- Uterine Polyps - (http://my.clevelandclinic.org/disorders/uterine-polyps/hic-uterine-polyps.aspx)
About
Uterine polyps are overgrowths that occur from the inner lining of the uterus.
Uterine polyps are oval or round overgrowths from the inner lining of the uterus called the endometrium. Hence, they are also known as the endometrial polyps. They are attached to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base. They vary in size - from a few millimeters to several centimeters, and also in number – from a single to several polyps.
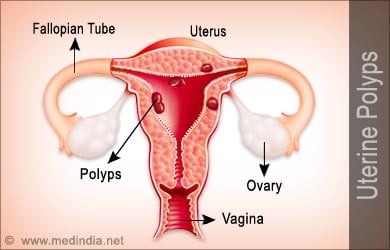
They are usually benign or non-cancerous but sometimes cause menstrual and fertility problems in affected females.
Although the exact cause of uterine polyps is unknown, hormonal factors are found to play an important role in their development. Uterine polyps are found to grow in response to estrogen circulating in the blood. Estrogen is an important female hormone which causes the endometrium to thicken every month.
Women in the age group between 40 to 50 years are at a greater risk in developing uterine polyps. Other major risk factors include obesity, and tamoxifen therapy, which is a drug used in the treatment of breast cancer.
Some of the most common signs and symptoms of uterine polyps are irregular menstrual bleeding, heavy bleeding during menstrual periods, vaginal spotting or bleeding after menopause or sexual intercourse, and infertility.
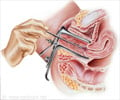
Uterine polyps are diagnosed by a gynecologist based on the menstrual history of the patient, a detailed gynecological examination and tests like transvaginal ultrasound, hysterosonography, hysteroscopy and curettage.
Small polyps which occur without any symptoms may resolve on their own without any treatment. Other cases of uterine polyps can be treated with hormonal medications or surgical procedures.