About
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic condition of the sebaceous glands that commonly occurs in those prone to
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic condition affecting the sebaceous or oil glands of the skin. It is a severe form of acne, also known as acne inversa. HS is commonly seen to occur in the armpits, groin and in the anal regions of the body, which are the main locations of the apocrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
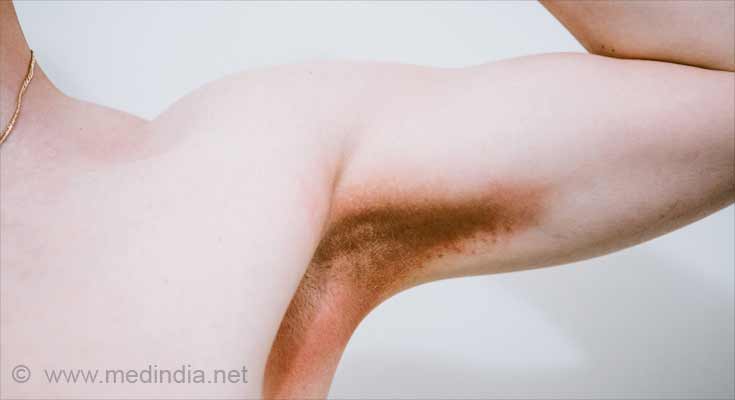
Hidradenitis suppurativa usually starts around puberty. It continues for several years and tends to worsen with time. It is important to diagnose the condition at an early stage in order to manage the
The condition can be confined to one area or it can occur in different parts of the body and can be very painful. It is characterized by the presence of blackheads and one or many red, tender, pus-filled lesions or abscesses which often enlarge, burst and drain pus. When this repeats, it can result in scarring. Long-term skin inflammation is a common feature.
The
Symptoms and Complications
Hidradenitis suppurativa commonly occurs in areas where oil and sweat glands are found in plenty, such as the armpits, groin and anal area. It is also likely to occur in areas of friction, where the skin rubs together, including the inner thighs, below the breasts or in between the buttocks.
Signs and symptoms of hidradenitis suppurativa are the following:
- Blackheads appearing in pairs, presenting a "double-barreled" pattern
- Red, tender bumps or lesions that grow in size break and drain pus giving out an unpleasant odor. Itching, excessive sweating and burning may also occur
- Painful lumps can develop under the skin. They are likely to persist for several years and may get inflamed
- Open wounds can also occur. They heal slowly and lead to scarring
- Weight, hormonal changes, stress, heat or excessive perspiration can aggravate the symptoms
- Hidradenitis suppurativa complications include:
- Network of sinus tracts or tunnels that prevent healing of the sores and cause more to appear
- Skin changes including scars, pitted skin and dark patches.
- Restricted and painful movement ofarmpits or thighs.
- Cellulitis
Mild cases of HS can be countered with self-care measures but if the condition persists longer, it would be advisable to consult a dermatologist.
Causes and Risk Factors
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) develops when the sebaceous glands and the openings of the hair follicles become blocked with a mixture of fluid, dead skin cells, sebum and secretions from the apocrine sweat glands. Bacteria accumulate causing infection and inflammation. HS can occur alone or in combination with Crohn’s disease or Graves Disease.
Many factors such as hormones, genetics and cigarette smoking play a role in predisposing a person to develop HS. The condition occurs equally among all ethnicities.
Hidradenitis suppurativa risk factors include:
- Gender- Women are more prone to develop hidradenitis suppurativa. The reason for this is not known.
- Age- Those between puberty and the age of 40 years are more likely to develop HS.
- Family history - Having a family history of HS makes one prone to the disease
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of hidradenitis suppurativa begins by assessing the medical history and clinical symptoms of the patients. Blood tests and culture of pus samples may have to be carried out. Other skin tests may be ordered to rule out tuberculosis of the skin.
There is no known cure for HS. But early
Mild cases of HS may be treated with self care while moderate and severe cases require medications including antibiotics, oral retinoids, non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors. Severe cases may be treated with incision, drainage and surgery.
Home remedies
Simple self treatment methods are listed below:
- Apply warm compresses to diminish swelling
- Clean the affected area with antibacterial soap and apply an over-the-counter antibiotic
- Zinc salts may be taken as supplements to minimize inflammation and prevent new outbreaks
- Wear loose fitting clothes to prevent skin irritation.
- Avoid shaving to prevent irritation of the affected area.
- Avoid smoking to allow the disease to improve
- Reduce weight as this would help to reduce areas with skin folds and thereby reduce friction







