- Ming Gopalan C, Rama Sastri B.V, Balasubramanian, S.C, Nutritive Value of Indian Foods, National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad, 2002.
- Dietary Guidelines for Indians – A Manual, Nutritive Value of Indian Foods, National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad, 2003.
- Mahtani R. The Ultimate Indian Diet Book, Macmillan India Ltd, 2005.
About
The right diet and a planned exercise regime is the mantra of healthy and sustainable weight loss.
Nutrition is a basic prerequisite for a healthy life. A proper diet is essential from the very early stages of life for being fit. As the saying goes - We are as young as our diet!
Good health makes us feel happy – both physically and emotionally. The two basic ingredients of a healthy lifestyle are:
- Right eating – Quantity and quality of food.
- Physical activity-Being active throughout the day and doing some kind of structured or conscious activity.
A healthy and sensible food habits should not merely satisfy hunger. It should add vitality, vigor, youthfulness, stamina and mental alertness in our daily lives. Above all we should be able to feel happy.
Health is not a virtue signifying absence of disease. It is something positive. It is about leading a healthy lifestyle. It is the cornerstone for the management of various diseases such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and coronary heart disease.
Food is the basic need of all living beings as it is the source of energy to carry out all the activities (breathing, heart beating, digestion etc). This energy is measured in terms of calories. Caloric requirement varies with age, sex and the level of activity. We should strive to always remain close to our desirable body weight and fat percent.
There is no single dietary regime for weight reduction. It is highly individualized. Weight loss regimes should be gradual for sustainable weight loss otherwise you put the pounds back on as quickly as you lost them. Modifications in dietary habits have to be incorporated into ones lifestyle along with adequate exercise to keep the body weight within the normal limits.
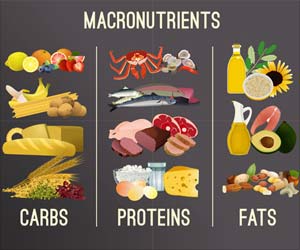
As fat gives more than twice the calories per gram of either protein or carbohydrate, weight reducing diets have to limit the fat intake. Refined sugars and alcohol provide empty calories and should be avoided.
Plant foods that provide complex carbohydrates and fiber may be preferred as they reduce blood glucose, cholesterol and triglycerides. Weight reducing diets must be rich in proteins and low in carbohydrates and fats.
Consumption of plenty of fruits and vegetables would not only result in satiety but would also help to maintain adequate micronutrient intake. Frequent fasting/semi-fasting (cyclic weight reduction) followed by adequate or excess food consumption only aggravates the problem of fat gain.



































after walking we can sleep or not...? why..?
hello i need to reduce my weight as in a 2 months i am getting merry. my height is 5'3" and my weight is 50 kgs. my husband is very slim and that's why i am worried about. please help me out.
Hello Jannat06, you needn't worry much about your weight even though 50Kgs is slightly on the higher side. Go for regular jogging in the morning and go to the gym in the evening. Drink loads of water and lemon juice. In quick time you will be able to see the changes in you. Happy married life in advance!!!
Losing weight has to be gradual that's why I don't believe in the promises of quick fix. Right now, I may have not been losing weight through exercise and diet as I'm just recuperating from a previous injury, but I do plan to go back as soon as I get back on my optimum state of well-being. however, I am currently using a weight loss aid to temporarily help me lose weight as I've put too much weight after I got hospitalized. Don't get me wrong, I did asked my doctor about it. Prescopodene has been a helping tool for me to not gain weight while on recovery. What I like about it is that my body seems to react well with it. Not all pills are bad, just try to be knowledgeable about what you'll take. Thanks
I have found an e-book which is very good, almost revolutionary, and believe me, works! It is quite unbelievable how easy it is to follow. Please feel free to follow link, and see for yourself. [http://] steve9802.eliteweightlosspackage.com I highly recommend it!!
Great blog! It is encouraging to be educated on healthy weight loss tips. I agree that weight loss is a lifestyle change and that it is important to eat healthy and exercise to prevent diseases. If you are interested in a special offer and tips on weight loss, check out my website fatlossfactorrebate-4you.weebly.com. Change you life now, check it out! : ]