Hysterectomy - Overview
Nomenclatures: Hysterectomy/Abdominal Hysterectomy/ Vaginal Hysterectomy/ Laparoscopic Hysterectomy/Total Abdominal Hysterectomy with Bilateral Salpingo- Oophorectomy
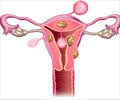
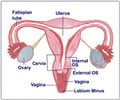
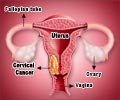
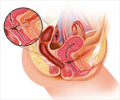
A Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus, which improves the prognosis for uterine cancer and provides relief from troublesome symptoms such as pelvic pain and heavy irregular periods.
A Hysterectomy is the second most common surgery among women. The most common is cesarean section delivery. It is usually performed by gynecologists.
There are several types of hysterectomies:
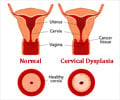
Total hysterectomy is removal of the entire uterus and the cervix. This is the most common type of hysterectomy.
Partial hysterectomy is a procedure done where the cervix of the uterus is left behind but the upper section of the uterus is removed.
Radical hysterectomy is usually done for cancer of the organ and it means removal of the uterus along with the cervix, the upper part of the vagina, and the surrounding tissues.
In many cases, surgical removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) is performed concurrent with a hysterectomy. The surgery is then called "Total Abdominal Hysterectomy with Bilateral Salpingo- Oophorectomy", abbreviated as TAH-BSO.
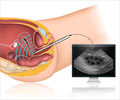
A hysterectomy may be done through an abdominal incision (abdominal hysterectomy), a vaginal incision (vaginal hysterectomy), or as a laproscopic procedure (laparoscopic hysterectomy).
Depending on the medical history and the indication for surgery, the doctor will help the patient decide which type of hysterectomy is most appropriate.