Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made based on the complaints, physical examination and certain investigations like:
- Keratometry – Images of the keratometry mires are commonly steep, highly astigmatic, irregular, and often appear small and compressed in Keratoconus. They are normally round or oval.
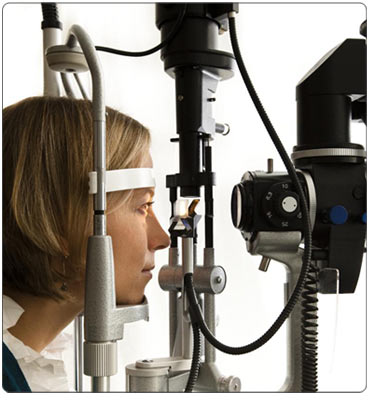
Based on keratoscopy it can be graded as:
- mild (K < 48D)
- moderate (K = 48–54D)
- severe (K > 54D)
- A handheld keratoscope, sometimes known as Placido's disk, can provide a simple non-invasive visualization of the surface of the cornea by projecting a series of concentric rings of light onto the cornea. The rings appear crowded where the cornea is steep.
- Videokeratography – Commonly shows inferior corneal steepening in Keratoconus and
- Topography – Reveals the exact area of corneal thinning and bulge. In case of Keratoconus both these areas of thinning and protrusion coincide. Topography can reveal very early Keratoconus before it is can be diagnosed clinically. Hence, it is a very sensitive test to detect Keratoconus.