- Leukocytosis: Basics of Clinical Assessment - (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2000/1101/p2053.html)
- Leukocytosis - An Overview - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11087187)
- What Is Leukocytosis? - (https://www.healthline.com/health/leukocytosis#treatment)
- Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis - (https://www.aafp.org/afp/2015/1201/p1004.html)
- Leukocytosis - All You Need to Know - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24750674)
What is Leukocytosis?
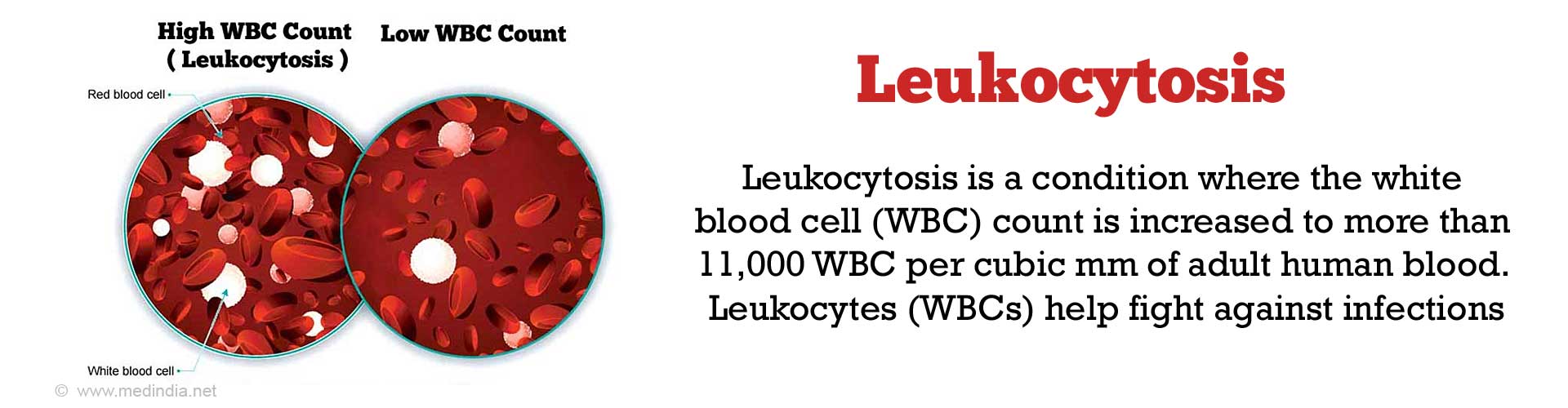
Leukocytosis is defined as a condition where the white blood cell (WBC) count is increased.
The white blood cells (WBC) or leukocytes play an important role in the body’s immune system to fight against infections. Various types of WBCs include the neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils. The neutrophils are the most numerous, followed by the lymphocytes. These cells are produced by the bone marrow.
A condition with an increased count of more than 11,000 leukocytes per cubic mm of adult human blood is termed as leukocytosis.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Leukocytosis: Basics of Clinical Assessment
Go to source)
The WBC count is often increased as a reaction of the bone marrow to infection or inflammation. Certain bacterial and viral infection can trigger leukocytosis. Leukocytosis is also related to strong immune reactions like asthma and other allergy attacks.
Some of the most serious and life-threatening cases of leukocytosis are associated with the diseases of the bone marrow. An elevated WBC count of greater than 30,000 per cubic mm of the adult human blood could indicate an underlying bone marrow disorder including leukemia or blood cancer.
Other causes of leukocytosis include stress, intake of certain medications like lithium and beta agonists, surgical removal of the spleen, hemolytic anemia and cancer. Both physical and emotional stress results in an elevation of the WBC count. Physical stress can be due to excessive exercising, anesthesia, seizures and other illness.(2Leukocytosis - An Overview
Go to source)

Depending on the type of individual cell increased, leukocytosis can be subclassified as below:
| Name of the cell | The condition caused by the abnormal increase |
| Neutrophils | Neutrophilia |
| Lymphocytes | Lymphocytosis |
| Monocytes | Monocytosis |
| Eosinophils | Eosinophilia |
| Basophils | Basophilia |
Laboratory findings suggest that increase in neutrophils makes a significant contribution to leukocytosis, although other component cells of WBC may also increase the WBC count.
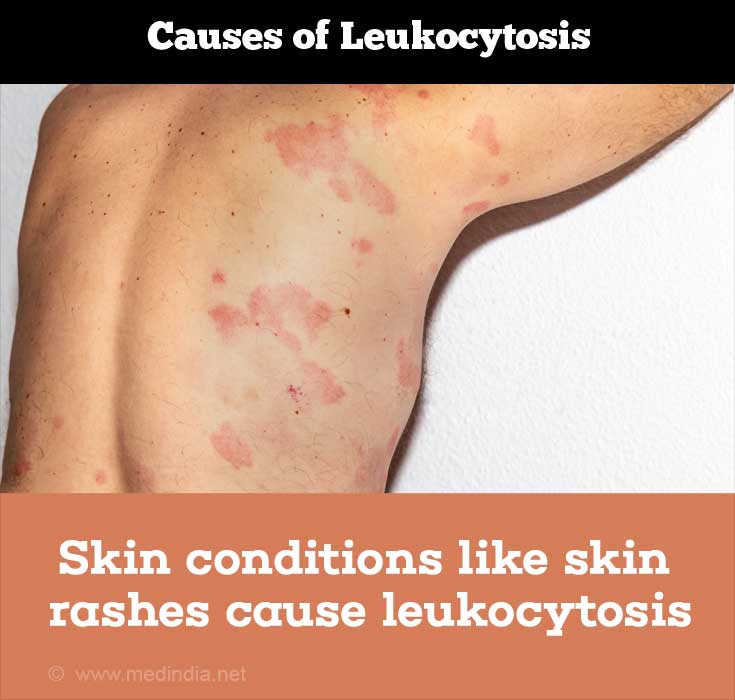
Eosinophils are the white blood cells that participate in immunological and allergic events. The most common causes of eosinophilia include immunological disorders like arthritis, allergic reactions, parasitic infections, and skin conditions like the skin rashes.
Basophils are usually few in number and are found to contribute less significantly to leukocytosis.
Lymphocytosis is seen in acute and chronic infections and disorders of the lymphoid system. Relative lymphocytosis is seen in infancy, thyrotoxicosis, and other connective tissue disorders.
The signs and symptoms of leukocytosis are basically due to the underlying disease, which causes an abnormal elevation in the WBC count.
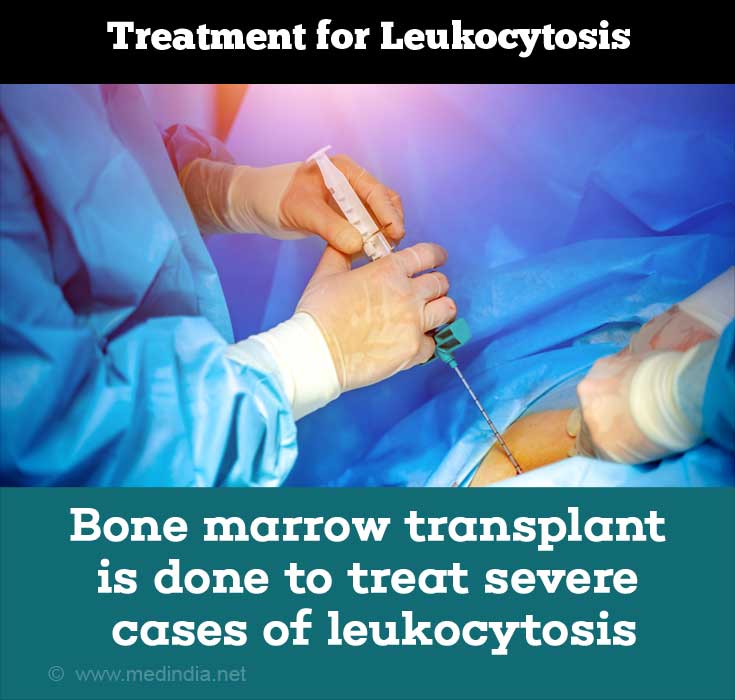
Diagnosis and treatment of underlying cause and disease plays an important role in the treatment of leukocytosis. Bone marrow transplant and blood transfusion are done to treat severe cases of leukocytosis.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
What Is Leukocytosis?
Go to source)