About
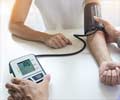
Pre eclampsia (pronounced as "pre-ee-clamp see-ah"), which is also called toxemia, is when a pregnant woman develops high blood pressure and proteinuria during pregnancy.
Pre-eclampsia is derived from a Greek word 'eklampsis' meaning ‘sudden flashing’.

Affecting at least 5 percent of all pregnancies, it is a complex condition characterized by high blood pressure, swelling in the limbs or face, and protein in the urine. Pre-eclampsia can prevent the placenta from getting enough blood. If the placenta does not get enough blood, the baby gets less essential nutrients. This can cause
Pre-eclampsia can be mild or severe, and progress slowly or rapidly. This condition mostly manifests after 37 weeks of pregnancy, but it can develop any time during the second half pregnancy i.e. after the 20th week. It can also show up during labor or after delivery.
The exact cause of pre-eclampsia is not known.
The high blood pressure can affect the brain, kidneys, liver, and lungs. If the woman develops seizures or coma, the condition is known as eclampsia.
Pre-eclampsia can be diagnosed with the help of blood pressure readings taken at regular intervals and urine test for proteins.
Delivery by caesarean section is the most preferred treatment for pre-eclampsia, if the fetus has grown enough to survive outside the womb.