- Tooth decay - Overview - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279514/)
- Tooth decay - Overview - ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279514/)
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Teeth - ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557543/)
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Teeth - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557543/)
- Demineralization-remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27695330/)
- Demineralization-remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27695330/)
- Pit and fissure sealants for preventing dental decay in permanent teeth - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28759120/)
- Pit and fissure sealants for preventing dental decay in permanent teeth - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28759120/)
About
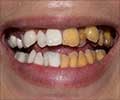
Tooth decay is a disease of the tooth that damages its structure. It is also known as cavities or caries and is brought on by bacteria in the plaque on your teeth,
sugary foods and beverages, and poor oral hygiene(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tooth decay - Overview
Go to source).
It is the most important cause of tooth loss in children and younger people. Tooth decay can easily be prevented by brushing and flossing the teeth regularly. Untreated tooth decay can result in death of the internal structures of the tooth with eventual loss of the tooth.
Tooth decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth make acids that form cavities in the teeth.
Cavities are usually painless until they grow very large inside the internal structures of the tooth (the dentin and the pulp at the core) and can cause death of the nerve and blood vessels in the tooth, leading to the formation of abscess. Toothache is the most common symptom of tooth decay.
Tooth decay can easily be diagnosed during routine dental check-ups.
The treatment for tooth decay depends on the extent of damage. Mild cavities can be fixed with the help of fillings. For more severe tooth decay, a crown or root canal is recommended. In extreme cases, the dentist extracts the damaged tooth.
What are the Causes of Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is often a combination of three things: plaque, poor oral hygiene and eating a lot of sugar.
Plaque is a film-like substance that covers the surface of the teeth and can feel ‘fuzzy’ It usually consists of bacteria, saliva, and food particles.
Acid forms on the surface of the teeth when bacteria break down the food particles and the sugar in them. If teeth are not regularly cleaned then this acid can attack the outermost covering of the tooth known as enamel slowly destroys the tooth. The spread of decay-causing bacteria can be through saliva.

Children are especially vulnerable to tooth decay because the enamel on baby teeth (milk teeth) is more sensitive than the enamel on permanent teeth. Too much sugary food and drink might damage baby teeth. Oral hygiene can sometimes be difficult, especially for younger children. Toddlers who often consume sweet tea or juice from a baby bottle are more likely to develop tooth decay.
Permanent teeth are also rather sensitive at first because, when they break through, their enamel hasn't yet formed completely, rendering them prone to decay(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tooth decay - Overview
Go to source).
Stages of Tooth Decay
There are 5 stages of tooth decay:
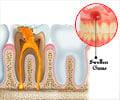
Stage 1: Initial Demineralization
The outer most layer of teeth is made up of a type of tissue known as enamel, which is the hardest tissue and made up of minerals(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Teeth
Go to source).
When the tooth is exposed to acids produced by plaque bacteria, this can cause loss of minerals in the enamel.
This can cause a white spot to appear on the teeth. This is also known as a white spot lesion. This is the start of tooth decay.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
When the process of tooth decay continues, the enamel breaks down further causing the white spot to turn into a
Since the enamel is weak, small holes in the teeth called
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
Under the enamel lies another layer of tissue called the dentin. It contains more organic matter than enamel, making it softer and more prone to attack by acid. This is the reason tooth decay proceeds at a quicker rate in the dentin(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Demineralization-remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone
Go to source).
Sensitivity is experienced when the decay reaches the dentin because it has tubes that lead to the nerves of the tooth. This happens particularly when having hot or cold foods.
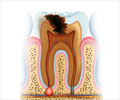
Stage 4: Pulp Damage
The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels and is the innermost layer of your tooth. These nerves are responsible for the sensation in the tooth.
When the pulp is damaged, it can cause irritation and swelling can occur. Since the surrounding tissues of the tooth are unable expand to accommodate this swelling, pressure can build in the nerves causing
Stage 5: Abscess
As tooth decay progresses to the pulp, the bacteria can invade and cause infection. Increased inflammation in the tooth can cause a pocket of pus to form at the bottom of the tooth, called an
Abscesses are quite painful and may radiate to the jaw. Other symptoms include swelling of the gums,
Be quick with an abscess and seek treatment immediately as the infection can spread into the bones of your jaw as well as other areas of your head and neck. In some cases, treatment may involve removing the affected tooth.
What are the Symptoms of Tooth Decay?
The first indication of dental decay is white or brown spots on your teeth. As the condition worsens, holes (cavities) form on the surface of the teeth. Tooth decay can injure the nerves in the teeth and the roots if the deeper layers of the teeth are impacted. The teeth become sensitive and painful, especially when you eat or drink something cold or sweet.
How can we Diagnose Tooth Decay?
To detect tooth decay, a dentist just needs to examine your teeth closely. X-rays can also be used to determine how much decay has occurred in your teeth and whether the spaces between your teeth or under any fillings are damaged(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Tooth decay - Overview
Go to source).
How can Tooth Decay be Treated?
As in other infections, tooth decay cannot be treated by giving medicines alone because the decayed tooth structure does not regenerate. However, the progression of dental caries can be stopped by treatment. Treatment often preserves the tooth.
Treatment of tooth decay may involve -
- Fillings : When there is a hole in the teeth, filling is preferred. In filling teeth, the decayed material is removed and replaced with a material such as silver alloy, gold or porcelain. Many dentists consider silver amalgam (alloy) and gold to be stronger and often use them on the back teeth.
- Crowns : If there is extensive decay then multiple fillings may break the remaining tooth. To prevent this, crowns are used. The decayed or weakened area is removed and repaired and a covering jacket (crown) is fitted over the remainder of the tooth. Crowns are often made of silver, gold or porcelain.
- Root canal : If the decay is severe, then the nerves of the tooth also get affected. A root canal is recommended in such cases. The center of the tooth, including the nerve and vascular (blood vessel) tissue (pulp), is removed along with decayed portions of the tooth. The roots are filled with a sealing material. The tooth is filled and a crown may be placed over the tooth.
- Tooth extraction : Tooth extraction is performed if the tooth is too far destroyed from the decay process to effectively restore the tooth or if the tooth will probably cause further problems in the future, as may be the case for wisdom teeth.
Prevention of Tooth Decay
Don’t Forget to Brush your Teeth
Adults and children can lower the risk of tooth decay by regularly brushing their teeth with fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride can help make the enamel stronger and protects the teeth from decay. Brushing the teeth eliminates plaque, which contains harmful bacteria and acid. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day after meals is typically advised.
Fluoride is your Friend
Fluoride toothpaste should be used as soon as a child's first baby teeth appear, according to dentists. Pediatricians frequently advise giving fluoride pills or drops to toddlers at first, followed by brushing their teeth with a small amount of non-fluoride toothpaste. However, children should not consume too much fluoride since it might produce adverse effects.
You are What you Eat
What you eat also matters: lowering your sugar consumption reduces your chance of tooth decay. Soft drinks, fruit juices, and sweets are high in sugar.
Regular Check-ups are a Must
Regular dental check-ups can help safeguard your teeth since tooth decay can be noticed early and treated. Your dentist can provide oral hygiene advice and apply fluoride varnish or gel to your teeth. Dental sealants are unique plastic compounds that may be used to fill the pits and grooves of your bigger back teeth (molars)(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pit and fissure sealants for preventing dental decay in permanent teeth
Go to source).
When you have tooth decay, home remedies are not advised as they usually end up having adverse effects. Make sure to follow daily dental care tips like brushing your teeth twice daily and flossing regularly.