About
Knee replacement surgery is performed for osteoarthritis and other conditions that severely affect the knee joint. Knee replacement is of two types – partial and total.
Knee replacement surgery is a procedure wherein the damaged cartilages of the knee joint are replaced by metal or plastic implants. 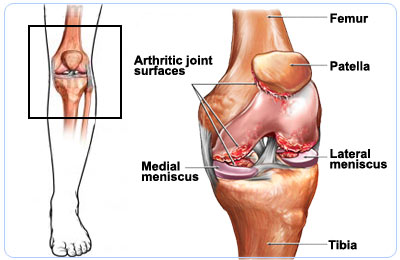
The knee joint lies between the lower end of the thigh bone and upper end of the shin. The surfaces that slide over each other are lined by cartilages and surrounded by fluid to prevent friction. Sometimes, due to age or disease, these cartilages get eroded. The damage may extend to the bone leading to severe pain while walking and stiffness of the joint. Thus the patient’s mobility may be affected which in turn affects the quality of life. Knee replacement surgery is an option for such patients.
This surgery is done to reduce the patient’s pain, improve the function of the joint and in turn improve the quality of life.The implants used for knee replacement usually consist of the following parts:
- The femoral part that covers the lower end of the thigh bone
- The tibial part covers the upper part of the shin
- The spacer, which is a plastic component that lies between the above two parts
Knee replacement surgery is of two kinds, partial or unicompartmental knee replacement and total knee replacement. In unicompartmental knee replacement, only one half of the knee, usually the inner half is replaced. In total knee replacement, the entire knee joint is replaced.
Indications for total knee replacement surgery are knee joint failure caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteonecrosis, and other types of inflammatory arthritis. Complications of knee replacement surgery include failure of implant, infection, clots in the deep veins with subsequent complications, injury to nerves or blood vessels and anemia.
Following surgery, patients need to undergo physical therapy and walk with the support of aids before they can put full weight on the operated knee. They may take around 6 weeks to recover. They should avoid sporting activities like football and basketball. They should take antibiotics whenever they undergo dental or other invasive procedures. They should also consult a doctor before undergoing MRI in case they need one to make sure that the implant will not get affected.
Knee Replacement Surgery - Types
Knee replacement may be partial or total.
Knee replacement surgery is of two types, partial or unicompartmental knee replacement and total knee replacement. In partial knee replacement, only one half of the knee, usually the inner half is replaced. In total knee replacement, the entire knee joint is replaced.
Partial knee replacement may be attempted if the knee joint is stable and the outer compartment of the knee is minimally affected. Advantages of this procedure over total knee replacement are:
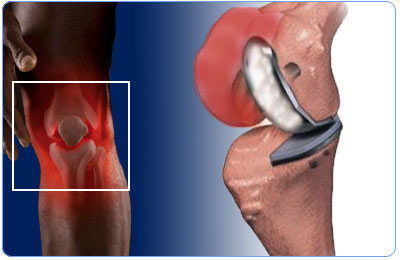

Smaller incision is needed resulting in less blood loss

Patient recovers faster after surgery

Range of motion after surgery is better

It can be converted more easily to a total knee replacement
Some types of total knee replacement are:
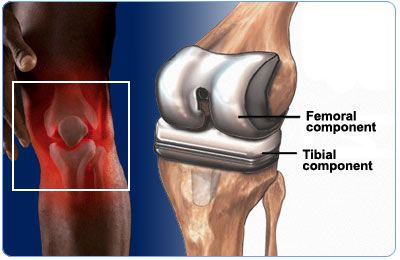
 Rotating knee replacements
Rotating knee replacements: A rotating knee replacement permits forward and backward movements as well as some rotatory movement similar to the normal knee.
 Gender specific implants
Gender specific implants: Some implants are available specific for males or females.
 Custom knee replacement
Custom knee replacement: The prosthesis in custom knee replacement remains the same as the one used in the standard procedure. However, in this procedure, an MRI of the knee is performed initially with the help of which special cutting guides are designed. These guides ensure that the surgeon removes very minimal normal tissue and assist in reducing the duration of the surgery.
Knee Replacement Surgery – Indications and ContraindicationsKnee replacement surgery is performed in patients suffering from severe osteoarthritis or other arthritis that causes severe pain and limit mobility.
Knee replacement surgery is performed to improve the function of damaged knees, alleviate the patient’s pain and improve the quality of life.
Indications for total knee replacement surgery are knee joint failure caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteonecrosis, and other types of inflammatory arthritis. Candidates should fulfill the following criteria for total knee replacement:

They should show evidence of knee damage on imaging studies

They should suffer from moderate to severe pain that cannot be relieved by nonsurgical methods tried over a long period

The knee function should be decreased to such an extent that it affects their quality of life.
Other indications include severe trauma or deformity to the knee in young individuals. The implant may wear off with time in younger patients, hence patients have to limit their activities and avoid sport like football, basketball and gymnastics.
Contraindications to knee replacement surgery include:

Active local or widespread infection

Other medical conditions that put the patient at an increased risk for complications or death during or after the surgery

Some surgeons may prefer to avoid surgery if the patient suffers from severe disease affecting peripheral blood vessels or nerves.
Knee Replacement Surgery - ComplicationsComplications of knee replacement surgery include failure of prosthesis, infection, deep vein thrombosis and injury to nerves or blood vessels.
Complications of knee replacement surgery are more common in older patients and those suffering from other illnesses including obesity. These include
 Failure of implant
Failure of implant which may require repeat surgery. It may occur due to wearing out of the prosthesis or loosening off of the components. Surgeons with experience show a higher success rate compared to those who perform rarer knee replacement surgeries.
 Delayed healing of wound
Delayed healing of wound Infection.
Infection. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, obesity and those taking corticosteroids may be at increased risk of infection
 Deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis. Clots may form in the deep veins. These could travel via the blood into the lungs and lead to a life threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. They could also travel to the heart and result in a heart attack. Blood thinners may be administered during surgery to patients who are at a very high risk of suffering from deep vein thrombosis
 Pneumonia
Pneumonia Fracture of the knee cap
Fracture of the knee cap Instability, stiffness and malalignment of the knee joint
Instability, stiffness and malalignment of the knee joint Injury to the nerves or blood vessels
Injury to the nerves or blood vessels Anemia
Anemia due to blood loss that may need blood transfusion
 Difficulty in squatting or kneeling
Difficulty in squatting or kneeling,
numbness near the surgical scar, and
mechanical noises from the knee
Knee Replacement Surgery - FAQs1.
Which doctors do knee replacement surgery?Orthopedic surgeons trained in knee replacement surgery perform knee replacement surgery.
2.
What is the disadvantage of doing knee replacement in young individuals?Knee replacement in young individuals has greater chances of wear and tear. Thus the patient may need a revision in the future.
3.
Why do people who have undergone knee replacement need to take antibiotics during dental procedures?During dental and other procedures, bacteria are released into the blood which could infect the implants. Antibiotics are prescribed during these procedures to prevent this infection.
Knee Replacement Surgery - Videos
| Videos |
|

Animation - Total Knee Replacement Surgery
|

Total knee replacement complications, risks & success rates
|

Minimally Invasive Total Knee Replacement Surgery
|
References1. http://consensus.nih.gov/2003/images
/2003TotalKneeReplacement
117PDF.pdf
2. Gidwani S, Fairbank A. The orthopaedic approach to managing osteoarthritis of the knee. BMJ 2004; 329: 1220-4.
3. http://orthopedics.about.com/
od/hipkneereplacement/tp/kneereplacement.htm
Author: Dr. Simi Paknikar
Editor: Dr. Shroff
Technical: Lingaraj





