About
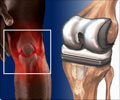
Knee replacement surgery is performed for osteoarthritis and other conditions that severely affect the knee joint. Knee replacement is of two types – partial and total.
Knee replacement surgery is a procedure wherein the damaged cartilages of the knee joint are replaced by metal or plastic implants.

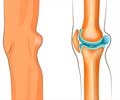
The knee joint lies between the lower end of the thigh bone and upper end of the shin. The surfaces that slide over each other are lined by cartilages and surrounded by fluid to prevent friction. Sometimes, due to age or disease, these cartilages get eroded. The damage may extend to the bone leading to severe pain while walking and stiffness of the joint. Thus the patient’s mobility may be affected which in turn affects the quality of life. Knee replacement surgery is an option for such patients. This surgery is done to reduce the patient’s pain, improve the function of the joint and in turn improve the quality of life.
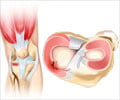
The implants used for knee replacement usually consist of the following parts:
- The femoral part that covers the lower end of the thigh bone
- The tibial part covers the upper part of the shin
- The spacer, which is a plastic component that lies between the above two parts
Knee replacement surgery is of two kinds, partial or unicompartmental knee replacement and total knee replacement. In unicompartmental knee replacement, only one half of the knee, usually the inner half is replaced. In total knee replacement, the entire knee joint is replaced.
Indications for total knee replacement surgery are knee joint failure caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteonecrosis, and other types of inflammatory arthritis. Complications of knee replacement surgery include failure of implant, infection, clots in the deep veins with subsequent complications, injury to nerves or blood vessels and anemia.
Following surgery, patients need to undergo physical therapy and walk with the support of aids before they can put full weight on the operated knee. They may take around 6 weeks to recover. They should avoid sporting activities like football and basketball. They should take antibiotics whenever they undergo dental or other invasive procedures. They should also consult a doctor before undergoing MRI in case they need one to make sure that the implant will not get affected.