Tracheostomy - Glossary
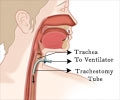
Trachea: The airway that leads from the larynx to the lungs. Also called the windpipe.Esophagus: The muscular tube through which food passes from the throat to the stomach.
Stomach: A muscular pouch that helps in the digestion of food by mixing it with digestive juices and churning it into a thin liquid.
Saliva: The watery fluid secreted into the mouth by the salivary glands that are in the mouth. It keeps the mouth moist, lubricates food to aid in swallowing, makes it possible to taste food, and contains digestive enzyme (a protein that begins the breakdown of food).
Bronchi: The large air passages that lead from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs.
Lungs: The two organs of respiration that bring air and blood into close contact so that oxygen can be added to and carbon dioxide removed from the blood.
Infection: Invasion of the body by agents (bacteria, viruses or fungi) that cause disease or tissue damage.
Edema: Swelling caused by excess fluid in body tissues.
Paralysis: Complete or partial inability to move a part of the body.
Tumor: A location where cells in the body multiply at an increased rate. Some tumors are benign (not cancerous), others are malignant (cancerous).
Trauma: The process or event leading to an injury or wound.
Pneumonia: An inflammatory infection that occurs in the lung.
Bronchitis: Inflammation (swelling and reddening) of the bronchi.
Emphysema: Emphysema is a disorder affecting the alveoli (tiny air sacs) of the lungs. The transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs takes place in the walls of the alveoli. In emphysema, the alveoli become abnormally inflated, damaging their walls and making it harder to breathe.
Barbiturate: A drug with sedative and hypnotic effects. Barbiturates have been used as sedatives and anaesthetics, and they have been used to treat the convulsions associated with epilepsy.
Tetanus: A serious disease affecting the central nervous system. Tetanus (lockjaw) results when a wound is infected with a type of bacteria that thrives without oxygen (particularly in deep wounds).
Aspiration: Removal of fluid by suction from cavities such as nose, throat, from a lump, often a cyst, with a needle and a syringe
Vomit: The ejection of contents of the stomach through the mouth; or, the material itself.
Glottis: The middle part of the larynx; the area where the vocal cords are located.
Anaesthesia: Loss of feeling or sensation resulting from the administration of certain drugs or gases.
Incision: A cut made in the body during surgery.
Scalpel: An instrument used in surgery for making incision.
Scar: A mark left on damaged tissue after it has healed.
Mucus: A thick, slippery fluid produced by the membranes that line certain organs of the body, including the nose, mouth, throat, and vagina.
Stenosis: The narrowing or closure of an opening or passageway in the body.