Treatment of Congestive Heart or Cardiac Failure
Restriction of salt and fluid intake is recommended in patients with congestive heart failure. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors are considered in all patients with heart failure.
A diagnosis of congestive heart failure mandates immediate treatment. Lifestyle modifications remain one of the most neglected aspects of treatment of congestive heart failure.
The following measures are of utmost important;
- Restriction of salt and fluid intake is recommended in patients with congestive heart failure. This is because of the inclination of fluid to collect in the lungs and surrounding tissues. The allowed intake of sodium is no more than 2 grams per day. Read the food labels.
- Avoid excess intake of water and other fluids.
- Keep a check on body weight.
- Once the patient is stable and well compensated he may start regular exercises based on the individual’s tolerance levels. Aerobic exercises used to be discouraged in the past, but they are now thought to be beneficial to attain a better quality of life in the patients.
The treatment of the cause is of utmost importance:
- Coronary artery surgery or catheter procedures (angioplasty, intra-coronary stenting) can be used to restore blood flow.
- Disease of the heart valves are cured by surgical intervention
- When hypertension is the cause, aggressive management of blood pressure may suffice to prevent heart failure.
- Avoid alcohol abuse.
Medications include:
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors are considered in all patients with heart failure. Those with heart muscle weakness are benefitted the most. They act by blocking the formation of angiotensin II, a hormone which adversely affects the heart and circulation in patients with heart failure. Captopril, Ramipril, Lisinopril, Enalapril are the common ACE inhibitors.
Side effects include: Dry cough, low blood pressure, kidney dysfunction, allergic reactions.
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) have fewer side effects than ACE Inhibitors (dry cough can be avoided by their use) and include Losartan, Candesartan, Irbesartan, valsartan, telmisartan, and olmesartan. Unlike the ACE inhibitors they directly block the action of angiotensin II at its receptor site.
Beta-blockers act by blocking the action of stimulating hormones (epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine, and other similar hormones) on the beta receptors of the body''s tissues. Studies have proved their clinical benefits. They are started with a low dose and then the dose is increased very slowly. Some of the side effects include: fluid retention, low blood pressure, low pulse, fatigue, and light headedness. Their use on patients with diseases of the airways like asthma is to be done with caution. Long acting beta-blockers metoprolol has been found to be highly effective. Carvedilol is being researched.
Digoxin is useful for many patients but the long term survival seems to be unaffected. Digoxin stimulates the heart muscle and brings forceful contractions. Nausea, vomiting, arrhythmias, kidney dysfunction and electrolyte imbalances are potential side effects. Their blood levels need to be monitored with care.
Diuretics are often the most crucial component of the treatment of congestive heart failure. They prevent fluid from building up in the lungs and other tissues by promoting the flow of fluid through the kidneys. Diuretics prevent or relieve the symptoms of fluid retention. Long-term survival seems to be unaffected though. Diuretics are often administered intravenously. Some of their side effects include:
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Low potassium levels
- Hearing disruptions, and
- Low blood pressure
Common diuretics include:
- Furosemide(Lasix)
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Bumetanide
- Torsemide
- Spironolactone
- Metolazone
Spironolactone (Aldactone) has been evidenced to have astonishingly favourable effects on survival in congestive heart failure patients with relatively advanced symptoms. It is an aldosterone inhibitor like eplerenone.
Mechanical therapies
- Extremes of cases may require Heart transplant
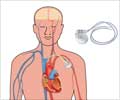
- Mechanical assist devices like biventricular pacemakers are of use in many cases.