What is Hypertension or High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure or hypertension is a chronic condition, which usually lasts a lifetime once it is developed.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
High Blood Pressure Also known as Hypertension
Go to source) It is defined as the force of the blood against the artery walls as the heart pumps the blood around the body. Each time the heart beats, it pumps out blood into the arteries. Hypertension is a ‘silent killer disease’ and it often presents without any signs and symptoms.
There are two measurements when a blood pressure reading is taken(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Measuring Blood Pressure
Go to source) -
- Systolic Pressure
- Diastolic Pressure.
Systolic pressure refers to blood pressure, when the heart beats while pumping blood and Diastolic Pressure refers to blood pressure, when the heart is at rest between beats.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Sphygmomanometer is a device used to measure the blood pressure The normal recommended blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. If the blood pressure measurement is between the range of 120/80 mmHg and 140/90 mmHg, it is termed as ‘pre-hypertension’.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Prehypertension: A Little Too Much Pressure, A Lot of Trouble
Go to source)
If hypertension is left untreated it can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, Kidney failure and eye damage. Some people may not realize they have high blood pressure until they have problems with their blood, heart or kidneys.
Facts on Hypertension
- Globally, 970 million people suffer from Hypertension(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
High Blood Pressure Facts
Go to source) - About 1.56 billion adults will develop hypertension by 2025.
- It is the leading cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD) worldwide.
- It is one of the most important causes of premature deaths worldwide and the problem is growing.
- People with hypertension are more likely to develop complications of diabetes.
- Almost one in every three people suffers from this condition, and this may be related to our modern sedentary lifestyle and dietary habits.
How do you Classify Hypertension?
The cause of hypertension may not be known or there maybe a known cause and accordingly it can be classified(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Primary and Secondary Hypertension
Go to source) -
- Primary (essential) hypertension - High blood pressure with no obvious underlying medical cause.
- Secondary hypertension - High blood pressure caused by conditions that may affect the kidneys, arteries, heart or endocrine system.
What are the Factors that can Lead to Primary or Secondary Hypertension?
The causes of high blood pressure may vary according to individuals.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Know Your Risk - Blood pressure
Go to source)
In 90 - 95% cases of high blood pressure, there is no specific underlying medical condition. When the cause is unknown, it is known as essential hypertension or primary hypertension.
The following factors contribute to primary hypertension:
- High intake of salt
- Hereditary (genetic) susceptibility (30%)
- Obesity
- Kidney failure (renal insufficiency)
- Lack of physical activity
- Aging inflammation

The remaining 5-10 % cases of hypertension are due to certain factors that can be corrected. This is known as secondary hypertension.
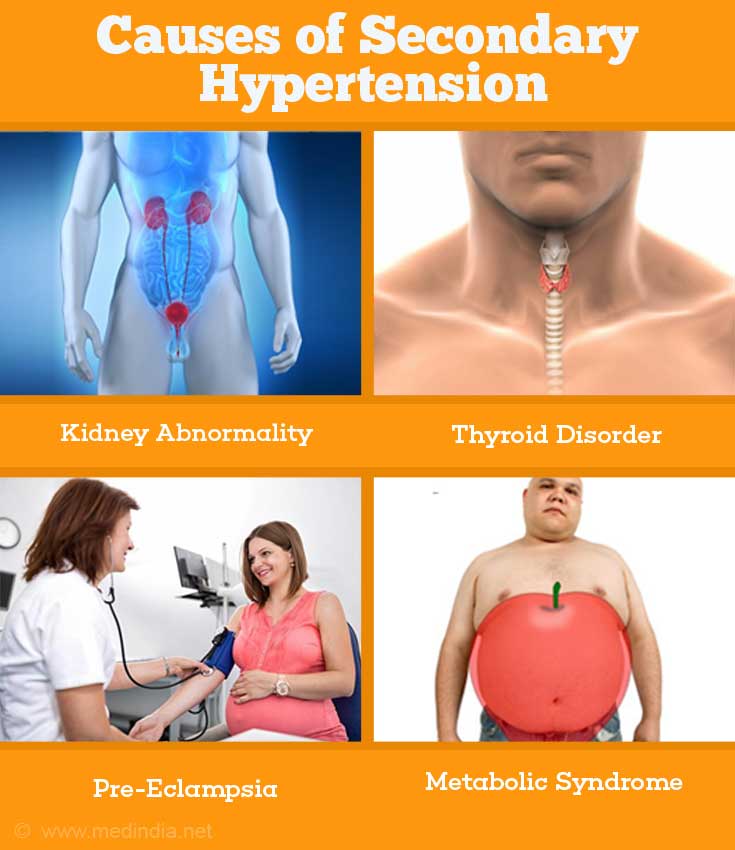
Causes of Secondary Hypertension:
- Narrowing of certain arteries
- Kidney abnormality
- Adrenal gland diseases
- Thyroid diseases
- Pre-eclampsia
- Use of illegal drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines.
- Medications like birth control pills decongestants, pain relievers.
- Metabolic syndrome
What are the Known Risk Factors for Hypertension?
- Age - Blood pressure increases as age increases.
- Race - High blood pressure is more common in blacks than in whites.
- Sex - It has been seen that young men and men during early middle age have high blood pressure more often than women.
- Genetics - High blood pressure tends to run in families
What are the Symptoms of High Blood Pressure?
Most people with high blood pressure have no signs or symptoms.
However, people with high blood pressure might sometimes notice the following symptoms:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Blurred vision
Nosebleeds (epistaxis) - Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Nausea
- Vomiting

If any one or more of the symptoms are present, these are warning signs and it is essential to get the blood pressure measured on more than one occasion.
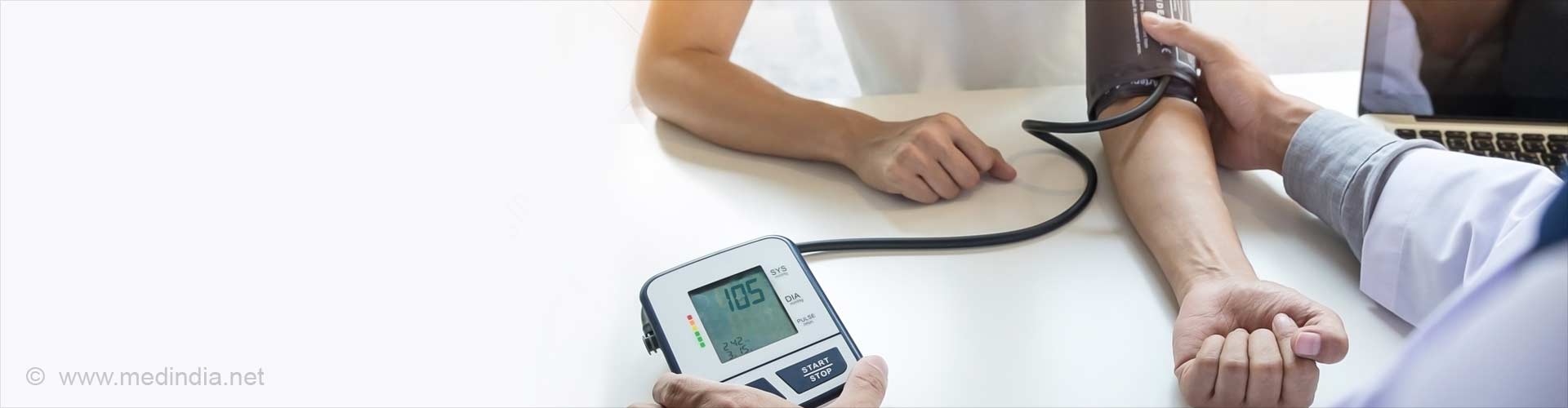
How is Blood Pressure Measured?
Blood pressure is measured with a small, portable instrument called a Sphygmomanometer.(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
How High Blood Pressure is Diagnosed
Go to source) The blood pressure instrument basically consists of an air pump, a pressure gauge, and a rubber cuff. The instrument registers the blood pressure in units called millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
The cuff is placed around the upper arm and inflated to a pressure that blocks the flow of blood in the main artery (brachial artery) that travels through the arm. Then, the pressure in the cuff on the arm and artery is gradually released. As the pressure decreases, the health practitioner listens with a stethoscope over the artery at the front of the elbow.
The pressure at which the practitioner first hears a pulsation over the artery is the systolic pressure. As the cuff pressure decreases further, the pressure at which the pulsation finally stops is the diastolic pressure.
Blood pressure maybe measured both sitting up and lying down.
How do You Diagnose High Blood Pressure?
The initial assessment of the hypertensive people includes a complete history and physical examination.
High blood pressure is usually diagnosed on the basis of a persistently high blood pressure measured with a sphygmomanometer.
One reading is not sufficient for this purpose and three separate sphygmomanometer measurements are taken at one-week intervals.
The blood pressure readings decide the severity of hypertension –
| Average Blood Pressure | |
| For young people | 120/80 mmHg |
| For old people | 140/90 mmHg |
| Level of Severity | Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) |
| Mild Hypertension | 140-160 | 90-100 |
| Moderate Hypertension | 160-200 | 100-120 |
| Severe Hypertension | Above 200 | Above 120 |
What Investigations Maybe Required for Hypertension?
The doctor may also ask the patient to undergo the following tests -
- Blood tests - Complete blood count (CBC), electrolytes level, BUN (blood urea nitrogen) and creatinine level are done to assess the risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
- ECG (electrocardiogram) - To evaluate heart rate and rhythm.
- Echocardiogram - It is an ultrasound examination of the heart and is used to evaluate the anatomy and the function of the heart.
- Chest X-ray - To assess the heart size, the shape of the aorta and the lungs.
- Doppler ultrasound - To assess the blood flow through arteries at pulse points in the arms, legs, hands and feet.
How can Hypertension or High Blood Pressure be Treated?
Blood pressure normally will rise and falls throughout the day in response to our daily activity and what we are doing and how our emotions get affected by our surroundings. If you are angry the blood pressure will go up but once you have calmed down the pressure will come down. However if the pressure does not come down and remains higher than normal on more than one reading high blood pressure or hypertension is suspected and may warrant regular treatment. Once you start the treatment you should not stop it without consulting your doctor.
Lifestyle modification is the first step in treating early hypertension, however if it fails to bring down the pressure medications are added. However if the blood pressure is very high, medication will be started without waiting for the results after lifestyle modification.
Medications
Diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers can be used for treating hypertension.(8Treatment - High blood pressure (Hypertension)
Go to source)
Diuretics - These medications act on kidneys to help the body eliminate sodium and water, reducing blood volume.
Beta-blockers- These medications block the effects of certain adrenaline-related chemicals, causing the heart to beat more slowly and less forcefully.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors - These medications help relax blood vessels by blocking the formation of a naturally occurring chemical that narrows blood vessels.
Calcium antagonists - Calcium antagonists are also known as calcium channel blockers. These medications help relax the muscles of blood vessels.
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits is an effective first step in both preventing and controlling high blood pressure
- Study shows that hypertension is reduced by an eating plan and cutting down on table salt. The eating plan should include fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy foods. The diet should include whole grains, poultry, fish and nuts and have reduced amounts of fats, red meats, sweets, and sugar sweetened beverages.
- Including foods high in potassium can lower your blood pressure
- Quit smoking and limit your alcohol intake.

Weight management:
- Normal weight is another factor that is crucial when trying to prevent hypertension. People who are overweight should lose weight, and people of normal weight should avoid adding on extra pounds.
- Exercise regularly. Get moving to prevent hypertension. Regular to moderate exercise for about 30 - 40 minutes three times a week can help manage or control high blood pressure.
Monitor your blood pressure levels regularly either at home or visit the general practitioner.
‘Health is correlated with quality of life. If you get regular physical activity, have social connections, control your cholesterol, keep your blood pressure at a normal level, don't smoke - these things can make an enormous difference not only in how long you live, but how much you enjoy your life in those years’. ~ Tom Frieden