What is Lung Cancer?
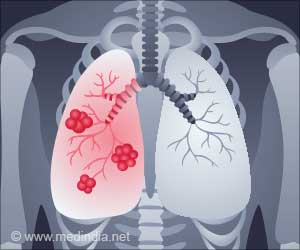
Lung cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the tissues of the lungs. If not treated, lung cancer may spread to the surrounding tissues and other parts of the body.
Lung cancer is also known as lung carcinoma or bronchogenic carcinomas. Lung cancer is the second most prevalent cancer diagnosed globally. The second most common cancer to be diagnosed worldwide is lung cancer.
What are the Different Types of Lung Cancer?
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
- Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) - It is a very common type of lung cancer and comprises almost 80% to 90% of lung cancers. There are three main sub-types of NSCLC: they are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma.
- Adenocarcinoma - Nearly 40% of lung cancers are adenocarcinoma. It is commonly observed in the outer parts of the lung tissue. Adenocarcinoma is found in both smokers and non-smokers population and is common in females than males. The subtype of adenocarcinoma is known as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, which is commonly observed in women who do not smoke.
- Squamous-cell Carcinoma- It constitutes approximately 30% of lung cancers. It is usually found in the middle section of the lungs, near the main airway, such as bronchus. This cancer mostly occurs due to smoking.
- Large Cell Carcinoma- They constitute about 9% of lung cancers. They are named as large cell carcinoma because the cancer cells are large, with large nuclei, more cytoplasm, and clearly visible nucleoli.
- Small-cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) - Around 10% to 15% of lung cancers is small cell lung cancer. They develop more quickly than NSCLC and show a positive response to chemotherapy.
What are the Causes of Lung Cancer?
The causes of lung cancer are-
- Air pollution
- Genetic factors
- Rubber production and crystalline silica dust
- Products of combustion (burning coal, incomplete combustion, coal gasification, soot, diesel engine exhaust)
- Toxic gases such as methyl ether, sulfur mustard
- Exposure to certain chemical substances such as asbestos, beryllium, nickel, arsenic and silica
- Exposure to radon gas
- Ionizing radiations (Gamma radiation, X-radiation, plutonium)
- Passive smoking
- Smoking

What are the Symptoms of Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer symptoms may not be evident until the lung disease is in its severe stage. Therefore, it is advisable to consult your physician if you have any unusual health complaints. The symptoms of lung cancer are-
- Breathlessness
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Coughing up blood
- Voice change or being hoarse
- Sputum color change
- Clubbing of fingernails (unusual rounded appearance)
- Pain in the chest, back and shoulders, not related to coughing
- Repeated lung diseases such as pneumonia or bronchitis
- Persistent and intense coughing

How Do You Diagnose Lung Cancer?
To diagnose lung cancer, initially, a chest X-ray is done if the person complains of lung cancer-related symptoms.
If lung cancer is present, then further investigations will be conducted to know more about the nature and extent of the lung disease. These tests include-
- Computerized Tomography (CT Scan) - This test is usually done after a chest X-ray and it can help identify the cancerous area.
- Bronchoscopy - This diagnostic procedure helps the doctor to look inside the airways. Your doctor will place a thin tube, bronchoscope into your nose or mouth and then down the trachea. Bronchoscopy may feel uncomfortable, but it is not painful. During this procedure, the doctor may take lung tissues samples for biopsy.
- Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB) - It is a diagnostic procedure largely done if the tumor is in the peripheral parts of the lungs. It is a safe and minor surgical procedure; it is contraindicated in situations when the tumor is close to the heart or any major blood vessels and in medical conditions like emphysema.
- Sputum Cytology - It is an evaluation of phlegm or mucus from the lungs (sputum). Microscopic examination of sputum is done to find out the presence of any unusual cells.
- Mediastinoscopy - In this procedure contents, examination of the mediastinum is done, mainly for biopsy. This test is recommended for the staging of lymph nodes in lung cancer.
- Thoracoscopy - This method involves an internal examination, biopsy or removal of the lung tumor. Thoracoscopy is done under general anesthesia.
- PET-CT Scan - It is called as positron emission tomography-computerized tomography. It is performed when the CT scan results show that your cancer is in its early stage. PET-CT Scan helps in detecting active cancer cells, which can help in the treatment of lung cancer.

How Do You Treat Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is treated in various ways, depending on the type of cancer and how far it has spread in the body. The treatments followed for lung cancer include-
- Surgery - It is an operation where the doctors cut out the cancerous tissue from the body. People suffering from early-stage cancer will usually undergo surgery to remove the tumor. There are three important types of lung cancer surgeries-
- Lobectomy: An affected lobe of the lung is removed
- Pneumonectomy: Here, a lung is removed
- Wedge Resection: A segment of the affected lung is removed
- Targeted Drug Therapy - Targeted therapy interferes with the ways cancer cells function, for example, they may affect specific metabolic pathways of cancer cells. The advantage is that normal cells are not affected unlike conventional chemotherapy.
- Radiotherapy - It can be given as sole therapy or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy. During the initial stage of lung cancer, it is used to eliminate cancer cells completely. In advanced stages, it aims to slow down the progress of cancer and lessen its symptoms.
- Chemotherapy- In this method, drugs are used to kill or retard the growth of cancerous cells. Chemotherapy aims to eliminate cancer cells and protect the healthy cells. These drugs can be given orally or intravenously, or sometimes both.
- Osimertinib is a drug used to treat non-small-cell lung carcinomas. A recent study has shown that osimertinib can reduce the risk of death by 51% in people with non-small-cell lung cancers.
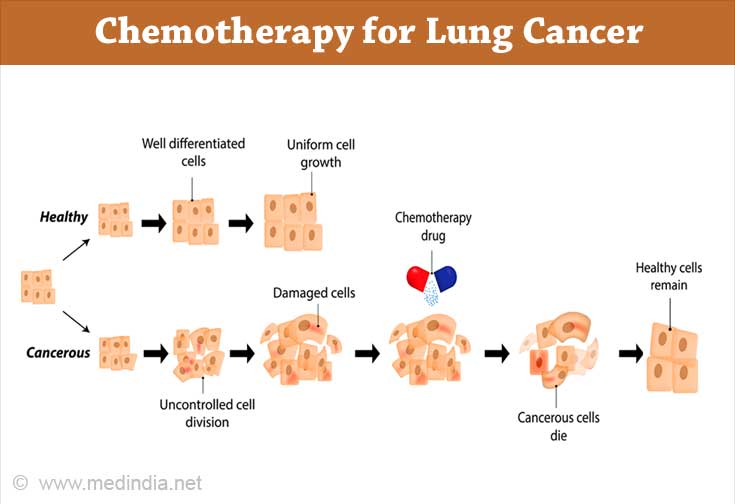
- Ablation- This treatment is preferred if you cannot undergo surgery or radiotherapy. In ablation, the treatment is given directly into the tumor, destroying only the cancerous cells without affecting the nearby healthy tissues. It includes radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation.
- Palliative care - Its objective is to improve the quality of life by reducing lung cancer symptoms without aiming to treat the lung disease. It controls symptoms like nausea and pain and assists to slow the progression of lung cancer to other parts of the body.
- Osimertinib is a drug used to treat non-small-cell lung carcinomas. A recent study has shown that osimertinib can reduce the risk of death by 51% in people with non-small-cell lung cancers.
Prognosis
Lung cancer is often difficult to cure because of its late presentation. It accounts for 6.9 percent of all new cancer cases and 9.3 percent of all cancer-related deaths in both sexes in India. The survival of a patient depends on the stage of cancer he or she has. The overall 5-year survival rate is only 5 percent in developing countries; it is slightly better at 15 percent in the developed nations.
Lung Cancer Prevention
- Stay away from smoking
- Keep away from passive smoking, i.e. stay away from others who smoke. Exposure to smoke is a risk factor for cancer by itself.
- Check your home for radon if you happen to reside at a place where radon is a problem
- Protect yourself from inhaling toxic gases
- Avoid harmful chemical substances
- Eat a healthy balanced diet
- Exercise regularly