About
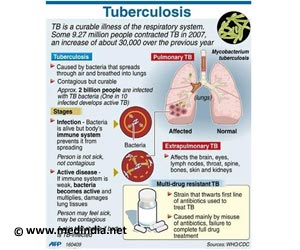
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
It is estimated that over 8 million new cases of TB occur each year worldwide.
Generally, tuberculosis affects the lungs (known as pulmonary tuberculosis) but may spread to other organs including the lymph nodes, gastro intestinal tract, genito-urinary tract, brain, coverings of the brain (meninges) or heart (pericardium), bones, joints, skin, eyes or almost any other organ in the body. Only the hair and nails are not affected by TB.
When a person is infected with pulmonary tuberculosis, the bacteria in the lungs multiply and cause pneumonia along with chest pain, hemoptysis and a prolonged cough. The lymph nodes near the heart and lungs become enlarged. As the TB bacteria tries to spread to other parts of the body, the body's immune system often interrupts the process and forms scar tissue or fibrosis around the TB bacteria. This helps fight the infection and prevents the disease from spreading in the body and to other people. If the body's immune system is unable to fight the bacteria the disease returns to an active state with pneumonia and damage to kidneys, bones, and the meninges that line the spinal cord and brain.
Tuberculosis can be classified as latent or active.
- Latent tuberculosis is when the bacteria in the body are in an inactive state and the person shows no symptoms. Latent tuberculosis is not contagious.
- Active tuberculosis is contagious and can make a person sick.
TB is spread through the air when people with an active pulmonary tuberculosis infection cough, sneeze, shouts or spit.
The treatment can continue for several months and the patient has to take the medicines at the given time regularly for the prescribed duration. If TB medications are not taken as per the healthcare providers recommendations the infection may become much more difficult to treat and sometimes the TB bacteria may become resistant to treatment.
TB is a preventable disease. BCG vaccination is given to people in countries where there is high prevalence of tuberculosis.
Lately the incidence of tuberculosis is increasing due to increased HIV cases and appearance of drug resistant strains of TB.
In 1826 a physician Laennec said this about tuberculosis - "Whatever the form in which the tuberculous matter develops, it begins as a grey, semi-transparent matter that little by little becomes yellow, opaque, and dense. Then it softens, and slowly acquires liquidity like pus. This pus when expelled through the airways leaves cavities, commonly called ulcers of the lung; that we will designate as tuberculous excavations." -Rene-Theophile-Hyacinthe Laennec, 1826