- PET Scanning - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559089/)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with (18)F-based radiotracers - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3478111/)
- Clinical Applications of PET and PET-CT - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4921358/)
- PET scan - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003827.htm)
- Brain PET scan - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007341.htm)
- PET/CT scan: How to prepare, what to expect & safety tips - (https://radiology.ucsf.edu/patient-care/prepare/pet-ct)
- A Cyclotron Decommissioning Radiological Assessment Exercise Performed by Student Mentees Underrepresented in the Radiation Safety Profession - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32897987/)
- PET/CT: Current status in India. Indian J Radiol Imaging - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2747449/)
- Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) and PET/computed tomography imaging characteristics of thyroid lymphoma and their potential clinical utility - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19089692/)
- PET/CT With 68Ga-DOTA-TATE for Diagnosis of Neuroendocrine: Differentiation in Patients With Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27775942/)
- 18F-Fluorothymidine PET is an early and superior predictor of progression-free survival following chemoimmunotherapy of diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a multicenter study - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8263539/)
- 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) Positron Emission Tomography in Oncology - (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00207298)
- PSMA PET Scan - (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2797264)
- Heart PET scan - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007343.htm)
- Advantages and Applications of Total-Body PET Scanning. Diagnostics - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8871405/)
- PET scan for breast cancer - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007469.htm)
- Lung PET scan - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007342.htm)
About
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a nuclear medicine procedure used to examine various body tissue functions to identify certain conditions. Biochemical changes in an organ or tissue can be traced with the help of PET images before the onset of anatomical changes. The combination of PET and CT scans shows promise in the diagnosis and treatment of many types of cancer(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET Scanning
Go to source).
Positron emission tomography uses a radioactive drug that emits positrons so that the drug can be traced using the gamma rays that it produces(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with (18)F-based radiotracers
Go to source). The three-dimensional images of the tracer concentration within the body help reveal how the tissues and organs are functioning. The tracer can be swallowed, inhaled or injected, depending on the target tissue, or organ.
The tracer, which is a radioactive drug, is a positron-emitting radionuclide that emits gamma rays. The Positron Emission Tomography machine detects these gamma rays and images are reconstructed by computer analysis. The tracer collects in the tissues and organs that have high levels of chemical activity, usually the diseased areas. Several abnormal conditions in the body such as cancer, heart disease and brain disorders are revealed using this technique, helping in the right diagnosis of the conditions.
The PET scan can measure blood flow, oxygen use, glucose metabolism and other physiological functions of the body(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET Scanning
Go to source). It is typically an outpatient procedure and the person can be discharged on the same day after the test is complete. It does not require any local or general anesthesia.
Why is the PET Scan Procedure Performed?
The PET scan procedure reveals the chemical activity in parts of the body. The PET scan images help to know more about the size, shape, position and functions of the organs that are scanned. Physiological functions detected through a PET scan include neural activity, blood flow, metabolism, uptake of sugar in the brain, the response of the tumor to treatment, damaged parts of the heart and so on. PET scan test for cancer helps not only in the diagnosis, but also keep a track of the response of cancer to the treatment procedure.
PET scan is different from other scans like MRI or CT scan. Abnormalities in tissues at the cellular level can be understood from PET images. This kind of information can help in identifying systemic diseases such as coronary artery disease, brain tumors and seizures. PET scanners are often used in combination with computed tomography or CT scan in modern PET-CT scan machines(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Clinical Applications of PET and PET-CT
Go to source).
Some of the specific reasons for performing PET scans include:
- To help in the diagnosis of dementia,
Alzheimer’s disease ,Parkinson’s disease , among others - To locate and identify the surgical site for brain surgery.
- To detect a blood clot, hemorrhage or other perfusion of the brain tissue.
- To detect the extent of cancer spread from a specific site to other parts of the body.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of the cancer treatment given.
- To examine the blood and oxygen flow into the heart muscles and the effectiveness of the therapeutic procedure used
- Detailed evaluation of lung lesions or masses detected on chest X-ray.
- To understand the effectiveness of lung cancer treatment(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET scan
Go to source)
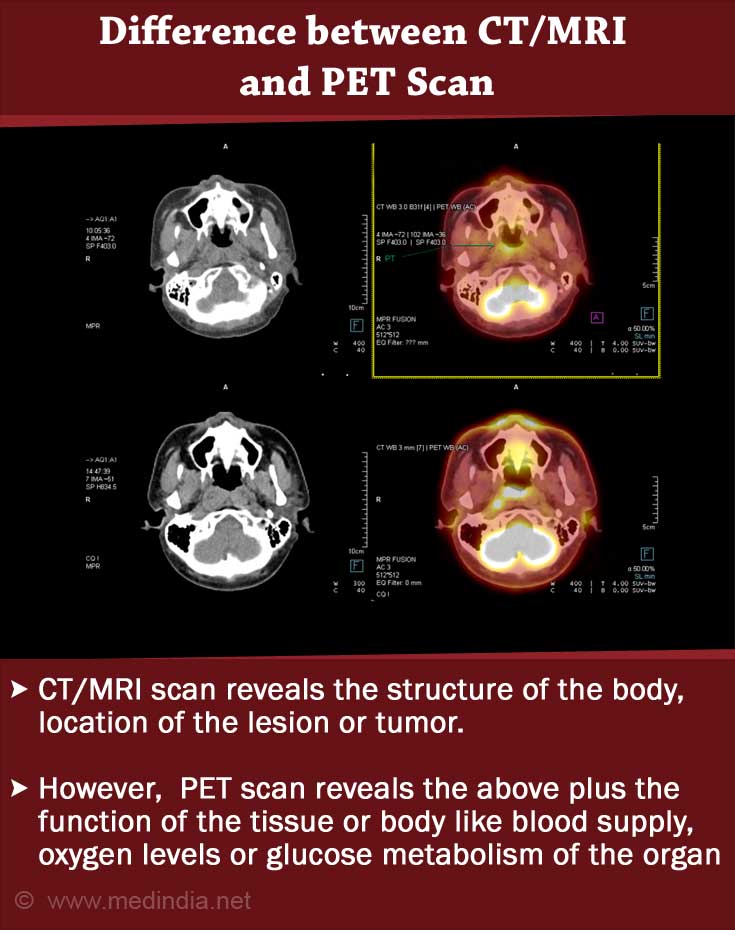
How is PET Scan Different from CT Scan and MRI Scan?
PET scans, Computerized Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging are all non-invasive surgical scans that help the doctor ‘look’ inside the body. All of them are based on the reactions to certain inputs in the form of contrast medium, magnetic rays or radioactive dyes.
PET scan is different from the other two in terms of the images it produces. While CT scan and MRI scan reveal the structure of the body, the location of the lesion or tumor, PET scan reveals the functions like blood supply, oxygen levels, glucose metabolism and so on(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Brain PET scan
Go to source).
How to Prepare for PET Scan Procedure?
Preparing for a procedure of PET scan involves gathering or giving information to the doctor.
Information to be given to the doctor:
- Any allergies that you may have
- Any prevailing medical conditions like diabetes
- If you are pregnant or have any possibility of being pregnant
- If you are breast-feeding
- Taking any medications, including prescription, over-the-counter or herbal supplements
- If you are claustrophobic, afraid of enclosed spaces
The doctor’s instructions to you may include:
- Avoid strenuous exercise for a couple of days
- Don’t eat anything for eight hours before the test, typically overnight fasting before the test in the morning. Drinking water may be allowed
- Do not consume any form of caffeine or alcohol, or use tobacco for at least 24 hours before the PET procedure
- You may be asked to take a pre-procedure insulin dose if you are an insulin-dependent diabetic and the sugar levels before the procedure are high
- Any other specific preparation instruction based on a particular medical condition(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET/CT scan: How to prepare, what to expect & safety tips
Go to source)
Just before the procedure:
- All jewelry and body piercings must be removed as metal can interfere with the testing equipment
- May be asked to change into a hospital gown
- Empty your bladder
- In certain types of scans of the pelvis or abdomen, a urinary catheter may be inserted into the bladder to drain urine during the procedure
After the PET scan:
- After the test, you may carry on with the usual activities of the day
- You’ll need to drink plenty of fluids to flush out the tracer from the body
- Stay away from pregnant women and lactating women for about 24 hours after the PET procedure. The radioactive tracer might be harmful to them(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET/CT scan: How to prepare, what to expect & safety tips
Go to source)

Imaging Procedure of PET Scan
A cyclotron is a machine that produces radioactive medicine. This medicine is tagged to a natural chemical like water, glucose or ammonia and the combination is called a radiotracer(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
A Cyclotron Decommissioning Radiological Assessment Exercise Performed by Student Mentees Underrepresented in the Radiation Safety Profession
Go to source).
A small amount of the radiotracer is given via a vein. Sometimes, the tracer can be given orally or inhaled. The patient is asked to wait for the tracer to travel inside the body for an hour or so. The tracer travels through the blood and gets collected in organs and tissues that use the natural chemical with which the medicine was tagged.
The patient is made to lie on a narrow table that slides into a large-tunnel-shaped PET scanner machine. The patient is asked to lie still during the scan to avoid blurring of images.
The machine may make buzzing and clicking sounds and sometimes the patient may feel uncomfortable due to the enclosed place inside the scanner. It takes about 30 minutes to complete the procedure.
A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) machine detects the energy emitted by positively charged particles called positrons. Positrons are emitted when the radiotracer is broken down inside the patient’s body.
The image displays the concentration of positrons according to brightness and color. Information obtained from the detected energy is converted into a 3-dimensional image on a computer monitor.
The images are displayed on a monitor. The images will be examined by a radiologist, a specialist in interpreting the images obtained from the MRI scan, CT scan, ultrasound and X-ray images.
Cost of PET scan:
PET scans in government institutes cost between Rs. 2000 and Rs. 10000, with an average of Rs. 6000. A total body PET/CT scan in the private sector costs between Rs. 15000 and Rs. 27000, depending on the protocol(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET/CT: Current status in India. Indian J Radiol Imaging
Go to source).
Types of PET Scans
The type of PET scans is based on the radioactive tracer used. A radioactive tracer binds with the natural chemical like sugar and water. So the part of the body and the purpose of PET scan determine the type of radioactive tracer used. Some of them are:
- Fluorodeoxyglucose PET or FDG-PET: FDG is a sugar-like substance that binds with the areas in the body where sugar accumulates. Tumors use sugars to grow and hence FDG-PET can find concentrations of the tracer around tumors. It is also helpful for imaging inflammation, infection and brain function(9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) and PET/computed tomography imaging characteristics of thyroid lymphoma and their potential clinical utility
Go to source) - DOTA-TATE or GaTate and DOTA-COC PET: This radioactive tracer is used for detecting neuroendocrine tumors and other types of neural tumors(10✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET/CT With 68Ga-DOTA-TATE for Diagnosis of Neuroendocrine: Differentiation in Patients With Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Go to source) - Fluoride Bone PET:Fluoride-based tracer useful for imaging bones
- Fluorothymidine PET or FLT-PET: This procedure is used currently for imaging bone marrow function and brain tumors. It is mainly used to image cells that are replicating(11✔ ✔Trusted Source
18F-Fluorothymidine PET is an early and superior predictor of progression-free survival following chemoimmunotherapy of diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a multicenter study
Go to source) - Fluorocholine PET or FCH-PET: Helps in imaging prostate cancer
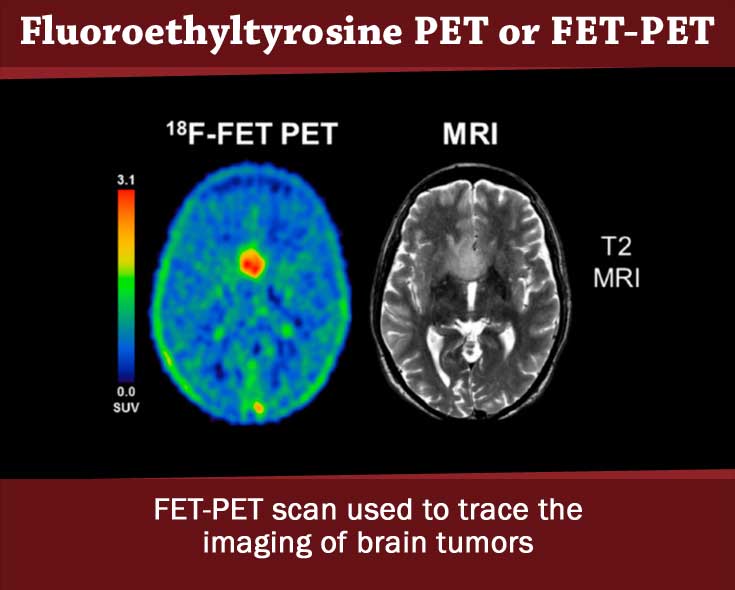
- Fluoroethyltyrosine PET or FET-PET: Imaging of brain tumors is possible with FET tracer
- 18F-FDG PET: It is utilized to identify aberrant glucose metabolism locations and can be used to describe and localize many different types of tumors(12✔ ✔Trusted Source
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) Positron Emission Tomography in Oncology
Go to source) - PSMA PET scan: A PSMA PET scan (prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography) is an imaging technique used to detect prostate cancer throughout the body. It employs a radioactive material that targets PSMA, or prostate-specific membrane antigen, a protein expressed by prostate cancer(13✔ ✔Trusted Source
PSMA PET Scan
Go to source) - Cardiac PET scan: A cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging diagnostic that looks for illness or inadequate blood flow in the heart by using a radioactive material called a tracer(14✔ ✔Trusted Source
Heart PET scan
Go to source) - Total body PET scan: Total-body PET scanning allows the entire body to be photographed at the same time, allowing changes in medication distribution throughout the body to be followed, and providing insight into how an agent can concentrate in tissues over time. As a result, doctors can evaluate the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of novel therapeutic medicines in all organ systems(15✔ ✔Trusted Source
Advantages and Applications of Total-Body PET Scanning. Diagnostics
Go to source)
PET of Various Organs
The images obtained from positron emission tomography is interpreted by a qualified radiologist, and explained to the patient by the doctor concerned. The results obtained depend on the area of the body to be examined. PET scans are used to produce detailed three-dimensional images of the various organs such as:
Brain PET scan: PET scan of the brain can help identify cancer, prepare for epilepsy surgery, diagnosing dementia and help in the differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease from other movement disorders(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Brain PET scan
Go to source).
Breast PET scan: A breast PET scan is usually done after the diagnosis of the breast cancer, to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body like lymph nodes, lungs, liver or bones. Breast PET scan is done during the treatment to see if the cancer is responding to treatment and identifying the relapse of breast cancer after treatment(16✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET scan for breast cancer
Go to source).
Heart PET scan: During the procedure of a heart PET scan, electrocardiogram is also done simultaneously to monitor heart rate. The size, shape, position and some functions of the heart are revealed in a heart PET scan. The procedure helps in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy or heart failure(14✔ ✔Trusted Source
Heart PET scan
Go to source).
Lung PET scan: A lung PET scan helps in detection of lung cancer and to see if it has spread to other parts of the body. It is done during the course of treatment to check the response of the cancer to the medicines and other treatment procedures. Abnormal results in a lung PET scan can be due to infection, inflammation of the lungs, lung cancer or solitary pulmonary nodule(17✔ ✔Trusted Source
Lung PET scan
Go to source).
Risks of PET Scan
PET-CT contains the difficulties associated with contrast injection, such as allergy, contrast-induced nephropathy, and so on. In general, the radiotracers utilized have no notable negative effects(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
PET Scanning
Go to source). The amount of radiation emitted by a normal PET scan is safe. Allergic reactions to the radiotracer may be present very rarely. It is advisable to keep the doctor informed about any allergies that the patient has.
If a pregnant woman undergoes a PET scan, there is a risk of injury to the fetus. Also, a woman who is breastfeeding her baby must avoid the scan as the radionuclide may contaminate the breast milk.
Lying on your back for a long time on a narrow table may cause some discomfort or body ache. Also, people who are claustrophobic need some assurance and counseling before the procedure.
Some conditions may interfere with the accuracy of the PET scan results:
- Caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, among othersare present in the blood due to consumption within 24 hours prior to the procedure
High blood sugar levels - Use of medications such as tranquilizers and sedatives
Apart from this, patients who undergo a PET scan are advised to stay away from pregnant or lactating women for about 2 days after the test.