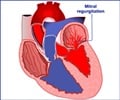
Diagnosis of Mitral Valve Stenosis
Most patients may not remember having Rheumatic Fever in their childhood. Doctors will be able to detect mitral stenosis on physical examination.
Auscultation will show a loud first heart sound (S1) followed by an opening snap. A diastolic murmur is present. Patients might also have signs of heart failure and pulmonary hypertension.
| Link - Listen to/Download |
Differential diagnoses for Mitral stenosis are aortic valve disease, atrial myxoma, emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Chest X-ray reveals the enlargement of heart chambers and pulmonary vein. It can also show signs of congestive heart failure.
Echocardiogram (Echo) is performed to confirm mitral stenosis. Size of the mitral valve and the chambers can be measured along with the pressure gradient across the valve and pulmonary artery. Severity of mitral stenosis can be evaluated. A Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) reveals the presence of small thrombus and vegetations present in the left atrium that is not picked up in regular echo.
Cardiac catheterization can also aid in the diagnosis of mitral stenosis. It helps the physician measure the pressures in each heart chamber, mainly the left atrium and left ventricle. The severity of Mitral Stenosis can also be determined.