What is Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery?
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery is an arthroscopic surgical procedure done to repair a tear in ligament of the knee called the anterior cruciate ligament.
The thigh and leg bones (femur and tibia, respectively) that contribute to the knee are held together with bands of tissue called ligaments with surrounding capsule and muscles supporting them. Considering the amount of movement at the knee that takes place against gravity, these ligaments have to be very strong to withstand the stress that they are subjected to. A total of four ligament support the knee joints. Two ligaments, the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament are cross-shaped ligaments present within the knee joint. Two other ligaments, the medial and lateral collateral ligaments are located on either side of the knee.
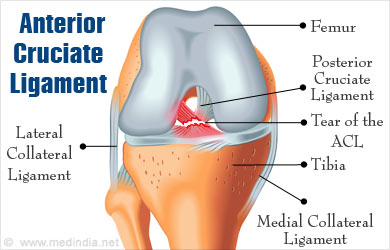
The femur and tibia have two eminences at their surface of contact with each other. The eminences on the inner aspect of the knee are called the medial condyles, while those at the outer aspect are called lateral condyles. The part between the medial and lateral condyles is called the intercondylar region.
The anterior cruciate ligament is attached to the intercondylar region of the tibia, more towards the front of the joint. It extends upwards and is attached to the inner aspect of the lateral condyle of the femur, more towards the back of the joint. It consists of two bundles - the anteromedial and posterolateral bundles. A third bundle called intermediate bundle may also be present. When the knee is bent, the anteromedial bundle becomes tight while the posterolateral bundle relaxes. The opposite happens when the knee is straightened.
An injury to the anterior cruciate ligament may make the knee unstable and warrant surgery. A torn anterior cruciate ligament is usually a consequence of sports injuries. It may be noted some patients who are born with weak ligaments, like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Though not all patients require surgery, reconstruction of the ligament is particularly recommended for patients who are very active, especially athletes involved in contact sports. Surgery can make the knee close to normal, and permit them to return to professional sports.
When Should the Surgery be Done?
Though the opinions vary among centers, surgery is often advised between 3 weeks and a year following the injury. If the surgery is carried out before 3 weeks, there is a chance that the patient may suffer from a condition called arthrofibrosis, where excess of fibrous tissue forms within the joint. If the surgery is delayed beyond a year, the patient may develop damage to other structures of the knee like menisci and ligaments, which can result in osteoarthritis.
What are the Tests Required before Knee Ligament Surgery?
Before an ACL reconstruction surgery is carried out, diagnosis of knee ligament injury is confirmed based on:
- History obtained from the patient to find out the type of injury sustained.
- Physical examination of the patient to look at the instability of the knee.
- An MRI test, which can detect injuries to ligaments and other soft tissues. During an MRI procedure, the patient is placed inside a narrow tube, which can make them claustrophobic if they have a fear of enclosed spaces. Few centers do offer special more open MRI machines, but the drawback is that the pictures may not be as clear. The MRI machine makes a loud clicking noises and it is advisable to ask for earplugs to help block these noises out.
Other tests done include routine tests necessary before any arthroscopic surgery. These include chest x-ray, ECG, blood tests to detect your hemoglobin level, presence of infection, blood group and urine tests.
Some hospitals may want to do test for hepatitis and HIV/ AIDS, however if the patient is not comfortable, they should discuss it with the doctor.
What are the Types of Grafts available for Reconstruction of Anterior Cruciate Ligament?
The anterior cruciate ligament cannot be repaired by merely stitching the torn ends together. A tissue called a graft is introduced into the knee during the surgery. The graft provides a scaffold on which new tissue grows. There are three main types of grafts:
- Allografts. Allografts are obtained from tissues of donors including cadavers. These include tibialis posterior tendon, Achilles tendon, tibialis anterior tendon, bone-patellar tendon-bone, and peroneus longus tendon. These graft materials have the possibility of transmission of infection like HIV or hepatitis - however when obtained from a standard tissue bank the possibility of such infection is very remote.
- Autografts. These grafts are obtained from the same patient. These include bone-patellar tendon-bone and hamstring grafts. Since an autograft is obtained from the patient, they are safe and the body does not react to it. However, an additional wound is created at the site from which the graft is obtained.
- Synthetic grafts. These are made of synthetic materials like polyester, carbon composites, etc. An example is Ligament Advanced Reinforcement System (LARS), which is made of polyester fibers. These are expensive and can cause a foreign body reaction.
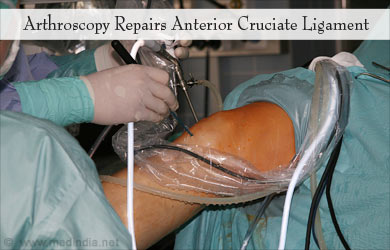
What is the Surgical Procedure for Repair of Anterior Cruciate Ligament?
Before the surgery, the doctor may advise the patient to stop taking certain medications. The patient may have to come to the hospital in a fasting state. The surgery is done under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. In general anesthesia, the patient is unconscious, while in spinal anesthesia, the patient is awake but does not have any sensations from the lower back downwards.
Anterior cruciate ligament surgery is performed with the help of an instrument called an arthroscope. An arthroscope is a small metallic tube with a camera and a light source at its end. It is inserted into the knee joint through a small incision. Live images taken by the camera are projected on a screen. Additional incisions are made around the joint to introduce various instruments required for the surgery. During the procedure, the joint is irrigated with fluid.
During the surgery, a probe is first introduced to inspect the knee joint. The damaged ligament is trimmed off. Damage to any other structure like the menisci is repaired. If an autograft is used for the repair, it is obtained from the desired site.
A tunnel is drilled at the lower end of the thigh bone and other tunnel is drilled through the upper end of the tibia or the larger leg bone. The graft material is passed through these tunnels and is fixed in place with the help of fixation devices like screws. The devices are sometimes biodegradable, that is, it can get absorbed in due course. Once the procedure is complete, the instruments are removed and the incisions are closed with stitches.
What is the Postoperative Care Required following ACL Repair?
Following ACL repair, the patient is observed for a few hours in the hospital, after which they are discharged. A knee brace may be used to support the knee, and the patient may be given crutches to avoid putting direct weight on the knee. Physiotherapy is started after a few days to strengthen the knee. Skin stitches are removed in around a week. Full recovery may take around 6 months, after which the patient may even be able to get back to competitive sports.
Possible complications of the procedure include:
- Failure of graft or other devices like screws
- Inflammation of the synovial tissue of the joint, called synovitis
- Infection
- Pain in the joint
- Stiffness of the knee
- Injury to a blood vessel or a nerve during the surgery
- Complications associated with anesthesia

What is the Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Healing of Ligament Injuries of Knee?
Platelet-rich plasma has been used to regenerate injured tissues. It contains a high concentration of growth factors, which help in tissue healing. It can be injected or placed as a gel in the knee joint following ACL reconstruction surgery. However, the results from various clinical studies indicate a variable response, and therefore its use currently cannot be definitely recommended.