Hysterectomy - Surgical Operation
B. Minimally Invasive Techniques - Vaginal hysterectomy
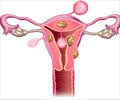
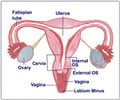
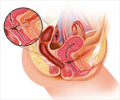
In a vaginal hysterectomy, the uterus is removed through the vaginal route. Prior to surgery, the patient is given a spinal or a general anesthesia.
After anesthesia the woman is positioned in a legs flexed and apart position called the Lithotomy position.
- The skin surrounding the vagina is cleaned with an antibacterial solution.
- A surgical incision is then made in circular fashion around the cervix and through the upper vagina to expose the tissue and blood vessels around the cervix and uterus.
- The tissues and vessels are cut and tied to achieve Haemostasis (controlling bleeding)
- The uterus and cervix are then removed from the top of the vagina.
- The upper part of the vagina where the surgical incision was made is closed with suture material.
There is no visible scar in vaginal hysterectomy and healing is faster in compaision to abdominal hysterectomy.
The disadvantages are -
- There is less room for the surgeon to visualise and operate.
- It can only be used for smaller sized uterus
- It requires that adjoining organs like the bladder is not damaged.