About
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is one of the most common types of adult leukemia, usually affecting individuals who are more than 50 years of age.
Synonyms: Chronic lymphoid leukemia, prolymphocytic leukemia, T-cell chronic Lymphocytic leukemia, hairy- cell leukemia.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is one of the four main types of cancer that affects the blood and the bone marrow. It is referred to as 'chronic' leukemia as its progression is very slow, unlike the acute variety. It is 'Lymphocytic' leukemia because it affects a type of white blood cells, called Lymphocytes.
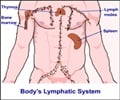
CLL is a malignancy that leads to the proliferation of B-cell lymphocytes in the bone marrow and blood. Along with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML), CLL is one of the most common types of adult leukemia. The affected individuals are usually more than 50 years of age. It is prevalent in Europe and North America and is a rarity in Southeast Asia and Japan, which points to the possible role of inheritance in its development.
Blood Cells formation in the Bone Marrow: Normally, the immature stem cells in the bone marrow mature and multiply into different blood cells according to the requirement. When these cells die, new ones replace them. This continuous cycle gets disturbed in people who have CLL. It begins with a change in a precursor lymphocyte cell, transforming it into a malignant one. This malignant cell multiplies and populates the bone marrow, replacing the normal lymphocytes. The leukemic cells are unable to fight infections the way normal lymphocytes do and this makes the affected individuals prone to several life–threatening conditions.
Advertisement
Ten years ago, waiting and monitoring was the favorite mode of management. With the advent of new diagnostic tests and medications, there has been a significant difference in the understanding of CLL. It is now realized that CLL is unpredictable. It may become aggressive in some or may progress differently in others. There is a need, therefore, for the affected persons to be handled individually.