- Ultrasound pregnancy - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003778.htm)
About
Ultrasound in a pregnant woman gives various kinds of information ranging from estimated date of delivery to understanding fetal heart beat and blood flow in the fetus.
Ultrasound during pregnancy has recently become an interesting part of prenatal care and is used to study fetal heartbeat, growth of the fetus, placental location, ectopic pregnancy and general fetal health. Pregnancy ultrasound gives an accurate picture of the week-by-week growth of the baby in the womb, baby’s movements in the womb and the position of the baby during later pregnancy.
Ultrasound or ultrasonography is a medical imaging technique that emits high frequency sound waves, records the echos and transforms the readings into an image, which can be viewed in a video monitor. The ultrasound images provide valuable information about the shape, size and structure of the body part of which the image is taken. This information is used to understand the changes in the body that result from diseases and conditions.
Pregnancy ultrasound uses the high frequency waves to find out the structural changes that the baby undergoes in the uterus. The procedure is usually done by placing transducer on the abdomen and is called abdominal ultrasound. Sometimes, vaginal ultrasound is also performed in early stages of pregnancy.
Ultrasound during pregnancy shows images of the fetus, whether the pregnancy is single or multiple, size of the fetus, growth and function of fetal internal organs, whether the pregnancy is uterine or ectopic pregnancy, etc. Information of the location of the placenta during pregnancy is of vital importance and pregnancy sonograms can help decide about the delivery method to be employed based on this information.
The first ultrasound in pregnancy is performed between six to ten weeks of pregnancy. Early ultrasound is performed if there is a history of miscarriage during previous pregnancy or bleeding in the first weeks of the current pregnancy.
How to prepare for an Ultrasound during Pregnancy
Ultrasound test may be transabdominal or transvaginal. Transabdominal ultrasound, requires a full bladder in the early months of pregnancy to view the shape and heartbeat of the fetus. Transvaginal ultrasound during pregnancy is done with bladder empty or partly filled.

It is advisable to wear lose fitting two piece clothing for an ultrasound pregnancy test, so that the examiner can run the probe on the surface of your abdomen.
Procedure of Pregnancy Sonogram
The first ultrasound in pregnancy could be abdominal or transvaginal.
For an abdominal ultrasound, the woman has to lie on her back on the examination table, with the abdomen exposed. A gel is rubbed over the belly for improving sound conduction and smooth movement of the transducer. The transducer, a hand-held device, is rubbed and moved up and down the abdomen to locate the right place from where it is possible to see the shape of the baby. Light pressure of the transducer may be felt by the pregnant woman, but there is no other discomfort.
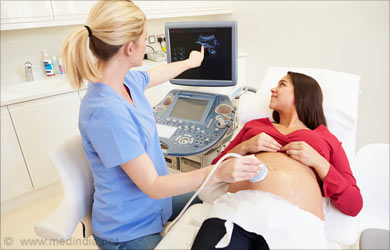
The sonographer slides the probe over the abdomen to transmit sound waves. The sound waves reflected off the bones and tissues of the mother and baby will be recorded and translated as images. These images can be seen on a video monitor. Before the end of first trimester, pulsating movements of the heartbeat of the baby can be seen on the screen.
During the scan, the sonographer records certain measurements, and takes still pictures or videos for the doctor and caregiver to interpret. Measurements of baby’s head, abdomen, thighbone and other structures will be done. The length of the baby from the head to bottom, called crown rump length, is measured and recorded. Certain selected images may be stored and printed for further interpretation.
A basic pregnancy sonogram takes about 15 to 20 minutes. However, some procedures require more details and may take up to 90 minutes.
Transvaginal ultrasound is done by inserting a probe covered with a condom into the vagina.
Why is Ultrasound test performed?
Pregnancy sonograms help to understand the week-by-week growth of the fetus. Various parameters, measurements of the fetus, fetal blood flow and many more can be seen in an ultrasound test during pregnancy.
Various parameters of a healthy pregnancy can be checked with an ultrasound during pregnancy. Sometimes, certain situations like bleeding during pregnancy, excessive abdominal pains and other such situations call for an ultrasound test. Ultrasound pictures are different in each trimester of pregnancy.
During the first trimester of pregnancy (weeks 1-12), ultrasound is done for the following purposes.
- Pregnancy confirmation
- Detecting fetal heartbeat
- Calculating estimated date of delivery
- Checking for single or multiple pregnancy
- Examining the placenta, ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and cervix
- Checking the position of the baby – uterine pregnancy or ectopic pregnancy
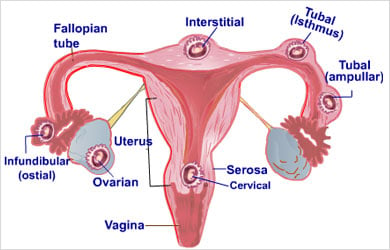
- Diagnosing any miscarriage
During the second trimester (12-24 weeks) and third trimester (24 weeks to 40 weeks), pregnancy ultrasound could reveal the following.
- Growth of the baby in terms of size, development of limbs
- Determine the baby’s gender. REVEALING THE GENDER OF THE FETUS IS BANNED IN INDIA
- Location of placenta during pregnancy
- Fetal structural abnormalities like Down syndrome. However, not all birth defects can be confirmed or ruled out with an ultrasound test.
- Fetal blood flow
- Length of the cervix
- Growth of the internal organs of the baby
- Any other problems in the mother’s uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries
- The amount of fluid around the baby
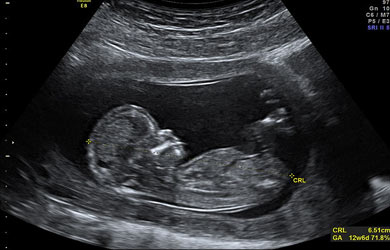
A sonogram of baby can detect or raise a doubt about some developmental structural abnormalities.
Abnormal pregnancy sonogram results could be associated with some kind of problems with the development of the fetus. But sometimes, just a suspicion may not mean that the problem is present. Further tests could be done to confirm or rule out any suspicions.
Some of the abnormalities that can be detected in baby sonograms are:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Multiple pregnancies
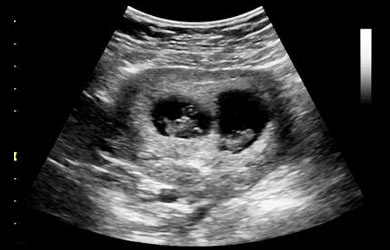
- Miscarriage or confirmation of intrauterine death
- Abnormal position of baby in the womb
- Placenta previa or placental abruption
- Intrauterine growth restriction
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid
- Pregnancy tumors
- Structural birth defects
- Other problems in the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes or other pelvic structures
Types of Pregnancy Ultrasounds
Traditional ultrasound exam uses a transducer over the abdomen to generate 2-D images of the uterus and fetus. There are various other types ultrasounds for pregnant women and some of the important ones are listed below:
Transvaginal Ultrasound: Probe transducers are specially designed and inserted inside the vagina, covered with a condom. The sonogram images are clearer than transabdominal images and the procedure is most often used during the early stages of pregnancy.
3D ultrasound: Specially designed probes and software are used to generate 3D images of the fetus. The 3D ultrasound allows the doctor to check the width, height and depth of the fetus and also other organs in the pelvic region.
4D ultrasound: Specially modified equipment is used for this type of ultrasound. A 4D ultrasound creates a moving video of the fetus, enabling the visualization of the baby’s face and movements. Better capture of highlights and shadows is possible in this type of ultrasound.
Fetal Echocardiography: Common congenital heart defects can be detected in a fetal Echocardiography, a procedure that captures in-depth image of the fetal heart, revealing the size, shape, structure and functioning of the fetal heart. This procedure takes longer than the usual ultrasound pregnancy tests.
Doppler Ultrasound: A Doppler Ultrasound measures blood flow in the umbilical cord, through the placenta or the blood flow in the heart and brain of the fetus. Doppler ultrasound can help understand the elasticity of the arteries of the fetus and the umbilical cord. The test results can reveal if the fetus is getting enough oxygen and nutrients. In case of multiple pregnancies, the blood flow for each fetus can be checked. The test can also help monitor fetal health in case of Rh sensitization. Conditions of mother such as preeclampsia or sickle cell anemia can cause restrictions in blood flow to the baby in the womb.
Risks of Ultrasound
There is no known risk of ultrasound tests during pregnancy. The sound waves emitted from the transducer are reflected off the surfaces and are recorded. Unlike X-rays and laser rays, these sound waves are not invasive nor do they interfere with the cells of the developing fetus. There is also no known contraindication for ultrasound tests during pregnancy.
Pregnancy ultrasounds form an integral part of monitoring prenatal development of the baby. Depending on various factors such as development of the fetus, history of miscarriage, possibility of congenital defects and others, the doctor can decide about how many ultrasound tests can be done in each pregnancy.