- Toothache - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/toothache/)
- Toothache and Gum Problems - (https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tooth)
- Dental (Odontogenic) Pain - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4590084/)
- Toothache and swelling - (https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/toothache-and-swelling)
What is Toothache?
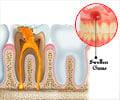
A toothache is described as any pain in or around the tooth when the nerve in the root of a tooth or surrounding a tooth is irritated. It can be a frustrating and unpleasant experience that often brings people to the dental clinic.
What are the Symptoms of Toothache?
The severity and duration of toothache varies from person to person based on their underlying cause, etiology. Other signs and symptoms that may lead to seek care include the following:
- Pain on touching the tooth or while chewing
- Fever
- Headache
- Sensitivity to hot or cold air and liquids
- Bleeding or discharge from around a tooth or gums
- Swelling around a tooth or swelling of the jaw/cheek
- Injury or trauma to the tooth area
- Bad breath
- Changed taste sensation
- Swollen glands
Sometimes, pain from a deeper structure (called referred pain) may be passed along the tooth nerve and can be felt in the tooth. In order to differentiate toothache from other sources of pain in the face and get relief, an evaluation by a dentist is appropriate(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Toothache
Go to source).
What are the Causes of Toothache?
Toothache can be caused by the following conditions:
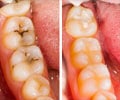
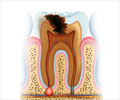
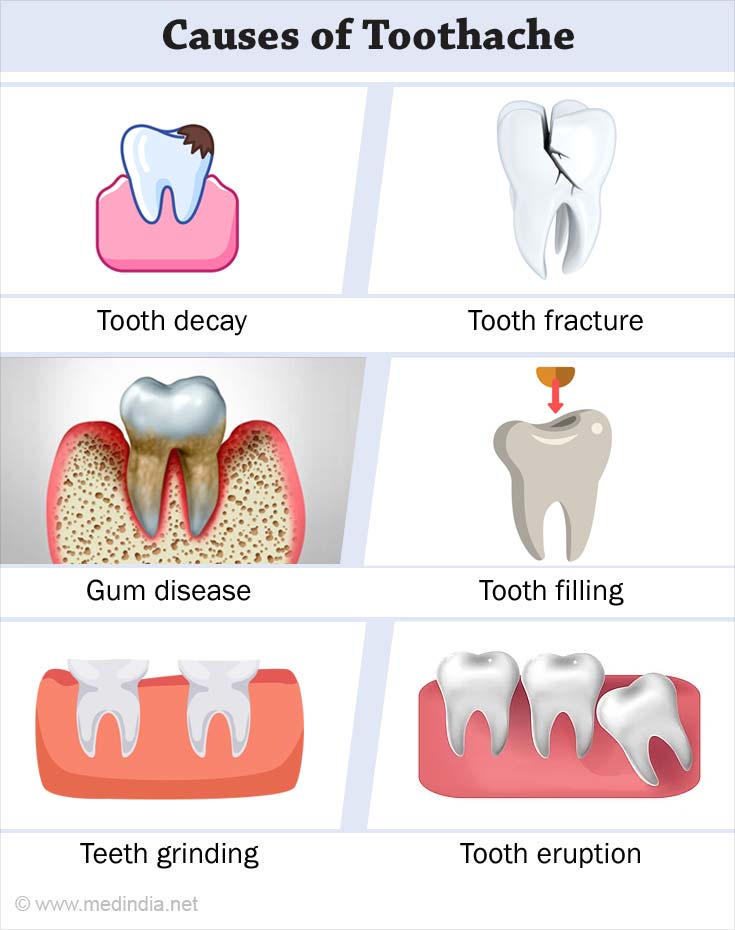
- Tooth Decay - It is the primary cause of toothache for most children and adults. Holes formed in the decayed tooth irritate the inner layer of tooth which contains blood vessels and nerves.
- Tooth Fracture - If crack is deep enough, it can let bacteria into the inner layer of the tooth, and that can lead to a build-up of pus called an abscess. The infection can spread to surrounding tissues and bone, too.
- Gum Disease - as gums shrink away from teeth exposing the roots, it can irritate the nerve endings and which is felt as pain.
- Tooth Filling - a recent tooth cleaning procedure or a new filling may wear off the outer protective layer of tooth for a short period, which is felt as pain. Many people feel it after whitening treatmentsand even a damaged old filling can cause it.
- Teeth Grinding - repetitive motions, such as chewing gum or grinding or clenching teeth brought on by stress, sleep disorders, or a bite issue can wear down the teeth surface to cause pain. This habit is called bruxism.
- Tooth Eruption (teeth coming out of the gums)
- Certain kinds of headaches, like cluster and migraine
- Clogged or infected sinuses
- Problems in the joint or muscles that connect jaw to skull
- In rare cases, a heart attack can also cause tooth pain(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Toothache and Gum Problems
Go to source).
How do you Diagnose Toothache?
In order to determine the cause of tooth pain, the dentist will proceed in a stepwise manner, beginning with history.
Medical History
- The following questions regarding the symptoms of toothache are asked:
- How long has the tooth pain been going on?
- Is the pain constant or it occurs only after a trigger (for example, drinking a cold beverage)?
- Is the tooth sensitive to cold or heat, sweet food, chewing, and/or brushing?
- Does the tooth pain get worse during night time?
- Are you experiencing any associated symptoms (e.g., face pain or swelling, headache, fever, or vision problems)?
- Have you experienced any trauma in the tooth?
- Have you undergone any recent dental procedures?
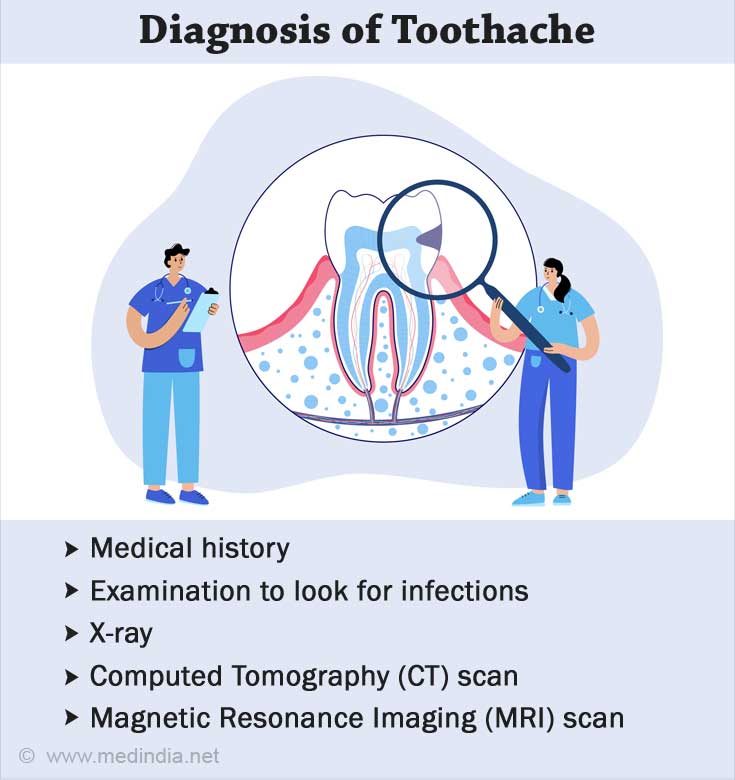
Examination
- After taking a history, the dentist will examine the teeth for decay or any signs of infection (e.g., swelling or discharge).
- Dentist may tap teeth within the area of identified pain and/or apply an ice cube or blow cold air on different areas of the tooth to figure out where the sensitivity is coming from
- After the examination, the dentist may want to take an X-rayof the bothersome tooth to check for abscesses, cavities, or any other hidden problems.
- A computed tomography (CT) scan or
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) test is rarely used(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Dental (Odontogenic) Pain
Go to source).
How can you Treat Toothache?
Once the cause of toothache is identified. Fixing the problem will be the next step.
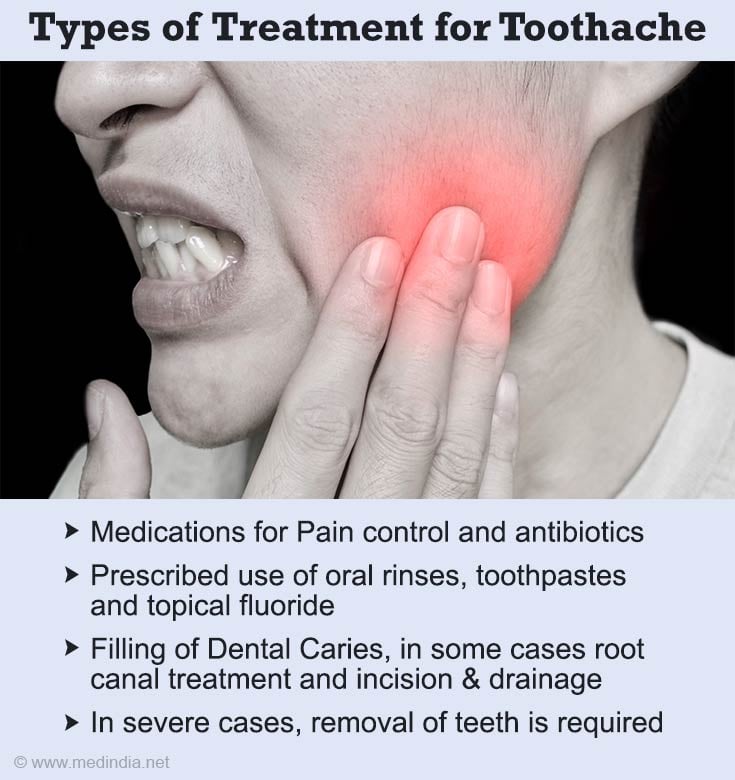
Medications
- Pain Control - Dentists may recommend taking Tylenol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID). For severe pain, an opioid may be prescribed or local nerve block injections may also be given.
- Antibiotics - It will usually be prescribed if a fever or swelling of the jaw is present. The reconstructive procedures will be performed at a later time (weeks to months) once the infection subsides.
- Oral Rinses and Topical Fluoride - Chlorhexidine mouthwashes may be prescribed to treat gum disease. Fluoride rinses or topical fluoride treatments may also be given to prevent or treat tooth decay.
- Toothpaste - A special Toothpaste made for teeth sensitivity, such as Sensodyne is recommended by dentist
Oral Devices
Excessive grinding of teeth can be prevented by wearing a mouthguard recommended by the dentist at nighttime. While a mouthguard will protect the teeth from damage, it won't decrease the number of clenching episodes. This is why addressing underlying triggers such as stress or drinking alcohol or caffeine at night will also be an essential part of a treatment plan.
Dental Procedures
- Toothache arising out of dental caries requires simple filling or may even go for root canal treatment if the caries due to bacterial or any other infection extends up to the tooth root.
- For an abscess, incision and drainage is the primary treatment, which is followed by root canal treatment or removal of tooth.
- Injury to tooth resulting in fracture of root or exposure to inner layer of tooth can be treated by placing crowns if trauma is minimal
- In severe cases, removal of a fractured tooth is required.
Home Remedies for Toothache
- A salt water rinse is an effective first-line treatment. Salt water is a natural disinfectant that can remove food particles and debris stuck between the teeth. To use this approach, mix 1/2 teaspoon (tsp) of salt into a glass of warm water and use it as a mouthwash.
- Applying cold packs on the painful side of the jaw to alleviate discomfort and reduce the swelling. Hold an ice bag to the affected area for 20 minutes at a time and repeat this for next few hours.
- Peppermint tea bags can be used to numb pain and soothe sensitive gums. Allow a used tea bag to cool down a little before applying it to the affected area. It should still be slightly warm.
- Crushed garlic has scientifically proven bactericidal properties which relieves pain and infection at the site for a shorter period. The crushed garlic can also be mixed with rock salt for better effect.
- Clove oil can effectively reduce tooth pain. It contains eugenol, which is a natural antiseptic, Dilute clove oil with a carrier oil, like sunflower or jojoba oil. Then dab onto a cotton ball and apply it to the affected tooth a few times a day.
- Chew on fresh guava leaves or add crushed guava leaves to boiling water to make a mouthwash. Guava leaves have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that can aid in oral care.
- Thyme oil can be used to treat toothache because it has powerful antibacterial and antioxidant properties.
- Vanilla extract contains alcohol, which can numb the tooth pain. It is also a proven antioxidant, which makes it an effective healer.
- Avoid taking an OTC antiseptic containing benzocaine without consulting a dentist(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Toothache and swelling
Go to source).
Note : Consult a dentist immediately if you have any of the following with a toothache:
- Pain that persists for more than a day or two
- Fever
- Signs and symptoms of infection, such as swelling, pain when you bite, red gums or a foul-tasting discharge
- Trouble breathing or swallowing.
How to Prevent Toothache?
The key to good oral health is preventing problems before they arise. Try following these preventive strategies for toothache.

- Wear a mouthguard during contact sports to avoid trauma to teeth
- Avoid biting hard candies or ice to prevent cracks in the tooth's surface
- To prevent tooth cavities, gum disease, and sensitivity
- Brush gently twice daily using soft-bristled toothbrush and a fluoridated toothpaste along with flossing
- Drink fluoridated water
- Get teeth cleaned by a dentist at least twice a year
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner
- Avoid smoking
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, protein, and fatty fish and minimize ingestion of sugar-rich foods or drinks regularly