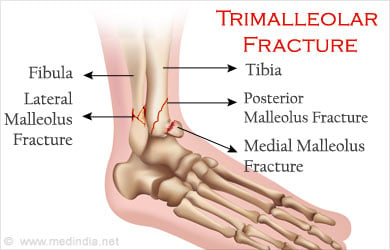
What is a Trimalleolar Fracture?
Trimalleolar fracture is usually common in accidents where a huge force is applied on the ankle, like in skiing sports or an automobile accident. Trimalleolar fracture is common in aging populations, who are active. Osteoporosis also increases the risk of a trimalleolar fracture.
Who is at Risk of developing a Trimalleolar Fracture?
- People driving without a seat belt
- Motorcyclists
- People working on heights
- Elderly people
- Osteoporosis patients
- People participating in sports like ice skating, skate boarding and skiing
Causes of Trimalleolar Fracture
- Overextension of the ankle
- Extreme impact while getting down from a height or in an automobile accident
- Twisting or tripping of the ankle
- Rolling of the ankle to the side
Symptoms of Trimalleolar Fracture
- Swelling of the joint
- Tenderness at the joint
- Severe pain in the lower leg
- Inability to bear weight on the joint
- Deformed joint
- Bruising of the joint
Diagnosis and Treatment for Trimalleolar Fracture
Diagnosis of a trimalleolar fracture may be done with X-rays in different positions, like anteroposterior (AP) and lateral to confirm the trimalleolar fracture. A CT scan can be ordered in case of a suspicion of fracture despite negative X –ray findings, to obtain cross sectional images of the bones. A stress test with fluoroscopy is done to assess the stability of the ankle, which helps to decide the mode of treatment.
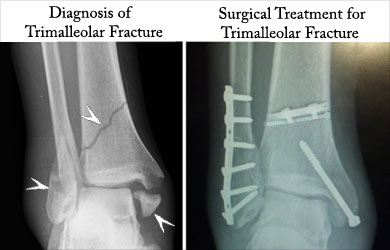
Considering the fracture is highly unstable, surgical treatment is usually advised to restore the ankle joint function. Surgical treatment involves open reduction and internal fixation. It is done either with screws, plates and screws, or with wiring/ grafting.
In patients who have a high risk for surgery due to existing medical conditions or significant health problems, non surgical treatment is advised. This form of treatment is performed by immobilization with a splint until the swelling comes down, followed by a leg cast for 6 to 8 weeks. This needs continuous follow-up by your doctor with x rays, to monitor healing.
Complications of Non-surgical Treatment of a Trimalleolar Fracture
- Malunion
- Arthritis in the ankle joint
- Delayed healing of the wound/bones
Chances of developing complications increases with age, diabetes, and smoking.