- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Physician: Visits for Musculoskeletal Symptoms
About
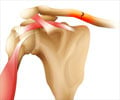
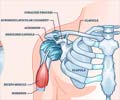
The shoulder is a joint supported by tendons and muscles to provide a wide range of movement. Owing to the mobility, the shoulder is susceptible to several conditions that stem from instability or impingement of soft tissues or bony structures. These lead to pain in the shoulder. Shoulder pain may range in severity from mild to severe; it may be temporary or long lasting warranting treatment.
While diagnosing the cause of shoulder pain, the doctor takes a detailed medical history about the pain, its onset, duration, severity, conditions that aggravate pain, other diseases that the person has. A physical examination is then done to assess the shoulder joint clinically. Various imaging modalities such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans or ultrasound may be employed. Nerve functions may be assessed using electrical studies (EMG- Electromyogram).
Arthrogram is an X-ray of the shoulder taken after injecting a dye; it helps in better visualisation of the joint. Those injuries that are not apparent from any other imaging modalities may be viewed by arthroscopy. This is a surgical procedure in which the doctor can visualize the joint with a fiber-optic camera. Arthoscopy can be used to find the cause of pain and also to correct the problem.
Giving rest to the joint often relieves pain and allows inflammation to subside. Prolonged immobilization may lead to frozen shoulder; hence caution has to be exercised. Local application of moist heat or ice can relieve mild pain. Pain killers like ibuprofen, naproxen or paracetamol (acetaminophen) are commonly prescribed for pain. Muscle relaxant drugs are also employed when required. Chronic pain may even require antidepressant drugs. Physical therapy and specific exercises are helpful in certain conditions. Your doctor may also prescribe injections of cortisone (steroid) to bring down inflammation at joints.
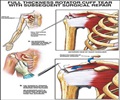
Surgery is indicated for a number of conditions that cause shoulder pain. Recurring dislocation is a common reason for employment of surgical correction. Arthroscopy may be used in certain cases. Open procedures may be required for larger reconstructions or shoulder replacement.
Causes of Shoulder Pain
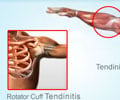
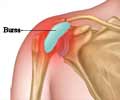
Bursitis and tendinitis of the rotator cuff are the commonest causes of shoulder pain. Bursae are small sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, muscles and joints. They contain a fluid called synovial fluid. Inflammation of a bursa is called
Rotator cuff tear: Separation of the tendons of the rotator cuff from bone due to injury leads to rotator cuff tear. This condition may need surgical correction.
Frozen shoulder (Adhesive capsulitis): In this condition, the joint capsule becomes inflamed and stiff. This greatly restricts motion and causes chronic pain. It usually follows an injury due to which the patient restricts movement of the arm at the shoulder joint.
Calcific tendonitis: Deposition of calcium within a tendon, especially within the rotator cuff tendons, leads to shoulder pain.
Shoulder dislocation: Injury or over use may compromise the stability of shoulder joint. The head of the upper arm bone (humerus) may be forced out of the shoulder socket. This may be partial (subluxation) or complete. Subluxations or dislocations may occur repeatedly in persons leading to increased risk of arthritis. The dislocation can be diagnosed through careful physical examination.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis is a painful condition resulting from chronic wear and tear, sports or work injuries. Arthritis may cause pain severe enough to force people to avoid shoulder movements.
Fracture: Fractures (broken bones) commonly involve the collar bone (clavicle), upper arm bone (humerus), and shoulder blade (scapula). Fractures follow an injury and lead to pain, swelling, and bruising about the shoulder.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. My shoulder clicks, snaps and pops. Is it dangerous?
Any disruption in the normal architecture of the shoulder joint, tendons, ligaments and muscles may be responsible for a snapping or popping shoulder, or a clicking sound. Chronic stress or trauma may lead to this. The condition is not significant all the time, especially when there is no associated pain. Condition like dislocation or labreal tears need correction.
2. What are labreal tears or SLAP (Superior labral anterior-posterior) lesions?
These are injuries to the part of the shoulder called labrum. The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous ligament that forms the margin of the glenoid cavity of the shoulder joint (the socket).
3. What is a ball and socket joint?
The particular arrangement of the shoulder where the ball like part of the upper arm bone (humerus) works within a socket (the glenoid cavity) is an example for a ball and socket joint.