- Knee Problems - (http://www.niams.nih.gov/health_info/knee_problems/default.asp)
What is Knee Pain?
Common causes of knee pain include osteoarthritis, torn menisci, torn ligaments etc.
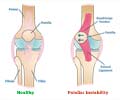
Knee pain is a common condition especially in older and overweight individuals. In order to understand the cause of knee pain, it is necessary to note the structures that contribute to the knee joint.
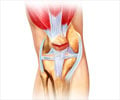
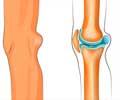
The knee joint is made up of three bones, the lower end of the femur or the thighbone, the upper end of the tibia or the shinbone and the patella or the kneecap. The articular surfaces of the bones are covered with cartilage. Between the femur and the tibia are two semilunar cartilages, the medial and the lateral menisci. The quadriceps muscles straighten the knee from the front, while the hamstrings bend the knee from behind. The knee joint is stabilized by ligaments, which are the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments within the knee joint, and the medial and the lateral collateral ligaments on the inner and outer sides of the knee respectively. Tendons or the fibrous ends of muscles cross the joint and add to its stability. The knee joint is enclosed in a capsule, which is lined on the inner surface by a tissue called the synovium. The knee joint also contains a fluid, which is often increased in disease conditions, resulting in swelling of the joint.
Knee pain can arise due to a disease or injury to any of the parts of the knee joint, which mainly include the:
- Articular surfaces of the bones
- Cartilages lining the bones
- Menisci
- Ligaments
What Causes Knee Pain:
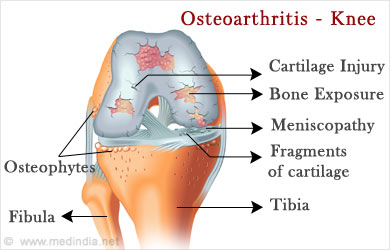
- Osteoarthritis: It is a condition that affects joints due to chronic wear and tear. The knee joint is commonly affected in Osteoarthritis. The patient complains of pain, joint swelling and eventually decreased range of motion. It usually occurs in older and/or overweight individuals, though it can occur in younger individuals who have suffered from knee trauma. It is diagnosed using x-ray of the joint.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It is an autoimmune condition where the patient’s body produces certain proteins that attack the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis causes pain and warmth in the joint, joint swelling, morning stiffness and decreased range of motion. The small joints of the hands and feet are usually affected first. Joints are affected symmetrically on both sides of the body.
- Other autoimmune conditions: Other autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriasis can also affect the knee joint. Other symptoms associated with the conditions like skin lesions are often obvious, thereby supporting the diagnosis.
- Gout: It is a condition that is caused by increased uric acid levels in the blood. Gout causes arthritis; the most commonly affected joint is the big toe. The knee can also be affected resulting in pain, swelling and redness in the joint. The joint is sometimes so sensitive that even a slight touch can cause pain. Blood and joint fluid testing for uric acid can help to diagnose the condition.
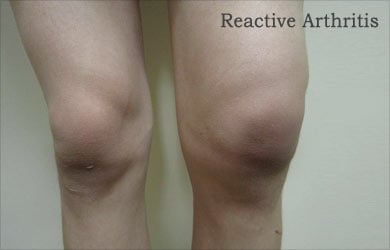
- Reactive arthritis: It occurs following an infection usually of the urogenital or the intestinal tract. Three symptoms are commonly associated with reactive arthritis – conjunctivitis, urethritis and arthritis.
- Chondromalacia: It is a condition where there is softening of the cartilage surface of the patella. It is more common in athletes like runners and cyclists. The patient experiences a dull pain around the patella, which worsens on moving down a slope or stairs, and sometimes while climbing up. X-ray or arthroscopy help to confirm the condition.
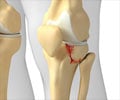
- Injuries: Injuries of structures in the knee can result in knee pain. Some of these injuries include:
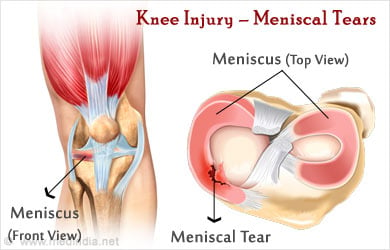
Meniscal tear: A tear in either the medial or lateral meniscus may result from a twisting injury. The patient complains of pain while straightening the leg, locking, clicking or giving way of the knee, and swelling. MRI or arthroscopy may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Cruciate ligament tears: Tears of the cruciate ligament may result in some pain, instability of the knee joint and tendency to buckle under. MRI or arthroscopy may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Medial and lateral collateral ligaments injuries: Injuries to the medial and lateral collateral ligaments often occur during contact sports. Symptoms include pain, swelling and instability of the joint. Diagnosis is with MRI.
Patellar tendon injuries: Inflammation or rupture of the patellar tendon may be due to frequent injuries. It results in severe pain, swelling and an inability to move the leg at the knee joint. Diagnosis is through physical examination and MRI.
- Infections:Some bacterial and viral infections can also cause kneepain. Bacterial infection of the knee joint causes pain, swelling and rednessof the joint with fever. Chikungunya is a viral infection associated with feverand severe pain in joints including the knee joint.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Knee Pain
1. Which doctor should I visit in case I suffer from knee pain?
You should visit an orthopedic surgeon or a rheumatologist in case you suffer from knee pain.
2. What is total knee replacement?
Total knee replacement is a type of surgery where the parts of the knee joint are replaced with prosthesis. It is commonly done for degenerative conditions affecting the knee joint, where the person in unable to walk.