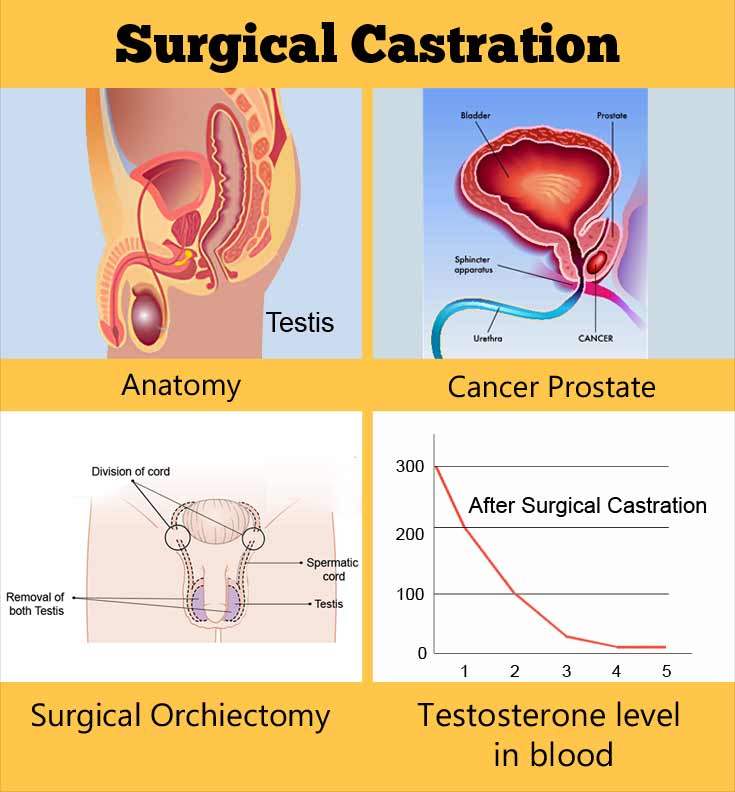
Surgical castration is a procedure where both the testes are removed. It renders the male infertile and reduces sexual urges. Surgical castration results in a permanent loss of sexual function.
The procedure is done for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer and rarely for some bilateral cancers of the testes. Sometimes it maybe necessary to remove both the testis where there is a severe injury to the scrotum.(1)

Surgical castration has been often carried out in history for other reasons too. It has been used as a form of punishment for rapists, homosexuals, as well as for prisoners of war. There has been a renewed demand in the recent past to introduce surgical castration in sexual offenders specially rapists. However, most countries have given up surgical castration for habitual sexual offenders and opt for voluntary medical castration instead, where a chemical drug is injected or a tablet is given regularly.
During surgical castration, a small incision is made in the scrotum under anesthesia and both the testes are removed. Sometimes, prostheses are placed in the scrotum to replace the testes. Following surgical castration, due to removal of testes, the person cannot father any children. Due to lack of testosterone following the procedure, the person loses sexual drive. However, it has been observed that the sexual drive is not lost immediately in all those castrated. Also, the sexual drive can be restored by taking testosterone injection. Thus, surgical castration may not be the treatment of choice in habitual sexual offenders.(2)
Side effects of the procedure include:
Surgical castration is a permanent procedure, which not only affects the sexual function of a male, but also causes changes in the appearance and important parts of the body. The person may get depressed and even attempt suicide. Its use in habitual sexual offenders raises ethical issues. On the other hand, the use of medical castration which causes temporary effects may be more justifiable in these cases.