Introduction
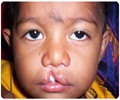
Pierre Robin syndrome, also called as Robin anomalad, is a condition, which could occur on its own or in association with a group of deformities. This condition was first described by Lannelongue and Menard in 1891 and subsequently in 1923 by Pierre Robin.
This condition is due to a genetic defect, which gives rise to three problem, a very small lower jaw, a slit like hole in the palate of mouth (called cleft palate) and the tongue appear to fall into the throat (condition called as retroglossoptosis)
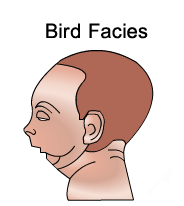
The condition occurs approximately in 1 per 8500 live births with an equal occurrence among boys and girl babies except when it is inherited as an X-lined genetic disorder. In such an inheritance the ratio among boys increases.