- Know more on Indigestion - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003260.htm)
- Upset Stomach (Indigestion) - (http://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_gastritis/hic_indigestion)
- Intestinal obstruction and Ileus - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000260.htm)
- Indigestion - (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/dyspepsia)
- Lactose Intolerance - (http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/digestive-diseases/lactose-intolerance/pages/facts.aspx)
- What is Celiac Disease? - (http://celiac.org/celiac-disease/what-is-celiac-disease/)
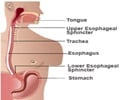
What is Indigestion?
Indigestion is the most common complaint in all age groups. The term itself is extremely vague and can refer to a host of conditions affecting the digestive tract and causing abdominal discomfort.
Symptoms of bloating, belching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and acidic taste in the mouth are commonly reported as indigestion.

Conditions in which indigestion is present are:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – It is a condition in which there is reflux of stomach contents which are acidic in nature into the esophagus causing heart burn, difficulty swallowing, dry cough, regurgitation of food and lump-like feeling in the throat. Risk of developing GERD increases with obesity, pregnancy, hiatal hernia, smoking, diabetes, asthma and scleroderma.
- Gastritis – It is the inflammation of the stomach lining. It can be caused due to infections (Helicobacter pylori), stress, consumption of alcohol, smoking, use of NSAIDs, reflux of bile into the stomach, allergies or immune conditions and exposure to radiation. Common symptoms include pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea, vomiting and melena (blood in stools). Helicobacter pylori infection is often treated with a course that includes two antibiotics, which are usually amoxicillin and clarithromycin. H2 blockers, proton pump inhibitors and –bismuth subsalicylate are often used for relief from symptoms.
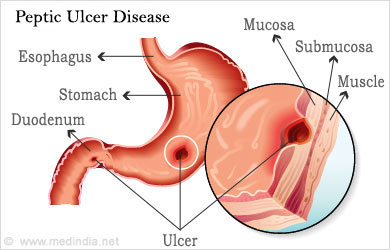
- Peptic Ulcer Disease – It is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or the first part of the duodenum. It can be caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. A rare condition called as Zollinger – Ellison syndrome can cause multiple ulcers in the stomach and duodenum. Incidence of peptic ulcers is raised with consumption of alcohol, smoking, stress, use of NSAIDs and radiation treatments. Feeling of fullness in the stomach, pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, tarry stools, weight loss and fatigue are common symptoms. Ulcers can complicate and cause perforation and bleeding.
- Celiac Disease – It is an autoimmune condition that affects the small intestine when foods containing gluten are consumed. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye and barley. Common symptoms found with this condition are abdominal pain, bloating, weight loss, pale foul-smelling stools, failure to thrive, diarrhea and skin rash. Iron deficiency anemia and deficiency of copper, zinc, selenium, calcium and vitamin D are often present due to malabsorption.
- Gallstones – These are hard structures formed in the gall bladder causing obstruction of the bile duct or inflammation of the gall bladder. The stones could be pigment stones or cholesterol stones or mixed stones. The condition affects women more often than men. Obesity and age over 40 years increase the risk of developing gallstones. It presents with right upper abdominal pain that is constant, either sharp or dull, yellowish skin and eyes, fever, clay colored stools, nausea and vomiting.
- Liver Disease – The liver secretes enzymes that are necessary for the digestion of food, particularly fat. Thus, diseases affecting the liver often cause indigestion. Symptoms of liver disease include abdominal pain or discomfort and jaundice. Conditions affecting the liver include acute hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
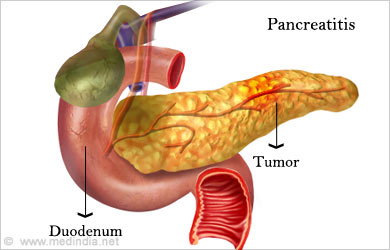
- Pancreatitis – It is the inflammation of the pancreas leading to damage and loss of function of the pancreas. It causes problems with digestion and can be acute or chronic. It is often caused due to alcoholism, obesity, gallstones, procedures in the abdomen like ERCP, infections, smoking, cystic fibrosis, high calcium levels and tumors of the pancreas. Common symptoms include upper abdominal pain that radiates to the back and is often worse after eating, vomiting, tenderness in the abdomen, nausea, fatty foul-smelling stools and unintentional weight loss.
- Intestinal Obstruction – It occurs due to physical obstruction of either the small or large intestine. This can happen due to diverticulitis, adhesions, hernia, intussusceptions, volvulus or tumors. Intestinal obstruction can also happen due to functional disturbances without any physical obstruction. It is also called as paralytic ileus. Gastroenteritis, electrolyte and mineral imbalances, mesenteric ischemia, post-abdominal surgery complications, kidney or lung disease and use of certain drugs like narcotics can cause paralytic ileus. It presents with abdominal distension with on and off cramping pain, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, inability to pass gas and bad breath.
- Stomach Cancer – It can affect any part of the stomach namely cardia, fundus, body, antrum and pylorus. There are different types of stomach cancer like adenocarcinoma, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, lymphoma and carcinoid tumor. It commonly presents with upper abdominal pain and discomfort after eating, blood in stools, fatigue, loss of appetite, vomiting with or without blood, and unintentional weight loss. Cancer of the esophagus may also be associated with dyspepsia. In addition, it may be associated with bleeding while coughing and difficulty with swallowing.
- Intestinal Ischemia – It is a condition that develops due to inadequate blood supply to small or large or both the intestines. It can be acute or chronic. Common symptoms of this condition are sudden cramping abdominal pain, swelling and tenderness in the abdomen, urgency to defecate, vomiting, bloating, fever, nausea and bloody stools.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome – It is a condition where the patient does not have any obvious pathology but suffers from symptoms like diarrhea or constipation. Stress and diet can aggravate existing irritable bowel disease.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease – It includes Crohn’s disease and regional ileitis. Family history of inflammatory bowel disease and faulty immune response play a role in the occurrence of this condition. It presents with diarrhea, blood in stools, fever, abdominal cramping pain, fatigue, weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Infection – Viral (rotavirus, norovirus), bacterial (E.coli, Campylobacter jejuni) and parasitic (Giardia lamblia) infections can cause gastroenteritis. Gastroenteritis presents with diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, pain, fatigue, headache, bloody stools and dehydration.
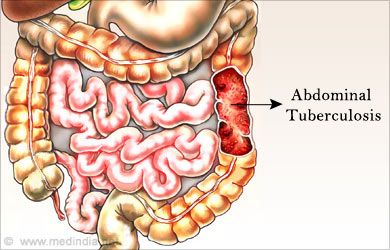
- Intestinal Tuberculosis – It is commonly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is caused due to ingestion of infected milk or food, swallowing of sputum in active pulmonary tuberculosis, spread from active pulmonary focus via blood stream and contagious spread from infected fallopian tubes or mesenteric lymph nodes. The ileocecal region is most commonly affected. Abdominal pain with distension, weight loss, diarrhea or constipation, fever and loss of appetite are common symptoms with intestinal tuberculosis.
- Malabsorption Syndrome – It is a condition in which small intestine is unable to absorb nutrients from the food consumed. Malabsorption occurs due to underlying conditions like celiac disease, lactose intolerance, short bowel syndrome, Whipple disease, genetic conditions and use of certain drugs.
- Lactose Intolerance / Food Allergy – It is a condition in which people experience indigestion, bloating, excess gas formation and diarrhea after consumption of milk or milk products. Milk contains a sugar called lactose. The small intestine produces an enzyme called lactase, which breaks the sugar lactose into glucose and galactose for absorption into the blood stream. Lactose intolerance happens either due to lactase deficiency or lactose malabsorption. Allergies to foods like peanuts, milk etc. are quite common especially in children and can cause symptoms of indigestion in these individuals.
- Systemic Illness – Some conditions that cause hormonal or other problems in the body may also cause indigestion. These conditions include anxiety, thyroid disorders, diabetes, other hormonal disorders and heart failure. Therefore, in a person complaining of indigestion, a general body examination is also necessary to rule out other conditions that may cause indigestion.

How is Indigestion Diagnosed?
Indigestion is often diagnosed by ruling out the common causes for its occurrence like gastritis, peptic ulcers, gastro-esophageal reflux disease, intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis and gallstones. X- rays, tests for Helicobacter pylori infection, endoscopy, gastroscopy and CT scan are done depending upon the requirement in the individual cases. Celiac disease is diagnosed with antiendomysial antibodies and endoscopy of the duodenum.
Gallstones can be diagnosed with lab tests, ultrasound or CT scan abdomen, gallbladder radionuclide scan, ERCP, MRCP and PTCA. CT/ MR angiography and arteriography aid in diagnosis of intestinal ischemia.
What treatment options are available for indigestion problem?
Indigestion is treated depending on the underlying cause. Conditions that cause gastritis, GERD and peptic ulcers are treated with antacids, H2 blockers, proton pump inhibitors and bismuth subsalicylate. In case of infections, a course of antibiotics is used. Avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol and taking steps to manage stress are useful in reducing indigestion. Surgical treatments are considered if medication does not help. In case of GERD, surgical procedures like Nissen fundoplication or linx device might be considered. ERCP procedure is used to remove gallstones from the common bile duct. In celiac disease, gluten-free diet along with supportive treatment reduces indigestion problem. Intestinal obstruction and ischemia are surgically treated if bleeding or necrosis of intestinal tissue is suspected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which doctor should I consult if I have indigestion?
You could visit a general physician or a Gastroenterologist for indigestion problems.
2. I am 28 weeks pregnant and recently developed burning sensation in my chest when I lie down. Is this serious?
No. It is common to have burning sensation upon lying down with progressing pregnancy, because with growing uterus the organs in the upper abdomen are pushed upwards, which could be causing reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus leading to burning sensation.
You could take small frequent meals, avoid lying down immediately after eating and lie down on your side to cope with this situation. If you still have the burning sensation, taking antacids with your doctor’s advice would be helpful.
3. What could be the cause of recurrent indigestion in spite of taking antacids?
Cause for indigestion can be infections, autoimmune conditions, functional disorders of stomach or intestines or tumors. If you are experiencing frequent episodes of indigestion, it is necessary to get evaluated. Endoscopy of the stomach and duodenum, ultrasound abdomen and laboratory tests are primarily done. Depending upon the results further evaluation can be considered.
4. Why do I have upper abdominal pain mainly on the right side, especially after a heavy meal?
Pain that is occurring after a heavy fatty meal is usually due to gall bladder related conditions like gall bladder stones or inflammation of the gall bladder. You need to get an ultrasound abdomen and lab tests done for confirmation of the cause.
5. I have bouts of diarrhea with some amount of upper abdominal discomfort whenever I eat whole wheat bread. What could be the cause?
Upper abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and nausea after consuming wheat, rye or barley products are usually related to gluten allergy. It could be due to celiac disease, which results in sensitivity of the small intestine to a protein called gluten present in wheat, rye and barley.
You need to get evaluated further for confirmation of the cause with lab work and investigations.