- Stools - foul smelling - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003132.htm)
- About Foul-smelling stools - (https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/symptoms/stools-foul-smelling)
- Infant Foul-Smelling or Greasy Stool - (https://www.birthinjuryguide.org/birth-injury/symptoms/foul-smelling-greasy-stool/)
- The Scoop on Poop - (https://www.badgut.org/information-centre/a-z-digestive-topics/the-scoop-on-poop/)
What is a Foul-Smelling Stool?
We're all familiar with the fact that stool typically carries an unpleasant odor, even under normal circumstances. However, when improper dietary choices and indigestion come into play, this natural scent can become significantly worse.
This heightened odor can be a source of discomfort, particularly in public settings. It's crucial to understand the underlying causes to take preventative measures.
The distinctive smell of regular stool is primarily attributed to the activity of bacteria within the digestive tract. While it's most commonly the result of an unhealthy diet, there are instances where an unusually strong odor may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires attention(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Stools - foul smelling
Go to source).
Types of Stool
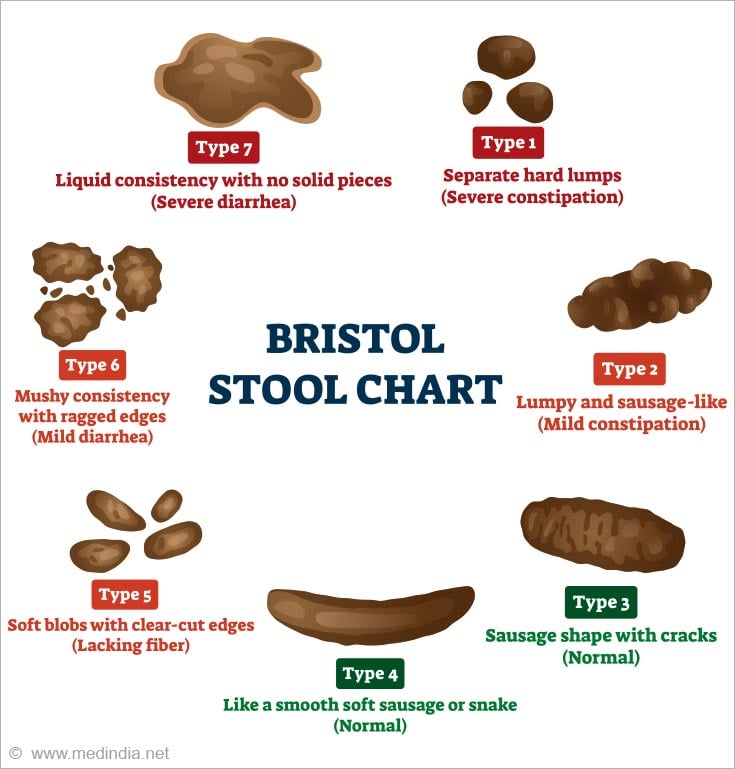
Stool is classified into seven types based on the Bristol Stool Scale, which is used as a diagnostic clinical tool. The Bristol Royal Infirmary in the UK created it in 1997. It is commonly used to assess the effectiveness of treatments for different bowel diseases, such as irritable bowel disease.
The classification of various types of stool is presented below:
| Stool Type | Consistency | Clinical Indication |
| Type 1 | Separate lumps; solid and hard | Severe Constipation |
| Type 2 | Sausage-shaped; lumpy | Moderate constipation |
| Type 3 | Sausage-shaped; cracked surface | Mild constipation |
| Type 4 | Sausage-shaped; soft and smooth | Normal stool |
| Type 5 | Soft blobs; clear-cut edges | Mild diarrhea |
| Type 6 | Fluffy/mushy; ragged edges | Moderate diarrhea |
| Type 7 | Watery; no solids | Severe diarrhea |
The Bristol stool chart can help assess your stool's consistency, making it easier to address the issue of foul-smelling stool.
What are the Causes of Foul-Smelling Stool?
The major causes of foul-smelling stool include the following(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Foul-smelling stools
Go to source):
Overeating:
When we overeat, more than the body can digest, it causes indigestion. Bacteria in the gut break down undigested food, leading to bloating, stomach pain, diarrhea, and smelly gas. Indigestion can make poop smell bad.Diet:
- Sulfur-containing foods: Consuming an excess of sulfur-containing foods can cause the stool to stink. Sulfur is an essential mineral and should be included in the diet in appropriate amounts.
- Some sulfur-rich foods include eggs, garlic, legumes, dried fruits, cruciferous vegetables (cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, bok choy, radish, turnips, German turnip/kohlrabi), and dairy products (except for butter).
- Processed foods: Processed foods contain synthetic substances and additives that cannot be digested and can lead to foul-smelling stool.
- Eating a high-fat diet can be difficult to digest if you lack sufficient lipase, an enzyme that aids in the breakdown of fat. The undigested fatty food can rot as it travels down through the digestive tract and causes the stool to stink.
- Eating excessive dairy or having a deficiency in the lactase enzyme can result in the collection of undigested lactose in the gut. This can lead to issues with dairy products and is acted upon by bacteria, resulting in bloating, abdominal pain and discomfort, diarrhea, and foul-smelling stool.
- Excessive intake of Antibiotics can change the bacteria in your gut and make bad bacteria grow, leading to smelly poop.
Infections
in the digestive tract caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites can lead to inflammation in the intestine. This can cause symptoms like stomach pain, diarrhea, and smelly stool.Unregulated Vitamin Supplementation:
Excess intake of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K can result in foul-smelling stool.Malabsorption
occurs when the body can't absorb food properly. This leads to undigested food staying in the intestine and being broken down by bacteria, causing smelly stool. Malabsorption can cause medical conditions like celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, bowel surgery, food allergies, and intolerance.Miscellaneous Causes:
Other causes include chronic pancreatitis, resulting in lipase deficiency, and cystic fibrosis, which also causes insufficiency of pancreatic secretions.

What are the Symptoms and Signs Associated with Foul-Smelling Stool?
The primary symptom is the 'foul smell' itself. Other symptoms depend on the cause and can include things that may help with figuring out the diagnosis(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Infant Foul-Smelling or Greasy Stool
Go to source).
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
| Abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea | Indigestion, malabsorption, lactose intolerance |
| Severe watery diarrhea with mucus or blood associated with fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting | Bacterial or viral infections |
| Bloody diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| Black tarry stool (melena) | Bleeding in the upper digestive tract |
| Unintended weight loss | Inflammatory bowel disease, malabsorption |
Additional tests such as blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis. These tests are based on the patient's medical history and examination results.
Other Signs and symptoms can be due to:
- Fishy-smelling stool or poop that smells like metal can be due to chronic constipation.
- Anal fissures and bad fecal odor can also be associated with constipation.
- Stomach acids and symptoms of indigestion may make it difficult to pass stool leading to constipation and foul-smelling stool.
It's important to understand your bowel movements and consult a healthcare professional or have a telemedicine consult with a doctor if you have concerns.
Foul Smelling Poop is not a Definitive Indicator of Cancer
Foul-smelling poop can be indicative of various gastrointestinal issues, and in some cases, it may raise concerns about more serious conditions like cancer. While an unpleasant odor alone is not a definitive sign of cancer, it can be associated with certain gastrointestinal cancers, particularly those affecting the colon or rectum
Additionally, foul-smelling stool accompanied by mucus may suggest inflammation or infection in the digestive tract, which may require medical attention. When coupled with persistent gas and abdominal pain, it could be an indication of a more complex underlying issue(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
The Scoop on Poop
Go to source).
Treatment and Prevention of Foul-Smelling Stool
The treatment and prevention of foul-smelling stool primarily involve addressing the underlying causes.
- Dietary adjustments play a crucial role; incorporating more fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate digestion and reduce odor.
- Avoiding excessive consumption of high-fat or processed foods is also advised. Staying well-hydrated supports proper digestion and helps maintain healthy bowel movements.
- Additionally, incorporating probiotics, either through supplements or fermented foods like yogurt, can promote a balanced gut microbiome, which in turn can improve stool odor.
Note: Recognize early the Signs of Foul-Smelling Stool and Seek Professional Advice for a Balanced Gut.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate diagnostic tests to determine the cause and necessary course of action for any concerning digestive symptoms. Early detection and treatment often lead to better outcomes in managing gastrointestinal health.