not appreciably affect the rate of cervical HPV infections and CANNOT combat an active HPV infection
This will be proved in 20 years when vaccines are shown to have failed
You're correct in stating that the vaccines will not combat those already infected. However, they have been proven to prevent infection of the HPV strains 6,11,16, and 18. Women don't have to have an "immune problem" caused by toxins, etc. to not clear the infection.I suggest you check your facts before posting such erroneous statements.
I made no errors. Over 90% of us clear all HPV infection without drugs doctors or vaccines [FDA], a properly functioning immune system doing it's job. Chronic infection is caused by an immune system problem as I described
Gardasil has NOT been proven to prevent HPV infection, except by conflicted Merck research
A humoral response cannot prevent HPV infection of epithelial tissue, but cell mediated response can. Vaccines to provoke a cell mediated response are being developed. Until then Merck will be defrauding its customers with your help
Gardasil is the largest medical fraud in history perpetrated by Merck, maker of Vioxx and Pargluva, their two previous medical frauds.
Less than 1% of women chronically infected with HPV develop cervical cancer. This is not a cause and effect relationship. Read the Markovics' (oncologists) opinion that HPV and cervical cancer are together merely by coincidence, due to HPV being common and cervical cancer being rare.