Glossary
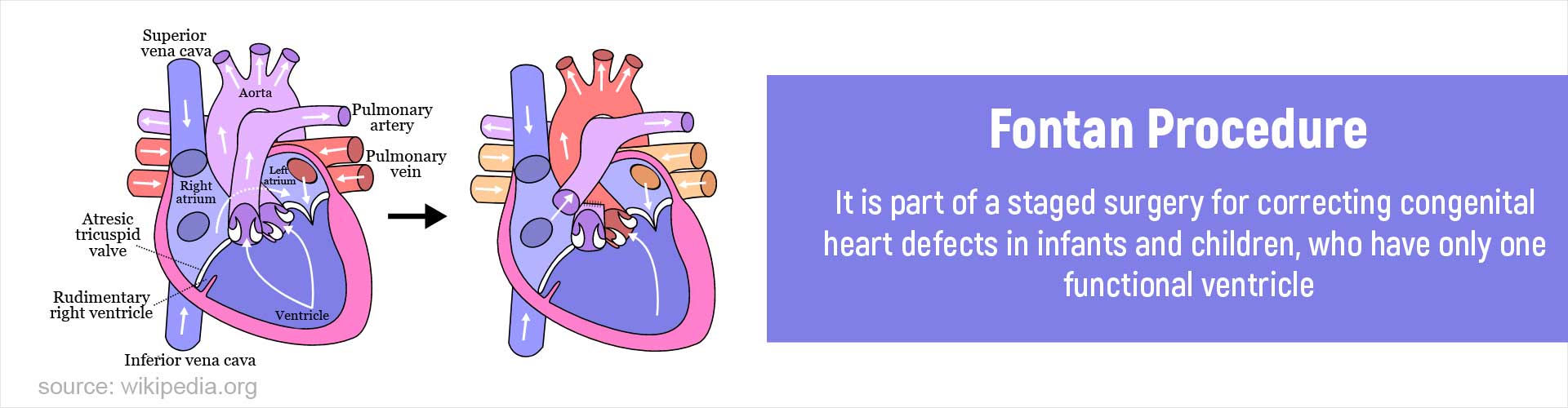
Atrium: Each of two upper cavities of the heart from which blood is passed to the ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the peripheral parts of the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.Cyanosis: A bluish discoloration of the skin due to inadequate oxygen supply in the blood.
Embolism: Obstruction of an artery by a blood clot (thrombus) or an air bubble.
Infarction: Obstruction of the blood supply to an organ or tissue, such as heart muscle, typically by a thrombus or embolus, leading to localized death of the tissue.
Inferior Vena Cava: A large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle parts of the body into the right atrium of the heart.
Ischemia: An inadequate blood supply to an organ, especially the heart muscles.
Mitral Valve: This is also known as “bicuspid valve”, since it has two leaf-like cusps that make up the valve. This valve connects the left atrium to the left ventricle in a normal heart.
Palliative: A treatment that reduces pain without curing the cause of the pain.
Pleural Effusion: Fluid build-up between the tissues that line the lungs and the chest.
Superior Vena Cava: A short vein having a large diameter that receives deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm.
Tricuspid Valve: This is so called because it has three leaf-like cusps that make up the valve. This valve connects the right atrium to the right ventricle.
Tricuspid Atresia: A congenital heart disease where the tricuspid valve is completely absent as a result of which there is no connection between the right atrium and right ventricle.
Ventricle: Each of the two main chambers of the heart, located on the left and right side.