- THE FACTS ABOUT PENICILLIN ALLERGY: A REVIEW - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3255391/)
- Drug Allergies - (http://acaai.org/allergies/types/drug-allergies)
What is Penicillin Allergy?
Penicillin allergy is a condition where the immune system of the body reacts to the drug in an exaggerated manner. The most common penicillin allergy signs are the presence of rash, hives and irritation. A more serious complication of the allergy is anaphylaxis, which could be life threatening. Penicillin is an effective constituent of several antibiotics and is prescribed for bacterial infections. The allergy occurs either with penicillin injection or with penicillin-like drugs.
Penicillin, was the first antibiotic to be discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. Penicillin belongs to an important group of antibiotics called beta (ß)-lactam antibiotics that are used commonly as they are not only effective at treating common bacterial infections but also relatively inexpensive.

This class of beta (ß)-lactam antibiotics includes penicillin and penicillin derivatives such as ampicillin and amoxicillin as well as cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems and ß-lactamase inhibitors.
All forms of natural and semisynthetic penicillin are known to cause allergy, but the cross-reactivity between penicillin and second and third generation cephalosporin is low. This means that if you are allergic to penicillin, you are not necessarily likely to be allergic to these antibiotics from the same group.
Allergy is seen with more intravenous or intra-muscular dose than with oral administration.
The incidence of allergy is highest with procaine penicillin, as procaine component of the antibiotic itself is allergenic. Penicillin G is the most common drug implicated in drug allergy.
Penicillin hypersensitivity is generally unpredictable. What this means is that if you tolerated penicillin once without any allergy, it does not mean that the allergic reaction may not occur on the subsequent administration of the drug.
What are the Causes of Penicillin Allergy?
All allergies occur because of the erroneous functioning of the immune system.
Allergy to penicillin too occurs because the immune system confuses the antibiotic for a foreign harmful substance and starts attacking penicillin as though it were a virus or bacteria.
After the first intake of penicillin, the immune system detects and remembers penicillin as a foreign body that is potentially dangerous. It therefore creates an antibody to combat penicillin. At this stage, the body is sensitized to penicillin and is ready for an attack on the next detection of penicillin. On the next intake of antibacterial drugs containing penicillin, these specific antibodies surround the penicillin antigen producing an inflammatory response. The substances released in this process produce the allergy reactions.
What are the Symptoms of Penicillin Allergy?
Most allergies are sub-acute reactions due to IgG antibodies. In the most common allergy, the allergic reaction to penicillin may result in signs and symptoms like:
- Skin rash
- Hives
- Watery Eyes
- Fever
- Redness and swelling
- Runny nose
- Itching

Rarer reaction or allergy to penicillin or penicillin-like drugs includes:
Acute allergy due to IgE antibodies and includes anaphylactic shock.
Anaphylactic shock due to Penicillin - Under severe circumstances however, the body may experience an anaphylactic shock. This uncommon and life-threatening reaction kick starts a chain reaction of malfunctions in body systems like contraction of the windpipe and throat causing trouble breathing, nausea or abdominal cramps, vomiting or diarrhea, low blood pressure, seizures and fainting.
Serum Sickness -Other conditions include serum sickness which leads to high temperature, body pain, swelling, nausea, and rash.
Anemia - Another medical condition is anemia induced by drugs, which produces the usual symptoms of anemia like low levels of red blood cells. This leads to fatigue, irregular heartbeats, breathing difficulties, etc.
DRESS - Penicillin especially reacts with patients having eosinophilia and leads to an adverse Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia Systemic Symptoms, also abbreviated as DRESS.
DRESS causes symptoms such as rash, surge in white blood cells, enlarged lymph nodes and relapse of hepatitis. Nephritis is another rare occurrence.i.e. the inflammation of the kidneys, which can produce fever, presence of blood in urine, etc.
What are the Risk Factors for Penicillin Allergy?
Certain factors increase one’s risk to penicillin allergy. These include past allergies like hay fever or a food allergy, other drug-induced reactions, hereditary drug allergy in the family, increased exposure to penicillin, or due to extreme dosage or persistent use.
How to Diagnose Penicillin Allergy?
An accurate diagnosis can be arrived at by a history followed by a thorough examination and diagnostic tests. Often penicillin allergies are self-reported by patients, but cannot be confirmed by doctors if the allergy has faded away. Additional tests or redirection to an allergy specialist (allergist) may be done.
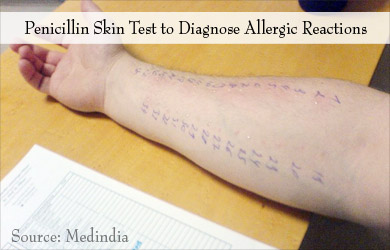
Penicillin Skin Test -With a penicillin skin test, the allergist or nurse oversees injection of an insignificant amount of penicillin on the skin by an injection or a small scratch. If the skin becomes red and itchy, then the person is said to be allergic to penicillin.
Graded Drug Challenge - A graded drug challenge is a more specialized diagnostic procedure conducted when the results of a skin allergy test are unclear. With this procedure, one gets approximately 4-5 doses of penicillin, with each dose progressively increasing to the final dose.
If no reaction is seen even after the desired dose, then it is concluded that the patient isn't allergic to that type of penicillin.
At all times during such tests, doctors are prepared to treat for any adverse reaction. All items for resuscitation should be ready and the patient should be under continuous observation.
How to Treat Penicillin Allergy?
Treatment for a penicillin allergy can be distributed into two broad approaches namely - treatment for the acute allergy symptoms and long term desensitization to penicillin.
The approaches that can be used to treat the acute symptoms of penicillin allergy are:
Drug Withdrawal - Once an allergy is confirmed, one should terminate using drugs containing penicillin for rest of the lifetime.
Antihistamines - These are substances that counteract or suppress the effect of the activated immune cells giving immediate relief in allergy symptoms.
Corticosteroids - Intake is either oral or injected, corticosteroids aid in reducing the effect of inflammation associated with more-serious reactions.
Epinephrine - For anaphylaxis reaction, an immediate injection of epinephrine is administered and clinical care is needed to maintain other body vitals.
Drug desensitization involves getting the body familiarized with the drug to curb the harmful hypersensitivity reaction. The treatment starts with minimal doses of penicillin which progressively increase every 15-30 minutes. Once the desired dosage is reached without any allergy, the treatment is completed.
How to Prevent Penicillin Allergy?
Prevention is better than cure, and if one is allergic to penicillin, then one should simply avoid penicillin.
Inform Health Care Workers - Always mention that you are allergic to penicillin to all your doctors.
Wear a Bracelet - Nowadays, medical bracelets are available that alert the patient if they are allergic.
Carry Emergency Epinephrine - Keep epinephrine in your bag and at your home for emergency drug reactions, if this is anticipated or if you are on the drug.